Welcome to the world of alternative operating systems, where flexibility and customization reign supreme. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the exciting realm of Linux installation, offering a step-by-step journey that will empower you to explore a new computing experience. Embrace the immense potential of open-source software and unlock a world of possibilities for your computer.
Are you tired of the limitations imposed by mainstream operating systems? Do you yearn for greater control over your computer's functions, performance, and security? Linux, an open-source operating system, offers a refreshing alternative. With its vast array of distributions and user-friendly interface, Linux has gained popularity among tech enthusiasts, developers, and privacy-conscious individuals worldwide.
Throughout this guide, we will walk you through the process of installing a Linux distribution on your computer. By following our step-by-step instructions, you will gain the knowledge and confidence to embark on this exciting journey. Along the way, we will highlight key concepts, provide useful tips, and equip you with the essential tools required to install Linux successfully.
Prepare to witness the seamless integration of reliability, flexibility, and security that Linux brings to the table. Whether you are a beginner enthusiast eager to explore the world of open-source software or a seasoned user looking to broaden your horizons, this guide will serve as your compass, guiding you from start to finish as you embark on a transformative computing adventure.
Exploring the Fundamentals of the Linux Operating System
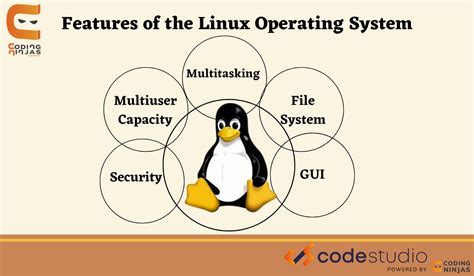
In this section, we will delve into the foundational aspects of the Linux operating system, uncovering its key components and essential concepts. By understanding these fundamentals, you will gain a solid grasp of the underlying principles that make Linux such a powerful and versatile platform.
- Kernel: At the heart of the Linux operating system lies the kernel, which serves as the core component responsible for managing system resources, interacting with hardware devices, and providing essential services. It forms the foundation upon which the entire operating system is built.
- Distributions: Linux distributions, also known as distros, are complete operating system packages that combine the Linux kernel with various software applications and tools. These distributions are tailored to suit different user needs and preferences, offering a range of pre-installed software bundles and system configurations.
- Command Line Interface (CLI): Unlike some other operating systems, Linux provides a powerful command-line interface that enables users to interact with the system through text commands. This interface offers extensive flexibility and control, allowing users to execute various operations and automate tasks efficiently.
- File System Hierarchy: Linux employs a specific file system hierarchy that organizes files and directories in a structured manner. Understanding the layout of this hierarchy is essential for navigating the system, locating files, and managing permissions effectively.
- Package Management: Linux relies on package management systems, such as APT (Advanced Package Tool) or YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified), to simplify the installation, upgrade, and removal of software packages. These tools provide a convenient way to manage software on Linux systems, ensuring easy access to a vast range of applications.
- Open Source Philosophy: One of the defining characteristics of the Linux operating system is its open-source nature. This means that the source code of Linux is publicly accessible and free for anyone to view, modify, and distribute. This fosters a collaborative and community-driven development environment, promoting innovation and flexibility.
- Security: Linux is renowned for its robust security features, making it a popular choice for systems that require high levels of protection. Through various mechanisms such as user permissions, firewalls, and encryption, Linux ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, bolstering overall system security.
By familiarizing yourself with these fundamentals, you will gain a solid foundation for further exploration and understanding of the Linux operating system. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the vast realm of Linux and harness its full potential.
Preparing Your System for Linux Installation
Before you can begin the installation process for an operating system based on the Unix-like Linux kernel, it is important to ensure that your computer meets the necessary requirements and is properly prepared. This section will guide you through the essential steps to get your computer ready for Linux installation.
Check System Requirements Before proceeding with the installation, it is imperative to verify that your computer meets the minimum system requirements to run Linux smoothly. These requirements typically include processor speed, RAM, disk space, and graphics capabilities. |
Backup Your Data It is highly recommended to create a backup of all your important files and data before installing Linux. This ensures that in case of any unforeseen issues during the installation process, your data remains safe and can be easily recovered. |
Partition Your Hard Drive Prior to installing Linux, you will need to partition your hard drive to allocate space for the new operating system. This can be done using different partitioning tools or through the Linux installation process itself. It is crucial to understand the concepts of primary, extended, and logical partitions to ensure an efficient partitioning setup. |
Create Installation Media Once your system is prepared and the necessary data backup is complete, you will need to create installation media, usually a bootable USB drive or DVD, to install Linux on your computer. This involves downloading the Linux distribution of your choice and using appropriate software to write it to the installation media. |
Secure Boot and BIOS/UEFI Settings Some modern computers come with Secure Boot enabled, which may prevent the installation of non-Windows operating systems. You will learn how to disable Secure Boot and configure the BIOS or UEFI settings to allow booting from the Linux installation media. |
Test Compatibility and Functionality Before proceeding with the actual installation, it is advisable to run a compatibility and functionality test to ensure that Linux will work properly on your hardware. This can be done by booting into a live distribution or running a virtual machine with the desired Linux distribution. |
By following these preparatory steps, you will be well-prepared to proceed with the installation of Linux on your computer. This will help ensure a smooth and successful installation, enabling you to benefit from the power and flexibility of the Linux operating system.
Gathering the Essential Hardware and Software Components
To successfully set up Linux on a computer, it is crucial to gather all the necessary hardware and software components. This section provides an overview of the essential elements required for a seamless installation process.
Hardware:
1. Computer System: Ensure that you have a compatible computer system capable of running Linux. Check the minimum system requirements for the specific Linux distribution you plan to install.
2. Storage Device: Prepare a storage device, such as a USB drive or DVD, to store the Linux installation files. Make sure it has sufficient capacity to accommodate the chosen Linux distribution.
3. Internet Connectivity: If you prefer to download the Linux distribution during the installation process, ensure that you have a stable internet connection available.
Software:
1. Linux Distribution: Identify and download the Linux distribution that best suits your needs. Research various distributions available and select based on factors such as user interface, package manager, and desktop environment preferences.
2. Bootable Media Creation Tool: Obtain a reliable tool for creating a bootable media from the downloaded Linux distribution. This may involve utilizing software like Rufus, UNetbootin, or Etcher, depending on your computer's operating system.
3. Backup Tools: While not mandatory, it is highly recommended to have backup tools available to safeguard your important data before proceeding with the Linux installation. This ensures that any unforeseen complications do not result in data loss.
By gathering the necessary hardware components and obtaining the relevant software, you will be well-prepared to embark on the Linux installation journey. The next section will guide you through the initial steps of the installation process.
A Comprehensive Walkthrough for Setting Up Linux
In this section, we will provide you with a detailed step-by-step explanation of the entire process involved in installing the Linux operating system on your personal computer. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, these instructions will guide you through each stage, ensuring a smooth and successful installation of the Linux software.
Step 1: Preparing for Installation
To get started, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the prerequisites for installing Linux on your computer. This involves checking the hardware compatibility, ensuring sufficient disk space, and making any necessary backups of your existing data. By carefully preparing beforehand, you will minimize any potential disruptions during the installation process.
Step 2: Choosing the Linux Distribution
Linux offers a wide range of distributions, each with its own unique features and user interfaces. In this step, we will discuss different Linux distributions and their suitability for various user preferences and requirements. By selecting the right distribution, tailored to your needs, you can ensure an optimal and satisfying Linux experience.
Step 3: Creating a Bootable USB or DVD
Next, we will explain how to create a bootable USB or DVD from the chosen Linux distribution. This bootable media will allow you to run Linux directly from the external device, facilitating a hassle-free installation process. We will guide you through this process, providing clear instructions to create the bootable media effectively.
Step 4: Initiating the Installation Process
Once you have your bootable media ready, we will demonstrate how to start the installation process. This step involves booting your computer from the USB or DVD, accessing the Linux installer, and initiating the installation wizard. You will learn how to navigate through the installation screens and configure necessary settings.
Step 5: Partitioning and Formatting
During the installation, you will be required to partition and format your hard drive or disks. In this step, we will explain the different partitioning options available and guide you in setting up your partitions to ensure efficient data management on your Linux system. We will provide recommendations and best practices to optimize your system's performance.
Step 6: Installing Linux Packages and Drivers
Once the basic installation is complete, we will focus on installing additional software packages and drivers to enhance the functionality of your Linux system. You will learn how to use package managers to install and update software, as well as how to identify and install compatible drivers for your hardware devices.
Step 7: Configuring User Accounts and Permissions
In this step, we will guide you through the process of creating user accounts, setting passwords, and managing user permissions on your Linux system. By properly configuring user accounts and permissions, you can ensure security and personalized access to various system resources.
Step 8: Finalizing the Installation
Finally, we will discuss the steps to complete the installation process and prepare your Linux system for everyday use. This includes removing the installation media, adjusting system settings, and performing any necessary updates. By following these final steps, you will have a fully functional Linux system ready to explore.
By following this comprehensive step-by-step guide, you will confidently navigate the installation process and successfully set up Linux on your computer. Enjoy the advantages of this powerful open-source operating system and unleash its potential for various computing needs.
Partitioning Your Hard Drive and Selecting the Linux Distribution
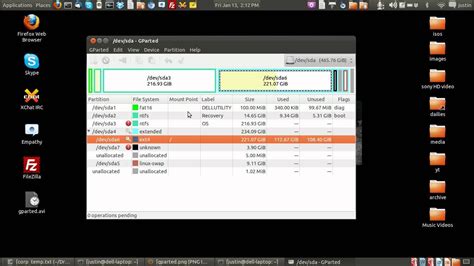
In this section, we will explore the process of partitioning your hard drive and selecting the Linux distribution that best suits your needs. Partitioning your hard drive involves dividing it into separate sections, or partitions, to organize your data and install the operating system. Selecting the Linux distribution refers to choosing a specific version or flavor of Linux to install on your computer.
Partitioning your hard drive is an essential step in installing Linux as it allows you to allocate different portions of your storage space for various purposes. This can include creating separate partitions for the operating system, user files, and additional data. By dividing your hard drive into partitions, you can better manage and protect your data, improve system performance, and even enable dual-boot configurations with other operating systems.
When selecting a Linux distribution, you have a wide range of options to consider. Each distribution offers a unique set of features, user interfaces, and supported software packages. Some popular distributions include Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and CentOS. It is important to research and evaluate each distribution based on factors such as your level of expertise, hardware compatibility, preferred desktop environment, and specific software requirements.
In addition to considering the features and characteristics of different Linux distributions, it is also important to understand the release cycles, community support, security updates, and stability of each distribution. Some distributions provide long-term support (LTS) versions, which offer extended support and regular updates for a specified period, while others focus on bleeding-edge technology and frequent updates.
| Linux Distribution | Description |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | A user-friendly distribution known for its ease of use and large community support. |
| Fedora | A cutting-edge distribution that focuses on providing the latest software and technologies. |
| Debian | A versatile distribution known for its stability and wide range of available software packages. |
| CentOS | A distribution popular in enterprise environments due to its robustness and long-term support. |
Before proceeding with the installation, it is recommended to backup any important data on your hard drive to avoid potential data loss during the partitioning process. Once you have chosen a Linux distribution and have a plan for partitioning your hard drive, you can proceed to the next steps in the installation process.
Post-Installation: Configuring and Customizing Your Linux Experience
Once you have successfully installed Linux on your device, it is time to dive into the exciting world of configuring and customizing your Linux operating system. This section will guide you through the process of personalizing your Linux experience according to your needs and preferences.
1. Modify your desktop environment: Linux offers a variety of desktop environments such as GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and others. Choose the one that suits your style and customize it by changing wallpapers, themes, icons, and fonts to create a visually appealing and personalized desktop environment.
2. Install additional software: Linux distributions usually come with a basic set of software, but you can expand your system's capabilities by installing additional software packages. Explore package managers like APT, DNF, or Pacman, and discover a vast collection of open-source software ready to be installed on your system.
3. Configure system settings: Take control of your Linux system by configuring various settings. Customize your keyboard shortcuts, adjust display settings, manage system notifications, set up security features, and fine-tune your network connections to optimize your Linux experience.
4. Explore software repositories: Linux offers extensive software repositories where you can find a wide range of applications, libraries, and tools. Familiarize yourself with package managers and repositories specific to your Linux distribution and discover the vast ecosystem of software available at your fingertips.
5. Customize the terminal: The command-line interface is an integral part of Linux, and you can personalize it to enhance your productivity. Set up aliases, customize the shell prompt, apply color schemes, and explore powerful command-line tools to make the terminal your efficient work companion.
6. Backup and restore configurations: As you make changes to your Linux system, it is essential to back up your configurations to ensure you can easily restore them if needed. Learn how to create backups of important files, system configurations, and application settings using tools like rsync, tar, or dedicated backup software.
By following these steps, you will not only be able to configure and customize your Linux system to meet your specific requirements but also discover the flexibility and versatility that Linux offers as an open-source operating system.
FAQ
What operating systems can Linux be installed on?
Linux can be installed on a wide range of operating systems including Windows, macOS, and different versions of Linux itself.
Do I need to have any technical knowledge to install Linux on my computer?
While having some technical knowledge can be helpful, it is not mandatory. Many Linux distributions provide user-friendly installation processes with step-by-step instructions that even beginners can follow.
Can I dual boot Linux with my existing operating system?
Yes, you can dual boot Linux with your existing operating system. During the installation process, you will be given the option to install Linux alongside your current OS, allowing you to choose which one to boot into each time you start your computer.