In the fast-paced digital world, ensuring accurate time synchronization across computer systems is paramount. From maintaining data consistency to facilitating smooth communication between devices, a well-configured Network Time Protocol (NTP) is vital. This article serves as your go-to resource for step-by-step instructions on how to efficiently implement and tailor NTP for Linux operating systems.
Timekeeping precision is indispensable in various domains, including finance, telecommunications, and network administration. Equipping your Linux system with a reliable time synchronization mechanism is crucial for seamless operations, fortified security, and enhanced network performance.
This in-depth tutorial will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the installation and configuration process for NTP. By following the detailed instructions outlined in this guide, you will obtain a firm understanding of the core concepts and steps required to establish a robust and accurate timekeeping framework on your Linux system.
Step 1: Understanding the Importance of Network Time Protocol (NTP) in Linux Environments
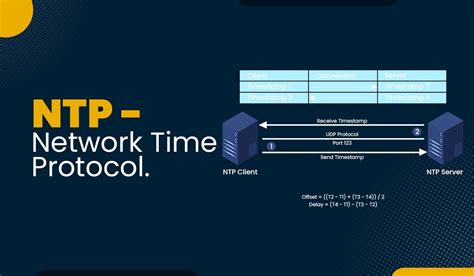
In this section, we will explore the significance of Network Time Protocol (NTP) in Linux systems. Having accurate time synchronization is crucial for various operations and services. NTP provides a reliable and standardized way to ensure that the time across different devices on a network is consistent.
Accurate timekeeping is vital for a variety of reasons, including coordinating events, logging activities, and maintaining database integrity. NTP allows systems to synchronize their clocks with a reference time source, which can be a local time server or an external time server connected to the internet. By synchronizing the clocks on Linux systems, NTP enables efficient and reliable communication between devices, enhances security through accurate event logging, and facilitates troubleshooting and debugging.
- Why is time synchronization important in Linux systems?
- What are the main benefits of using NTP?
- How does NTP ensure accurate timekeeping?
- What are the potential issues and challenges related to time synchronization?
In the upcoming sections, we will delve into the practical steps to install and configure NTP on a Linux system, which will help you effectively implement accurate time synchronization for your Linux environment.
Step 2: Getting Ready for NTP Installation – Verifying System Requirements
Before proceeding with the installation of the Network Time Protocol (NTP) on your Linux system, it is essential to ensure that your system meets all the necessary requirements. This step will help you verify the compatibility and availability of the required components and software.
Here are the key factors to consider when checking the system requirements:
- Operating System Version: Check if your Linux system is supported by the NTP software. Refer to the NTP documentation or official website for the list of compatible operating systems.
- Available Disk Space: Ensure that your system has sufficient free space to accommodate the NTP installation. Check the disk space using the appropriate command for your Linux distribution.
- Network Connectivity: Make sure that your system has a reliable internet connection. NTP relies on network time servers to synchronize time, so a stable internet connection is crucial.
- Administrator Privileges: Verify that you have administrative privileges on your Linux system to install and configure NTP. Most NTP installation procedures require root access.
- Software Dependencies: Identify and install any necessary software dependencies required by NTP. This may include libraries or packages that are needed for the successful installation and functioning of NTP.
By carefully examining these aspects and addressing any necessary prerequisites, you will be ready to proceed with the smooth installation and configuration of NTP on your Linux system.
Step 3: Setting up NTP on Your Linux Machine
Now that you have a clear understanding of the importance of NTP and its role in ensuring accurate time synchronization on your Linux system, it's time to dive into the installation process. In this step, we will discuss the steps required to install NTP on your Linux machine.
The first step in the installation process is to check if NTP is already installed on your system. You can do this by running a simple command in the terminal. If NTP is already installed, you will see the version information displayed. However, if NTP is not installed, you can proceed with the installation process by following the steps outlined below.
To install NTP, open a terminal window and use the package manager specific to your Linux distribution. For example, if you are using Ubuntu, you can use the apt package manager, while if you are using Fedora, you can use the dnf package manager. Simply run the appropriate command with administrative privileges, and the package manager will take care of the installation process.
Once the installation is complete, you will need to configure NTP to ensure accurate time synchronization. This involves editing the NTP configuration file, usually located at "/etc/ntp.conf". Open the file using a text editor and make the necessary changes according to your requirements. Pay attention to options like the NTP servers you want to use, time zones, and any additional configuration parameters you may need.
After making the necessary changes, save the configuration file and restart the NTP service using the appropriate command for your Linux distribution. This will apply the changes and ensure that NTP is running correctly on your system.
Now that NTP is installed and configured on your Linux machine, your system will be able to automatically synchronize its time with the NTP servers you specified. This will ensure that the time on your Linux system remains accurate and consistent, which is essential for a variety of applications and services.
With NTP successfully installed and configured, you can now proceed to the next step in this guide, where we will discuss how to verify the synchronization status and troubleshoot any potential issues that may arise.
Step 4: Setting up NTP for Time Synchronization with Reliable Servers
In this step, we will explore the process of configuring the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to precisely synchronize the system time with trustworthy time servers. By establishing a connection with reliable servers, your Linux system will ensure accurate timekeeping, which is critical for various applications and processes.
The NTP software utilizes a hierarchical structure of time sources, where lower-level servers synchronize their time with higher-level servers. This enables a cascade effect that ultimately leads to synchronization with highly accurate reference clocks.
To begin configuring NTP, you will need to locate and edit the NTP configuration file, typically found in the /etc/ntp.conf directory. This file contains a list of NTP servers that your system will synchronize with.
You can specify the IP addresses or domain names of reliable NTP servers in the configuration file. It is recommended to use NTP servers provided by reputable organizations or authoritative timekeeping facilities to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the time synchronization.
Once you have updated the NTP configuration file with the desired servers, save the changes and restart the NTP service to apply the new configuration. By doing so, your Linux system will establish connections with these reliable servers and initiate the time synchronization process.
After successfully configuring NTP, you can verify the synchronization status by using NTP-related commands such as ntpq or ntpstat. These commands provide information about the current synchronization status, time offsets, and the selected time sources.
By following this step-by-step guide, you have successfully configured NTP on your Linux system to synchronize the system time with reliable servers. This ensures accurate timekeeping, which is essential for various tasks and applications that depend on precise timing.
Step 5: Verifying NTP Installation and Ensuring Accurate Time Synchronization
After completing the installation and configuration processes, it is crucial to verify the successful installation of NTP on your Linux system and ensure accurate time synchronization. This step will help you confirm that the NTP service is running correctly and that your system is synchronizing time with reliable NTP servers.
The following table provides an overview of the essential commands and actions you can perform to verify the NTP installation:
| Command/Action | Description |
|---|---|
ntpstat | Displays the synchronization status of the NTP service on your system. |
ntpq -p | Lists the remote NTP servers that your system is synchronized with. |
timedatectl status | Provides information about the system clock status, including the NTP synchronization state. |
By using these commands, you can determine whether your NTP installation is working correctly and if your system is accurately synchronized with reliable NTP servers. It is recommended to run these commands periodically to ensure continued time synchronization.
Additionally, it is essential to monitor the NTP service and verify that it automatically starts upon system boot. This can be done by checking the system's startup services using the appropriate commands for your Linux distribution.
Overall, verifying the NTP installation and ensuring accurate time synchronization are essential steps to maintain the reliability and consistency of your Linux system's timekeeping. By following these steps, you can ensure that your system stays synchronized with accurate time sources, contributing to the overall stability and functionality of your environment.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What is NTP and why is it important for Linux systems?
NTP stands for Network Time Protocol, which is a protocol used to synchronize the time across computer systems on a network. It is important for Linux systems because accurate timekeeping is crucial for various system functions and applications.
How can I install NTP on a Linux system?
To install NTP on a Linux system, you can use the package manager specific to your distribution. For example, on Ubuntu, you can run the command "sudo apt-get install ntp" to install NTP. On CentOS, you can use "sudo yum install ntp".




