Embarking on a journey that transcends the boundaries of operating systems, this guide empowers you to unlock a realm of possibilities. It offers you the chance to delve into the world of Linux, a versatile and customizable platform that beckons you to shape it according to your desires.
As you step into this new territory, brace yourself for an adventure like no other. Discover the true potential of your machine as you navigate through the intricacies of Linux installation and configuration. With every command you execute, you will unveil the power behind a system that boasts not only impressive stability, but also unparalleled security.
Your fingertips will dance across the keyboard, working the terminal like a maestro conducts an orchestra. The strength of your commands will bring forth a symphony of efficiency, casting aside the shackles of constraints imposed by proprietary systems. Through the use of packages, software applications will morph into instruments of your creation, melding seamlessly with your workflow.
Immerse yourself in the endless possibilities of customizability, as you shape the Linux environment to match your personality. Each line of code becomes an opportunity to mold and sculpt, transforming your machine into a digital manifestation of your dreams. Feel the exhilarating rush of control as you strip away unnecessary bloatware, leaving behind only what truly serves your purpose.
This guide will empower you to take charge of your computer, infusing it with both stability and adaptability. With each step, you will gain a deeper understanding of the Linux ecosystem, acquiring the knowledge and skills to tame the untamed. Embark on this journey, and let the power of Linux unleash your inner technologist.
Choosing the Perfect Linux Distribution for Your PC

When it comes to selecting a Linux distribution, the vast array of options available may seem overwhelming. However, taking the time to carefully consider and choose the right distribution for your computer is essential to ensure a smooth and efficient operating system experience.
First and foremost, it's important to understand the different types of Linux distributions available. Each distribution has its own unique characteristics, including its target user base, hardware requirements, package management systems, and desktop environments. By familiarizing yourself with these distinctions, you can narrow down your options and make an informed decision.
Furthermore, considering your intended use for Linux on your computer is crucial in selecting the right distribution. Are you a beginner looking for a user-friendly interface? Are you a developer seeking a distribution with extensive software development tools? Or perhaps you have specific hardware requirements that need to be fulfilled? Answering these questions will help determine which distribution is best suited for your needs and preferences.
Additionally, researching the community and support system surrounding each Linux distribution is vital. Active and helpful communities provide a wealth of resources, such as forums, documentation, and tutorials, that can greatly assist users, especially those new to Linux. It's essential to choose a distribution with a vibrant community to ensure you can access the necessary support and troubleshooting assistance when needed.
- Consider your computer's hardware requirements.
- Identify your intended use for Linux.
- Research the community and support system available.
- Take into account the package management system and desktop environment preferences.
- Seek recommendations from experienced Linux users.
Taking into account these factors and conducting thorough research will lead you towards finding the ideal Linux distribution that perfectly aligns with your computer's capabilities and your personal needs. Remember, choosing the right distribution will ensure a seamless and enjoyable Linux experience for years to come.
Understanding the Variations Among Linux Distributions
In the vast world of Linux, it's important to grasp the distinctions between different distributions. While they all share the same foundation, each distribution offers its own unique features and attributes. Understanding these variations will help you choose the Linux distribution that best suits your needs and preferences.
Core Principles:
Despite their differences, all Linux distributions adhere to a common set of core principles. These principles encompass concepts such as open source software, community-driven development, and a focus on stability and security. By upholding these principles, Linux distributions ensure a reliable and adaptable operating system.
Distribution Selection:
When selecting a Linux distribution, it's essential to consider factors such as your technical expertise, intended use, and personal preferences. Some distributions, like Ubuntu or Fedora, are known for their user-friendly interfaces and extensive software repositories. Others, such as Arch Linux or Gentoo, provide a high level of customization and control, but require more advanced technical knowledge.
Package Managers:
Different distributions utilize specific package managers, which are tools that manage software installations and updates. Popular package managers include apt (used by Debian-based distributions), RPM (used by Red Hat-based distributions), and Pacman (used by Arch Linux). Understanding the package manager of your chosen distribution is crucial for managing software installations efficiently.
Desktop Environments:
Linux distributions often offer a variety of desktop environments, which define the appearance and functionality of the user interface. Common desktop environments include GNOME, KDE, XFCE, and Cinnamon. Each environment provides its own set of features and design choices. Selecting the right desktop environment ensures a comfortable and intuitive user experience.
Specialized Distributions:
In addition to the mainstream distributions, there are specialized Linux distributions tailored to specific purposes. For example, Kali Linux is widely used for penetration testing and security auditing, while CentOS is popular for server deployments. Exploring these specialized distributions can open up new possibilities and opportunities in certain fields.
By gaining a thorough understanding of the differences between Linux distributions, you can select the one that aligns with your needs and preferences, ensuring a successful and fulfilling Linux experience.
Discover the Compatibility of Your Device's Hardware
Before embarking on the journey of utilizing the capabilities of Linux on your computing device, it is crucial to assess whether your hardware meets the necessary requirements. Evaluating the compatibility of your machine's hardware is the first step towards a successful Linux installation and configuration.
Begin by scrutinizing your computer's specifications, taking into consideration the processor, memory (RAM), storage space, and graphics capabilities. A thorough examination of these components will enable you to determine the feasibility of running Linux effectively on your device.
Additionally, consider the specific distribution of Linux you intend to install as different distributions have varying hardware requirements. Research and identify the distribution that matches your device's capabilities to ensure a seamless and optimized performance.
Furthermore, consult the documentation or support forums provided by the Linux distribution you have chosen. These resources can provide valuable insights on the ideal hardware specifications and compatibility information required for successful installation and configuration.
Lastly, don't underestimate the importance of keeping your hardware drivers up to date. Ensuring that all the necessary drivers are compatible with your operating system can significantly enhance the overall functionality and performance of your Linux installation.
By thoroughly assessing your computer's hardware requirements and taking the necessary steps to ensure compatibility, you are setting yourself up for a smooth and successful Linux experience. So, invest the time at the beginning to save yourself from potential frustrations down the road.
Research Popular Linux Distributions for Novice Users
In order to embark on your Linux journey, it is essential to conduct thorough research and gain an understanding of the various Linux distributions available that are catered towards beginners. By exploring the diverse range of options, you can make an informed decision and select a distribution that aligns with your needs and preferences.
- Ubuntu: Known for its user-friendly interface and extensive community support, Ubuntu is a popular choice for Linux newcomers. It offers a wide range of pre-installed applications and is suitable for both desktop and server environments.
- Linux Mint: This distribution focuses on simplicity and elegance, providing a user-friendly experience similar to Windows. Linux Mint includes various desktop environments, making it adaptable to different user preferences.
- Zorin OS: Designed to mimic the appearance of familiar operating systems like Windows or macOS, Zorin OS is an ideal option for beginners. It offers a straightforward interface and provides seamless compatibility for running Windows applications.
- Elementary OS: With its sleek and intuitive interface, Elementary OS is often praised for its resemblance to macOS. This distribution emphasizes simplicity and minimalism, making it easy to navigate for newcomers.
- Manjaro: Manjaro offers a user-friendly experience while providing a powerful and flexible environment. It focuses on providing the latest stable packages and offers different desktop environments to suit various user preferences.
These are just a few examples of popular Linux distributions tailored for beginners. However, it is highly recommended to explore and compare different options to find the distribution that best suits your needs and preferences. Remember to consider factors such as user interface, available software, ease of use, and community support when conducting your research.
Creating a Bootable USB Drive with Linux

In this section, we will explore the process of creating a portable and versatile Linux installation by crafting a bootable USB drive. By following these steps, you can easily transform any compatible device into a Linux-powered tool to experience the flexibility and power of this dynamic operating system.
- Choose the Linux Distribution: Begin by selecting the Linux distribution that best fits your needs and preferences. There are numerous options available, each offering unique features and user interfaces.
- Obtain a USB Drive: Find a suitable USB drive with sufficient storage capacity, ensuring it is empty or has data that can be erased. This drive will become the platform to install Linux and make it easily accessible.
- Download the Linux ISO: Access the official website of your chosen Linux distribution and download the ISO file. This file contains a complete copy of the distribution's installation image and will be used to create the bootable USB drive.
- Choose a Tool for Creating the Bootable Drive: Select a reliable tool to create the bootable USB drive with the Linux ISO. Popular options include Rufus, Etcher, and UNetbootin, each offering a straightforward and intuitive interface.
- Connect the USB Drive: Insert the USB drive into an available USB port on your computer.
- Launch the Tool: Open the chosen tool and select the downloaded Linux ISO file as the source. Ensure the USB drive is correctly recognized as the destination.
- Create the Bootable USB Drive: Initiate the creation process, allowing the tool to copy the Linux installation image onto the USB drive. This may take some time, depending on the size of the ISO file and the speed of your computer.
- Verify the Bootable USB Drive: Once the process is complete, it is crucial to verify the integrity of the bootable USB drive. Some tools offer built-in verification features, while others require the use of additional software.
- Set Up Your Computer to Boot from USB: Before using the bootable USB drive, adjust the boot order in your computer's BIOS settings to prioritize USB devices. This will allow your computer to boot directly from the USB drive.
- Enjoy Linux on Any Computer: With the bootable USB drive ready, you can now enjoy the benefits of Linux on any computer by simply plugging in the drive and restarting the system.
By following these steps, you can easily create a bootable USB drive with Linux, providing you with a portable and customizable Linux experience wherever you go.
Acquire the Linux ISO File
To begin using the Linux operating system on your personal system, the first step is to download the Linux ISO file. This file contains the necessary files and data to install and run Linux on your computer. It is essential to obtain the correct ISO file for your specific requirements, as there are numerous distributions available, each tailored to different purposes and user preferences.
When acquiring the Linux ISO file, it is crucial to verify the authenticity and integrity of the source. It is recommended to download the ISO file from the official website of the Linux distribution you have chosen. This ensures that you are obtaining a trusted and genuine copy of the software.
Before initiating the download process, ensure that your internet connection is stable and reliable. Downloading the ISO file may require a significant amount of data, so a reliable network connection is essential to avoid any interruptions or corrupted downloads.
Once you have selected the appropriate distribution and verified the authenticity of the source, locate the download section on the official website. Look for the specific version and architecture of the ISO file that matches your computer's specifications. It is typically labeled as a downloadable link or button.
When you click on the download link, the ISO file will begin to transfer to your local storage. Depending on the size of the file and the speed of your internet connection, this process may take some time. It is recommended to be patient and allow the download to complete without interruption.
After the download is finished, it is advisable to verify the integrity of the ISO file to ensure its integrity and prevent any potential issues during the installation process. This can usually be done by comparing the checksum provided by the official website with the calculated checksum of the downloaded file. If they match, you can proceed with confidence.
With the Linux ISO file successfully downloaded and verified, you are now ready to move on to the next steps in the installation and configuration process, which will allow you to unleash the power and potential of Linux on your computer.
Using Rufus to Create a Bootable USB Drive
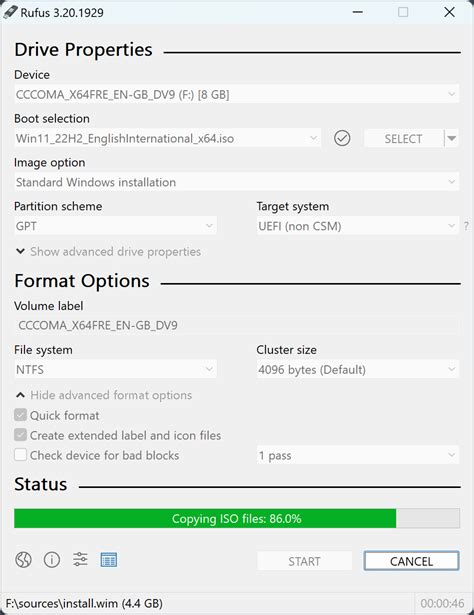
One of the essential steps in the process of setting up a Linux system on your computer is creating a bootable USB drive. In this section, we will explore how to use Rufus, a popular tool, to create a bootable USB drive that will allow you to install Linux.
Rufus is a user-friendly application that offers a simple and efficient way to create bootable USB drives. It provides various options and features that make the process of creating a bootable USB drive quick and hassle-free.
- First, download Rufus from its official website and install it on your computer.
- Next, insert a USB drive with sufficient storage capacity into your computer.
- Launch Rufus and select the USB drive you want to use from the list of available devices.
- Choose the appropriate partition scheme. For most installations, the MBR partition scheme is suitable.
- Select the file system format. It is recommended to use FAT32 for optimal compatibility.
- Ensure that the "Create a bootable disk using" option is selected and choose the ISO image of the Linux distribution you want to install.
- Review all the settings you have chosen, and click on the "Start" button to initiate the process.
- Wait for Rufus to create the bootable USB drive. This may take a few minutes.
- Once the process is complete, you will have a bootable USB drive ready to install Linux on your computer.
Using Rufus to create a bootable USB drive is a straightforward and efficient method that ensures a smooth installation of Linux on your computer. Make sure to follow the steps carefully and double-check all settings before starting the process.
Adjusting BIOS Configuration for Booting via USB
Configuring the settings in your computer's BIOS is a crucial step in order to boot from a USB drive. By adjusting the BIOS settings, you can prioritize the boot order and enable the USB boot option, allowing you to install or run Linux on your computer. Here are the steps:
- Start by accessing the BIOS settings. This can usually be done by pressing a specific key (like F2 or Del) during the computer's startup process. Consult your computer's manufacturer documentation for the specific key.
- Once inside the BIOS settings, navigate to the Boot menu or Boot tab.
- In the boot menu, locate the Boot Order or Boot Priority section.
- Adjust the boot order so that the USB drive is listed as the first boot device. This will ensure that the computer attempts to boot from the USB drive before other devices.
- If there is an option to enable the USB boot, make sure it is enabled.
- Save your changes and exit the BIOS settings.
After adjusting the BIOS settings, restart your computer with the USB drive plugged in. The computer should now boot from the USB drive, allowing you to install or configure Linux on your computer as desired.
Setting up Linux on Your Device
In this section, we will explore the process of installing a Linux operating system on your personal device. Whether you are looking to switch to Linux for its versatility, customization options, or security features, this guide will walk you through the steps involved in getting Linux up and running on your computer.
Step 1: Research and Choose a Distro Before diving into the installation process, it is important to research and decide on a Linux distribution that suits your needs. Linux offers a wide range of distros, each with its own set of features and functionalities. Consider factors such as the user interface, software package management, and community support when making your selection. |
Step 2: Create a Bootable USB Once you have chosen your preferred Linux distribution, the next step is to create a bootable USB drive. This will allow you to install the Linux operating system onto your device. Follow the instructions provided by the distro's official website or use third-party software to create the bootable USB. Ensure that you have backed up any important files as the installation process may involve formatting your device. |
Step 3: Prepare Your Device Before proceeding with the installation, it is important to prepare your device. Make sure it meets the recommended system requirements for the chosen Linux distribution. Backup any important data, as the installation process may involve partitioning or formatting the hard drive. Also, ensure that you have a stable internet connection as you may need to download additional packages during the installation. |
Step 4: Install Linux Now it's time to install Linux on your computer. Boot your device from the bootable USB drive and follow the on-screen instructions provided by the installer. You will be guided through various steps, such as selecting the installation type (dual-boot or wiping existing OS), partitioning the hard drive, and configuring basic system settings. Take your time to review each step and make the necessary selections based on your preferences. |
Step 5: Post-Installation Setup and Configuration Once the installation process is complete, you may need to perform post-installation setup and configuration. This includes tasks such as setting up user accounts, updating the system, installing additional software or drivers, and customizing the desktop environment. Follow the instructions provided by the Linux distro's documentation or explore online resources to help you with this step. |
By following these steps, you can successfully install and set up Linux on your personal device. Embrace the freedom and flexibility that Linux offers and enjoy exploring the vast ecosystem of open-source software!
Setting up Linux Boot from USB Drive
In this section, we will explore the necessary steps to enable your computer to start up using a USB drive containing the Linux operating system.
Booting your computer from a USB drive provides an alternate method to traditional methods such as booting from a CD or DVD. This option allows you to easily try out and install Linux without making any permanent changes to your existing system.
| Steps to Boot from USB Drive |
|---|
| 1. Prepare the USB drive |
| 2. Access the computer's BIOS settings |
| 3. Adjust the boot order in the BIOS |
| 4. Save changes and exit the BIOS |
| 5. Restart the computer with the USB drive |
| 6. Follow the on-screen prompts to install Linux |
Begin by preparing the USB drive, ensuring it is properly formatted and contains the necessary Linux ISO file. Next, access the BIOS settings of your computer, usually done by pressing a specific key during the startup process. Adjust the boot order in the BIOS to prioritize USB devices, enabling the system to recognize and boot from the USB drive. Save the changes made in the BIOS and exit. Restart the computer, making sure the USB drive is connected, and follow the on-screen instructions to install Linux.
Remember to remove the USB drive after the installation is complete to allow your computer to boot into the newly installed Linux operating system.
Follow the Steps of the Installation Wizard
Discover the streamlined process of configuring and setting up your Linux operating system by following the intuitive instructions presented in the Installation Wizard. This straightforward and user-friendly guide will walk you through the necessary steps to get your Linux system up and running efficiently, allowing you to explore and experience the power of this versatile operating system.
Step 1: System Requirements Check
Prior to the installation process, ensure that your computer meets all the system requirements necessary for running Linux smoothly. The installation wizard will perform a detailed check, evaluating factors such as processor speed, available memory, and disk space. It will also verify the compatibility of your hardware components, such as graphics and network cards, to ensure optimal performance.
Step 2: Language and Regional Settings
Personalize your Linux environment by selecting your preferred language and regional settings. The installation wizard provides a wide range of language options and allows you to customize date, time, and currency formats based on your geographic location. This ensures that your Linux system aligns perfectly with your linguistic and cultural preferences.
Step 3: Disk Partitioning
Configure your disk partitions to optimize the storage space and improve the efficiency of your Linux system. The installation wizard offers various partitioning schemes, allowing you to create separate partitions for system files, user data, and swap space. This flexibility enables you to allocate disk space according to your specific needs, ensuring a well-organized and responsive Linux environment.
Step 4: User Account Setup
Create your personalized user account, establishing a unique identity within your Linux system. The installation wizard enables you to set a strong password for enhanced security and grants the option to configure user privileges and access controls. This step ensures that you have full control over your Linux system, while maintaining a secure and individualized user experience.
Step 5: Software Selection
Customize your Linux system by selecting the software packages and applications that best suit your needs. The installation wizard provides a wide array of options, ranging from basic system utilities to advanced development tools. With this flexibility, you can create a tailored environment that matches your specific interests and requirements, maximizing your productivity and enjoyment.
Step 6: Installation Progress
Sit back and relax as the installation wizard takes care of the technical aspects, ensuring a smooth and efficient installation process. The progress bar updates in real-time, providing you with a clear indication of the installation status. Once completed, the installation wizard will prompt you to reboot your computer, allowing you to finally embark on your Linux journey.
Partitioning the Hard Drive: Organizing the Disk Space for Linux
In the vast world of operating systems, allocating the appropriate space on your hard drive is essential for a flawless Linux experience. Partitioning your hard drive involves creating distinct sections to store various types of data and improve system performance. In this section, we will explore the process of partitioning your hard drive specifically for Linux, ensuring an organized and well-structured operating environment.
Understanding the Importance of Partitioning
Partitioning your hard drive for Linux allows you to segregate and efficiently manage different components of the operating system. By allocating space specifically for system files, applications, user data, and swap space, you can optimize system performance and ensure better data protection.
Primary and Extended Partitions
When partitioning your hard drive, you will encounter primary and extended partitions. Primary partitions are the main sections where you install the operating system, applications, and store user data. Extended partitions, on the other hand, act as containers for logical partitions, allowing you to divide your disk space further.
Note: It is recommended to have at least one primary partition for the root file system (/) and a separate partition for the /home directory to store user-specific data.
Allocating Swap Space
Swap space, also known as virtual memory, plays a vital role in Linux systems. It serves as an extension of physical memory when the RAM becomes insufficient. It is highly recommended to allocate an appropriate amount of swap space during the partitioning process to avoid system crashes and improve overall performance.
Note: A commonly practiced rule is to allocate twice the amount of physical RAM as swap space.
Using Partitioning Tools
Partitioning can be done using various tools, such as GParted, fdisk, or the Linux installer itself. These tools provide intuitive interfaces and step-by-step instructions to help you create, edit, and manage partitions. It is essential to choose the tool that best suits your familiarity and requirements.
Note: Make sure to back up any important data before performing any partitioning actions to avoid data loss.
By following the partitioning guidelines outlined in this section, you can create an optimized and well-organized hard drive layout for your Linux system. This will enhance your overall experience, improve system performance, and ensure a smooth operating environment.
FAQ
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source operating system that is based on the Unix operating system. It provides users with a free, customizable, and secure alternative to proprietary operating systems like Windows and macOS.
Why would I want to install Linux on my computer?
There are several reasons why you might want to install Linux on your computer. Firstly, Linux offers a wide range of distributions (versions) with different features and user interfaces, allowing you to choose one that suits your needs and preferences. Additionally, Linux is known for its stability, security, and speed. It also provides a vast amount of free and open-source software, making it an attractive choice for developers and enthusiasts. Finally, Linux allows you to have more control over your computer's hardware and software, giving you the freedom to customize your system as you wish.
How do I install Linux on my computer?
Installing Linux on your computer is a relatively straightforward process. First, you need to choose a Linux distribution that you want to install. Then, you can create a bootable USB or DVD installer using the ISO file of your chosen distribution. After creating the installer, you need to restart your computer and boot from the USB or DVD. The installation process will guide you through selecting your language, partitioning your hard drive, and configuring your system. Once the installation is complete, you will have a fully functional Linux system on your computer.
Can I dual-boot Linux with my existing operating system?
Yes, it is possible to dual-boot Linux with your existing operating system (such as Windows). This allows you to choose which operating system to use every time you start your computer. To dual-boot, you would need to resize your existing partitions to create space for Linux, then install Linux on the newly created partition. During the installation process, you will be prompted to choose the option for dual-booting. Once both operating systems are installed, you can select the desired one from the boot menu every time you start your computer.




