Embarking on the journey of setting up a Linux operating system can be an exciting and rewarding experience. However, as with any complex endeavor, unforeseen obstacles may arise along the way. In this article, we will explore the necessary steps to tackle any unexpected issues that might occur during the installation process.
When configuring a new Linux environment, encountering challenges is not uncommon. It could be a compatibility problem with your hardware, a missing dependency, or even a simple oversight in the configuration settings. The key is to remain calm and approach the situation methodically.
Identifying and resolving these hurdles requires a combination of attentiveness and problem-solving skills. By paying close attention to the error messages and understanding the context in which they occur, you can gain valuable insights that will lead you towards a solution. It is important to note that panicking or hastily trying random fixes may exacerbate the situation, making it harder to diagnose and rectify the problem.
One of the first courses of action when encountering an error during Linux installation is to consult the available documentation and resources. Online forums, community support groups, and official documentation provide a wealth of information that can guide you in the right direction. Remember to describe your issue accurately and comprehensively, as community members are more likely to assist when presented with a clear and concise problem statement.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Errors

When installing an operating system based on Linux, it is not uncommon to encounter various errors that may hinder the installation process. In this section, we will discuss some of the frequently encountered errors during Linux installation and provide troubleshooting solutions to overcome them.
- 1. Boot Device Not Found
- 2. Disk Partitioning Error
- 3. Kernel Panic
- 4. Invalid or Corrupt ISO File
- 5. Driver Installation Failure
1. Boot Device Not Found
If you receive an error message indicating that the boot device cannot be found, it may be due to incorrect BIOS settings or issues with the boot order. To troubleshoot this error, navigate to the BIOS settings, ensure that the correct boot device is selected, and adjust the boot order accordingly.
2. Disk Partitioning Error
During the installation process, you may encounter errors related to disk partitioning. This could be caused by existing partitions that are not properly formatted or incompatible partitioning schemes. To resolve this, you can try deleting existing partitions, recreating them with the appropriate filesystem type, or using a different partitioning tool.
3. Kernel Panic
A kernel panic refers to a critical error that occurs within the Linux kernel, which leads to the system being unable to continue. This error can be caused by hardware issues, incompatible drivers, or faulty configurations. To troubleshoot kernel panics, you can try booting into a recovery mode, updating drivers, or performing a clean installation with different kernel parameters.
4. Invalid or Corrupt ISO File
If you encounter an error indicating that the ISO file is invalid or corrupt, it is essential to verify the integrity of the downloaded file. This can be done by comparing the hash values or performing a checksum. If the file is indeed corrupt, redownloading it or using a different source is recommended.
5. Driver Installation Failure
Sometimes, you may face difficulties installing specific device drivers during the Linux installation. This could be due to unsupported hardware or missing dependencies. To troubleshoot driver installation failures, you can check the manufacturer's website for updated drivers, search for community-supported drivers, or consult relevant online forums and documentation.
By understanding and effectively troubleshooting common installation errors encountered during the Linux installation process, you can ensure a smoother and more successful installation experience.
Checking Compatibility of your Hardware Before Starting the Linux Installation Process
Ensuring that your hardware components are compatible with the Linux operating system before initiating the installation process is crucial for a successful setup. By conducting a thorough compatibility check, you can identify potential issues and avoid errors that may arise during the installation. This section will guide you through the necessary steps to assess the compatibility of your hardware with Linux, allowing you to proceed with confidence.
- Research the Linux Distribution: Choose a Linux distribution that best suits your hardware requirements. Different distributions may have specific hardware requirements, so it is essential to select one that matches your system's specifications. Researching and understanding the hardware requirements of your chosen distribution will help ensure a smooth installation.
- Review Hardware Specifications: Familiarize yourself with the hardware specifications of your system. This includes the processor, amount of RAM, graphics card, storage devices, and other peripherals. Refer to the documentation or manufacturer's website to gather accurate information about each component.
- Check Hardware Compatibility Lists: Browse through hardware compatibility lists provided by the Linux distribution's official website or community forums. These lists often contain information regarding certified hardware and any potential compatibility issues. Look for your specific components to determine whether they are officially supported or known to cause problems.
- Search for User Experiences: Look for online forums, discussion boards, or social media groups where users share their experiences with Linux installations and hardware compatibility. You may find valuable insights and troubleshooting tips from individuals who have similar hardware configurations.
- Consult Documentation and Support: Study the documentation provided by the Linux distribution, as it may contain specific hardware recommendations or troubleshooting steps. Additionally, reach out to the distribution's support channels, such as forums or online chat, to clarify any doubts or concerns regarding hardware compatibility.
By following these steps to check the compatibility of your hardware with Linux, you can mitigate potential errors and ensure a smooth installation process. This pre-installation preparation will save you time and frustration, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of Linux without any hardware-related complications.
Resolving Error Messages During Partitioning
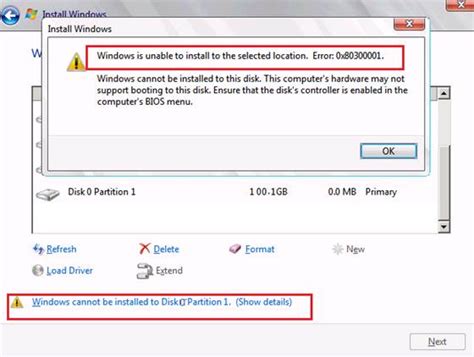
In the process of setting up your Linux system, you may encounter certain obstacles when it comes to partitioning your hard drive. This section will guide you through common error messages that you might encounter during the partitioning phase and provide effective solutions to resolve them.
1. Disk Space Allocation Issue:
If you receive an error message regarding insufficient disk space during partitioning, it is important to analyze your disk usage and reallocate space accordingly. Consider removing unnecessary files or resizing existing partitions to free up space for the installation process.
2. Partition Table Corruption:
In case you come across an error message indicating a corrupted partition table, it is crucial to repair it before proceeding. You can use tools like fdisk or parted to identify and fix any corruption issues in the partition table, ensuring smooth installation.
3. Invalid Partition Layout:
An error message concerning an invalid partition layout suggests that your current partition structure does not meet the requirements for Linux installation. It is recommended to review and modify your partition layout, considering the specific guidelines and recommendations for Linux file systems and their respective partitions.
4. Damaged or Unreadable Hard Drive:
If you encounter an error message indicating a damaged or unreadable hard drive, it is crucial to investigate and troubleshoot the issue. Checking the hard drive's physical connections, running disk checks using utilities like fsck, and considering data recovery options can help resolve this error and ensure successful installation.
5. Insufficient System Resources:
When an error message suggests a lack of system resources during the partitioning process, it is necessary to examine your system's hardware capabilities. Check if your computer meets the minimum requirements for the Linux distribution you are installing, and consider upgrading hardware components if necessary.
In conclusion, encountering errors during the partitioning stage is not uncommon, but with proper troubleshooting and resolution methods, these issues can be overcome. By following the guidelines and implementing the solutions provided, you can successfully overcome error messages and achieve a smooth Linux installation.
Resolving Bootloader Installation Issues
When setting up your Linux operating system, certain complications may arise during the installation process. In this section, we will explore a range of possible solutions to address problems that occur when installing the bootloader component.
If you encounter difficulties related to installing the bootloader, it is important to remain calm and take the following steps to troubleshoot the issue:
- Verify the integrity of your installation media – Ensure that the source from which you are installing Linux is reliable and error-free. Check for any physical damage on the installation media, such as scratches on a DVD or USB flash drive.
- Try a different installation method – If the problem persists, consider switching to an alternative installation method. For instance, if you were using a live CD, you may attempt a network installation instead.
- Review system requirements – Confirm that your hardware meets the necessary requirements for running the particular Linux distribution you are installing. Inadequate hardware specifications can lead to installation issues, including problems with the bootloader.
- Check BIOS settings – Access your computer's BIOS settings and ensure that they are correctly configured for Linux installation. Pay close attention to options related to boot order and secure boot settings, as these can affect the installation process.
- Partitioning considerations – Understand the importance of proper partitioning during the installation procedure. Take care to accurately allocate the necessary partitions for Linux, including the root partition and any additional partitions required.
- Consider alternative bootloaders – If you continue to encounter difficulties, it might be beneficial to explore other bootloaders. Research alternative options that are compatible with your Linux distribution and try their installation instead.
- Seek community support – Don't hesitate to seek assistance from Linux user forums, community websites, or official documentation. The Linux community is typically very helpful, and others may have encountered similar issues during installation.
By following these troubleshooting suggestions, you will be well-equipped to address any issues that may arise during the bootloader installation process, ensuring a successful Linux installation.
Solving Network Configuration Problems
In the process of setting up your Linux system, you might encounter difficulties in configuring your network settings. This section provides guidelines and troubleshooting steps to help you resolve network configuration issues effectively.
- Check Network Connectivity: Start by verifying that your network cables are properly connected and that there are no physical issues causing the problem. Ensure that your network devices, such as routers or switches, are powered on and functioning correctly.
- Configure IP Address: If you are unable to connect to the network, check your IP address settings. Make sure that your computer is configured to obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP server. Alternatively, you can manually assign a static IP address within your network's subnet range.
- Verify DNS Settings: Incorrect DNS (Domain Name System) settings can lead to network connectivity problems. Confirm that your DNS server addresses are accurate and configured correctly in your network settings. You can also try using public DNS servers, such as Google DNS or OpenDNS, to see if that resolves the issue.
- Check Firewall Settings: Firewalls can block network traffic, preventing your Linux system from accessing the network. Review your firewall settings and ensure that they are not excessively restrictive. You might need to modify your firewall rules to allow the necessary network services and ports.
- Reset Network Interfaces: If you continue to experience network configuration problems, restart your network interfaces. You can do this by disabling and re-enabling your network adapter or restarting the network service.
- Update Network Drivers: Outdated or incompatible network drivers can cause network issues. Check for updates for your network drivers and install the latest versions available. This can often resolve compatibility problems and improve network stability.
- Seek Help and Resources: If you have exhausted all troubleshooting options and still cannot resolve the network configuration problem, seek assistance from community forums, online resources, or support channels specific to your Linux distribution. Experienced users and experts can provide valuable insights and guidance in resolving complex network issues.
By following these steps and seeking appropriate assistance, you can effectively solve network configuration problems and establish a stable and reliable network connection on your Linux system.
Seeking Help from the Linux Community and Forums
When encountering difficulties during the installation process of your Linux operating system, it can be beneficial to seek assistance from the vast and knowledgeable Linux community. By reaching out to forums and engaging with experienced Linux users, you can find valuable insights, troubleshooting tips, and possible solutions to resolve your installation errors.
One effective strategy is to join online Linux forums where users can freely discuss and share their experiences. These forums provide a platform to seek guidance from experts and connect with individuals who have encountered similar issues. By describing your problem in detail and providing relevant system information, you increase the likelihood of receiving accurate advice that can help you rectify the error.
When posting on a forum, it is important to be respectful and clear in your query. Be sure to use appropriate subject lines and categorize your post to ensure it reaches the right audience. It can also be helpful to include error messages or logs, if available, as this can assist contributors in understanding the root cause of the problem.
In addition to forums, many Linux distributions have official support channels, such as mailing lists or dedicated community websites. These resources often have experienced volunteers or developers who actively engage with users and provide assistance. Utilizing such resources can significantly increase your chances of finding a solution or receiving guidance directly from those involved in developing and maintaining the Linux distribution.
Another valuable approach is to consult online documentation and search for existing solutions to similar installation errors. Many Linux distributions have extensive documentation, including troubleshooting guides, which can be accessed through their official websites. By thoroughly examining these resources, you may find step-by-step instructions or workarounds that address your particular installation issue. It's important to note that while personal experiences and advice from the community can be insightful, they should always be supported by reliable sources and cross-referenced with official documentation.
Remember, the Linux community is vast and diverse, meaning that you are likely to find individuals who have encountered and resolved similar issues before. Leveraging the collective knowledge and support within this community can significantly improve your chances of overcoming installation errors and successfully setting up your Linux operating system.
FAQ
What should I do if I encounter an error during the Linux installation?
If you encounter an error during the Linux installation process, the first thing you should do is carefully read the error message. The error message can provide valuable information about the cause of the issue and help you troubleshoot it. Once you understand the error message, you can try searching for a solution online. Many Linux distributions have active communities and forums where users can ask for help and find solutions to common installation errors. If you cannot find a solution online, you can also try reaching out to the Linux distribution's support team for assistance.
I received an error that says "Unable to write to disk" during the Linux installation. What should I do?
If you receive an error message stating "Unable to write to disk" during the Linux installation, there are a few steps you can take to resolve the issue. First, make sure that you have selected the correct disk or partition to install Linux on. Sometimes, the error can occur if you are trying to install Linux on a disk with insufficient space. In such cases, you should free up some space on the disk by deleting unnecessary files or resizing partitions. If the issue persists, you should also check if the disk you are trying to install Linux on is in good health. Use disk utility tools to check for any errors or bad sectors on the disk. If the disk is faulty, you may need to replace it before proceeding with the installation.
I encountered an "Error loading operating system" message after installing Linux. What can I do to fix it?
If you receive an "Error loading operating system" message after installing Linux, it usually indicates an issue with the bootloader. The bootloader is responsible for loading the operating system on the computer. To fix this error, you can try reinstalling the bootloader. You can do this by booting from a Linux installation USB or DVD and selecting the option to repair or reinstall the bootloader. Another solution is to use a boot repair tool, such as Boot-Repair, which can automatically fix common bootloader issues. If you are dual-booting with another operating system, make sure that the bootloader is configured correctly to allow you to choose between different operating systems at startup. If none of these solutions work, you may need to seek help from the Linux community or consult a professional for further assistance.




