Do you ever find yourself curious about the intricate inner workings of your computer? Are you itching to explore the fascinating universe of Linux distributions? Look no further! In this article, we will guide you on an exciting journey to uncover the distinct identity of your operating system.
As you delve into the realm of Linux, you will encounter a vast array of flavors, each with its own set of features and characteristics. It's like stepping into a bustling marketplace filled with diverse cultures and traditions, where each distribution stands out with its unique blend of software, design, and philosophy.
With a little detective work and the help of a few simple commands, you can become a skilled investigator – a Sherlock Holmes of the Linux world. Together, we will unravel the mysteries that surround your system, uncovering the secrets hidden in the terminal and deciphering clues left behind by the creators of your distribution.
Prepare to embark on a thrilling adventure as we equip you with the necessary tools and knowledge to identify your Linux flavor. Whether you're a novice seeking to satisfy your curiosity or a seasoned Linux user looking to uncover the secrets of a newly installed distribution, this article will serve as your trusty guide along the way.
Ways to Determine Which Linux Distro is Present on Your System

Discovering the specific Linux distribution running on your machine can be a valuable piece of information for troubleshooting or compatibility purposes. By examining various characteristics and system indicators, you can unveil the identity of the Linux distro without relying on explicit terms. By exploring distinct aspects of your system, such as software repositories, package managers, and visual elements, you can effectively identify the Linux distribution installed on your computer.
1. Investigating the Package Management System
The package management system used by your Linux distribution can help determine its identity. Different distros utilize unique package managers, such as APT, DNF, Pacman, or Zypper. By exploring the package management commands and their associated syntax, you can gain insights into the specific Linux distro present on your system.
2. Analyzing the Software Repositories
Each Linux distribution has its own set of official software repositories, which are used to obtain software packages securely. By examining the repositories configured on your system, you can deduce the Linux distro. Repositories may include specific keywords or URLs that can be indicative of the underlying distribution.
3. Assessing the Graphical User Interface and Default Applications
The visual elements of the graphical user interface (GUI) can offer valuable clues about the Linux distro in use. By examining the layout, icons, and default applications, you can identify common visual indicators associated with specific distros. Pay attention to distinctive desktop environments like GNOME, KDE, or Xfce, as they often correlate with certain Linux distributions.
4. Examining System Configuration Files
System configuration files can provide information about the Linux distro's identity. Analyzing configuration files like /etc/os-release or /etc/lsb-release can reveal essential details about the distribution, including its name, version, and other pertinent information.
5. Looking for Distribution-Specific Commands and Utilities
Many Linux distributions have their own set of unique commands and utilities. By researching and executing distribution-specific commands, such as zypper, yum, or apt-get, you can narrow down the potential options and identify the Linux distro with greater precision.
By utilizing these diverse methods and evaluating distinctive aspects of your system, you can successfully determine the Linux distribution present on your computer. Gaining this knowledge enhances your understanding of the system environment and enables you to make informed decisions relating to compatibility, customization, and troubleshooting.
Checking the Release File
Examining the release file can provide valuable information about the specific version of the Linux operating system running on your device. This text file contains essential details regarding the installed distribution, including its name, release number, and any customizations made by the manufacturer.
To begin, navigate to the directory where the release file is typically located on your Linux machine. This file is commonly named either "release" or "version" and is often found within the /etc/ directory. Open this file using a text editor program or utilize the command-line interface to view its contents.
Once you have accessed the release file, scan through the text to locate the pertinent information about your Linux distribution. Look for identifiers such as the distribution name, version number, and codename, if applicable. These details will help you determine the specific flavor of Linux running on your computer.
| Release Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Distribution Name | Provides the name or brand of the Linux distribution. |
| Version Number | Specifies the release number or version of the installed Linux distribution. |
| Codename | Indicates a unique codename associated with the release of the Linux distribution, if applicable. |
After identifying the essential details from the release file, you can cross-reference this information with official documentation or online resources to gather further insights into your Linux distribution. This knowledge can be beneficial for troubleshooting, obtaining specific software packages compatible with your system, or seeking support from the Linux community.
By checking the release file, you can obtain valuable information about the Linux distribution installed on your device, helping you understand its characteristics and enabling you to make informed decisions regarding software compatibility and system maintenance.
Using the lsb_release Command
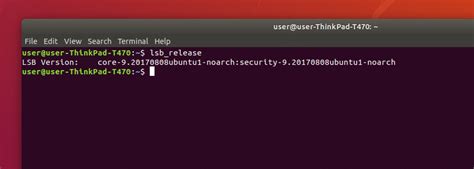
In this section, we will explore a useful command called lsb_release that allows you to determine the specific Linux distribution running on your system. By utilizing this command, you can easily identify the unique characteristics and version of your Linux distribution without the need for complex steps.
To access the lsb_release command, open your terminal and type lsb_release followed by the appropriate options. One of the most commonly used options is -a, which provides comprehensive information about the Linux distribution, including its ID, description, release number, and codename.
- Using the
-ioption with lsb_release will display the ID of your Linux distribution, providing a clear identification of the system you are running. - By employing the
-doption, you can obtain a descriptive summary of your Linux distribution, giving you insights into its unique features and characteristics. - The
-roption will provide you with the release number of your Linux distribution, enabling you to determine the specific version you are using. - If you want to know the codename associated with your Linux distribution release, you can use the
-coption.
By utilizing the lsb_release command with these various options, you can easily identify and gather essential information about the Linux distribution installed on your system. This command simplifies the process of determining the specific characteristics and version of your Linux distribution, allowing you to effectively manage and troubleshoot your system.
Analyzing System Configuration Files
Understanding the structure and contents of system configuration files can provide valuable insights into the specific distribution and settings of your Linux operating system.
Analyzing these files allows us to examine key aspects of the system, such as the installed packages, network configuration, kernel parameters, and user settings. By scrutinizing the contents of these files, we can discern the unique features and characteristics of your Linux distribution.
One important system configuration file is the /etc/os-release file, which provides details about the distribution, version, and codename. Additionally, the /etc/apt/sources.list file enables us to analyze the software repositories used by the system.
Other files, such as /etc/network/interfaces and /etc/sysctl.conf, store network and kernel configuration settings respectively, providing further insights into the system's setup and performance optimizations.
By examining these system configuration files, we can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying components and settings of your Linux distribution, which can be valuable for troubleshooting, customization, and optimizing your system.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
How can I identify the Linux distribution installed on my computer?
You can identify the Linux distribution installed on your computer by using different commands. One way is to use the 'lsb_release' command, which displays information about the Linux distribution. Another method is to check the contents of the '/etc/os-release' file using the 'cat' command.
Is there a graphical way to identify the Linux distribution installed on my computer?
Yes, there are graphical tools available to identify the Linux distribution. One popular tool is 'Hardinfo', which provides detailed information about the hardware and software on your computer, including the Linux distribution. Another tool is 'Neofetch', which displays system information in a visually appealing way.
What is the importance of identifying the Linux distribution on my computer?
Identifying the Linux distribution installed on your computer is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps you understand the specific features and capabilities of your operating system. Secondly, it allows you to find and install software packages that are compatible with your distribution. Lastly, knowing the distribution helps in troubleshooting issues and seeking support from the Linux community.
Can I have multiple Linux distributions installed on my computer?
Yes, it is possible to have multiple Linux distributions installed on your computer. This is known as running a "dual-boot" system. During the installation process, you can allocate separate partitions or disk space for each distribution. This allows you to choose between different distributions when booting up your computer.
Are there any command-line tools specifically designed to identify Linux distributions?
Yes, there are command-line tools designed specifically to identify Linux distributions. One such tool is 'inxi', which provides detailed information about your system, including the distribution name and version. Another tool is 'uname', which displays basic information about the operating system, including the Linux kernel version.




