Are you new to the world of server administration and looking to create a secure and efficient network infrastructure? One essential tool you'll want to familiarize yourself with is Active Directory. This powerful directory service allows you to manage users, computers, and resources in a networked environment, providing centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting.
In this article, we will dive into the basics of setting up and customizing an Active Directory environment on a Windows server. From understanding the essential components to configuring domain controllers and organizing your structure, we will guide you through the process step-by-step, ensuring you gain a solid foundation in managing your network effectively.
As you embark on this journey, be prepared to explore various concepts like domains, trees, forests, and organizational units. By grasping these fundamental building blocks, you'll be better equipped to configure your network to best suit your organization's needs. But don't worry - we will break down complex concepts into digestible portions and provide real-world examples to help you apply your newfound knowledge.
Whether you are a small business owner, an IT enthusiast, or a student seeking to expand your skill set, this beginner's overview will equip you with the necessary knowledge to create and manage an Active Directory environment on your Windows server. By the end, you'll be empowered to streamline user management, enhance security measures, and optimize network administration, laying a strong foundation for your organization's growth and success.
Introduction to the Concept of Active Directory
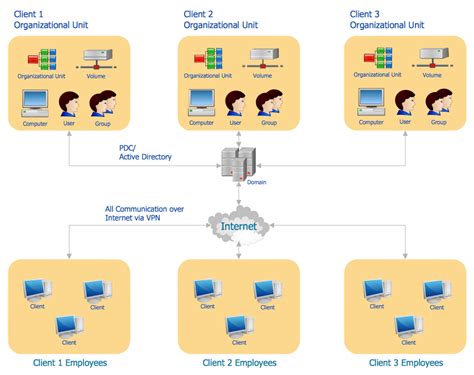
Understanding the key concept of Active Directory is essential to grasp the overall functionality and significance of this crucial component in the realm of network administration. Active Directory serves as a centralized database that facilitates the management and organization of various network resources, such as user accounts, computers, printers, and security policies. It provides a structured and hierarchical framework that allows network administrators to efficiently manage and control access to these resources.
Active Directory acts as a repository for information about the network's objects, storing their attributes and relationships, and enabling efficient searching and querying. It enables administrators to define and enforce security policies and access controls across the network, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized access. With its flexible and scalable nature, Active Directory offers a robust platform for managing complex networks, from small businesses to large enterprises.
- Centralized Resource Management: Active Directory provides a convenient and efficient way to manage user accounts, computers, and other network resources from a single location, simplifying administrative tasks and improving productivity.
- Secure Authentication and Authorization: By acting as an authentication and authorization platform, Active Directory ensures that users and devices can securely access the network resources they are authorized to use, while keeping unauthorized parties at bay.
- Seamless Integration with Windows Ecosystem: Designed by Microsoft, Active Directory seamlessly integrates with various Microsoft products and technologies, making it the go-to solution for Windows-based networks.
- Scalability and Extensibility: Active Directory can scale to support networks of different sizes and complexities, from simple local networks to globally distributed environments, accommodating the growth and evolution of organizations.
In summary, Active Directory serves as the backbone of network management, streamlining administrative tasks, enhancing security, and providing a robust and scalable foundation for efficient resource management. Mastering its installation and configuration is essential for any network administrator looking to optimize their Windows-based network infrastructure.
Requirements for Setting Up Active Directory
In order to successfully set up and configure Active Directory on your Windows Server, it is important to ensure your system meets the necessary requirements. These requirements encompass both hardware and software elements, which will be outlined in this section.
When it comes to hardware, it is crucial to have a server that meets the minimum specifications to support Active Directory. This includes sufficient processing power, memory, and storage capacity to handle the demands of directory services. Moreover, a stable network connection is essential for optimal performance and reliability.
On the software side, the appropriate version of the Windows Server operating system must be installed. Active Directory can be installed on different versions, such as Windows Server 2012, 2016, or 2019, depending on your specific needs and preferences. It is imperative to have the correct edition and service pack installed to ensure compatibility and access to all features and functionalities.
Additionally, it is important to have a working knowledge of the Windows Server operating system and its administration tools. Familiarity with concepts such as domains, forests, and domain controllers is crucial to properly configure and manage Active Directory.
Lastly, to successfully install and configure Active Directory, administrative privileges are required. This ensures that the necessary changes can be made to the system settings and effectively manage the directory service. Therefore, it is important to have the appropriate permissions and log in with an account that has administrative rights.
Step-by-Step Walkthrough for Setting up the Active Directory: Setting up Your Network Infrastructure

In this section, we will take you through the process of installing and configuring the Active Directory on your Windows Server. This step-by-step guide will provide you with a clear and concise walkthrough, helping you set up the necessary network infrastructure for your organization.
Setting up the Active Directory is a crucial step in establishing a centralized network management system. It allows you to create and manage user accounts, control access to resources, and streamline the administration of your network. By following this step-by-step guide, you will be able to install and configure the Active Directory with ease and efficiency.
The first step in setting up the Active Directory is to prepare your network infrastructure. This involves ensuring that your servers and networking devices are properly configured and connected. You will need to establish a reliable network connection, set up the appropriate IP addressing scheme, and configure DNS settings to enable name resolution within your network.
| Key Steps: |
| 1. Verify network connectivity between your Windows Server and other network devices. |
| 2. Set up a static IP address for your Windows Server to ensure consistent network communication. |
| 3. Configure your DNS settings to enable name resolution and domain controller location. |
| 4. Verify that your Windows Server can communicate with the internet to ensure access to necessary updates and resources. |
By completing these network infrastructure setup tasks, you will establish a solid foundation for installing and configuring the Active Directory on your Windows Server. Once your network is properly prepared, you can proceed to the next section of this guide, which will walk you through the actual installation and configuration of the Active Directory.
Setting up your Active Directory Configuration
Efficiently configuring your Active Directory is crucial for establishing a strong foundation for your network. This section will guide you through the process of customizing your Active Directory settings to ensure optimal performance and security.
Organizational Units and Hierarchies
One of the key aspects of configuring your Active Directory is designing a logical structure using Organizational Units (OUs) and hierarchies. OUs provide a way to categorize and organize objects within your network, allowing for efficient management and delegation of administrative tasks. By carefully structuring your OUs and hierarchies, you can meet the specific needs of your organization, enhance security, and improve overall management efficiency.
User and Group Management
Managing user accounts and groups is a critical part of configuring Active Directory. This involves creating user accounts, assigning appropriate permissions, and setting up group policies to enforce security and access control. By effectively managing users and groups, you can streamline user authentication, simplify file and resource sharing, and implement consistent security policies across your network.
Domain and Forest Functional Levels
Configuring the appropriate domain and forest functional levels is essential for leveraging the latest features and capabilities of Active Directory. Functional levels determine the available features, replication capabilities, and compatibility with older domain controllers. By upgrading your domain and forest functional levels, you can take advantage of advanced functionalities and ensure compatibility with newer Windows Server versions.
Trust Relationships
Establishing trust relationships with other domains or forests is necessary for enabling secure collaboration and resource sharing. This section will guide you through the process of creating trust relationships and configuring the appropriate trust settings to allow users from trusted domains to access resources in your Active Directory domain.
Security and Auditing
Ensuring the security of your Active Directory environment is essential for protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access. Configuring security settings, such as password policies, account lockouts, and auditing, can enhance the overall security posture of your network. This section will cover the essential security measures you should implement to safeguard your Active Directory infrastructure.
Replication and Site Configuration
Configuring replication and site settings is crucial for maintaining a consistent and resilient Active Directory infrastructure. This involves defining sites, subnets, and replication schedules to ensure efficient replication of directory data between domain controllers. By accurately configuring your replication and site settings, you can improve fault tolerance, optimize network traffic, and enhance the overall performance of your Active Directory environment.
Backup and Recovery
Implementing a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy is vital to protect against data loss and ensure business continuity. This section will guide you through the process of configuring regular backups of your Active Directory data, along with recovery techniques to quickly restore your directory services in case of any unexpected failures or disasters.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you will be able to configure your Active Directory environment effectively and unleash the full potential of its features and capabilities.
Essential Tasks for Setting up Active Directory

In this section, we will explore the fundamental tasks required to configure Active Directory and ensure it is properly functioning in your Windows environment. These tasks are crucial for managing user accounts, organizing resources, and securing network resources efficiently. Understanding and implementing these common configuration tasks will enable you to leverage the full potential of Active Directory for your organization.
Firstly, we will discuss the process of creating and managing user accounts within Active Directory. This includes defining user attributes, such as usernames, passwords, and user profiles. We will also explore methods for organizing users into logical groups to streamline the management process and enhance security measures.
Next, we will delve into the important task of configuring group policies in Active Directory. Group policies allow administrators to enforce specific settings and restrictions on user accounts, ensuring compliance with organizational policies and enhancing the overall security of the network. We will examine the process of creating and editing group policies, as well as assigning them to specific user groups or organizational units.
Another significant task for Active Directory configuration is the management of computer accounts. We will explore the process of joining client computers to the domain, configuring computer policies, and ensuring seamless communication between the client machines and the Active Directory infrastructure. Understanding these tasks is essential for establishing a robust network environment that maximizes productivity and security.
Lastly, we will touch upon the process of managing and securing shared resources within Active Directory, such as file servers and printers. We will explore techniques for creating and configuring shared folders, applying access control permissions to files and folders, and managing printer resources effectively. By mastering these tasks, you will be able to optimize resource availability and enhance data security within your organization.
By addressing these common Active Directory configuration tasks, you will gain the knowledge and skills necessary to establish a solid foundation for your Windows network environment. Understanding how to create and manage user accounts, configure group policies, manage computer accounts, and secure shared resources will empower you to utilize the power of Active Directory to its full potential.
Troubleshooting and Tips for Active Directory Installation and Configuration
In this section, we will explore common issues and provide useful tips for troubleshooting and optimizing the installation and configuration process of Active Directory. Whether you are new to this technology or have prior experience, these insights will help you navigate potential problems, improve the overall performance, and ensure the smooth operation of your Active Directory environment.
| Common Issues | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|
| Failed or Incomplete Installation | Ensure that system requirements are met, double-check prerequisites, and review installation logs for any error messages or warnings. Restarting the installation process after resolving any issues encountered during the initial attempt can often solve the problem. |
| Authentication and Access Problems | Verify that correct credentials are used and check domain and user permissions. Ensure the appropriate trust relationships are established and that firewall settings allow for necessary communication between the Active Directory components. |
| Replication and Replication Errors | Check the replication topology and connectivity between domain controllers. Use monitoring tools and logs to identify and troubleshoot replication errors. Address network issues or any inconsistencies found in directory data to restore proper replication. |
| Performance and Scalability Challenges | Optimize hardware resources, such as CPU and memory, to ensure efficient Active Directory operation. Use performance monitoring tools to identify bottlenecks and prioritize system tuning. Implement appropriate replication and site design strategies to support growing directory services. |
| Data Integrity and Recovery | Regularly back up Active Directory databases and system state to prevent data loss. Test backup and recovery procedures periodically to ensure data integrity and expedite recovery in case of failures. Implement proper tombstone reanimation and authoritative restore processes. |
By applying these troubleshooting tips to address common issues encountered during Active Directory installation and configuration, you can enhance the stability, reliability, and functionality of your Active Directory environment. Proper knowledge and proactive measures will enable you to effectively manage and maintain an optimal Active Directory infrastructure.
FAQ
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory is a directory service developed by Microsoft that is used to manage and organize resources on a network. It is commonly used in Windows server environments to centralize network administration and provide secure access to network resources.
Why would I need to install and configure Active Directory on Windows Server?
You would need to install and configure Active Directory on Windows Server if you want to create a centralized network administration environment, improve security by implementing user authentication and authorization, and manage network resources efficiently.
What are the steps to install and configure Active Directory on Windows Server?
To install and configure Active Directory on Windows Server, you need to first install the Active Directory Domain Services role, run the Active Directory Installation Wizard, create a new forest or join an existing one, specify the forest and domain functional levels, configure the DNS server, and finally, promote the server to a domain controller.




