In today's interconnected world, the smooth functioning of a network is vital to the success of any organization. Being able to efficiently manage various aspects of your network, including the Domain Name System (DNS) entries, can greatly contribute to the overall performance and security of your network infrastructure.
Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or just starting to delve into the complexities of network administration, understanding how to remove DNS entries on your Windows-based server can be a valuable skill to possess. By effectively removing unnecessary or obsolete DNS entries, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your network, minimizing potential issues and ensuring seamless communication between devices.
However, the process of removing DNS entries can be perplexing for those who are not familiar with the intricate workings of DNS servers. That is why this article will guide you through the step-by-step process of removing DNS entries on your Windows-based server, empowering you with the knowledge to confidently manage and optimize your network connections.
Understanding the Functionality of a Domain Name System (DNS) Entry
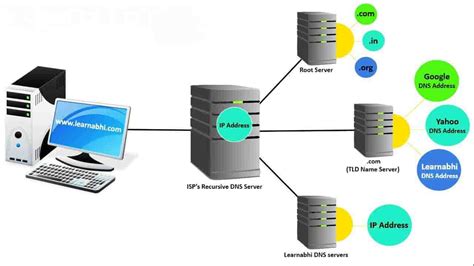
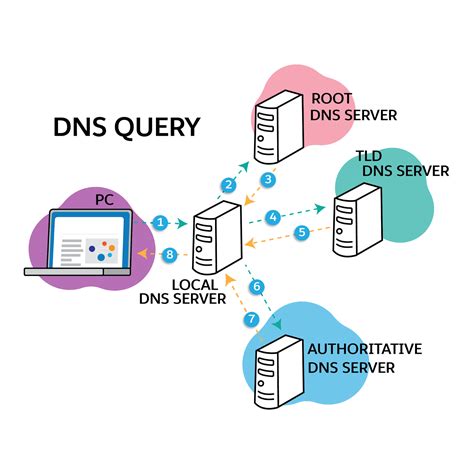
A domain name system (DNS) entry plays a crucial role in the functioning of a network infrastructure. It serves as a vital component that connects human-readable domain names to their corresponding IP addresses. By translating domain names into IP addresses, DNS entries facilitate communication between devices and enable users to access websites, servers, and various network resources effortlessly.
When a user enters a domain name into a browser, the DNS entry comes into action. It acts as a directory or a phone book that matches the name of the website or resource with its corresponding numerical IP address. Essentially, DNS entries serve as a link between the user's request and the server that hosts the requested content.
These DNS entries are stored in DNS servers, which are responsible for managing and resolving domain names. They store records that provide important information, such as the IP address associated with a specific domain name, the time-to-live (TTL) value, and other relevant data that helps in efficient network communication.
With a well-maintained DNS entry, network administrators can ensure smooth and reliable access to various resources within the network. It allows for efficient routing of data packets, reduces latency, and improves overall network performance.
To summarize, understanding the functionality of a DNS entry is crucial for network administrators and IT professionals. It enables them to manage and troubleshoot DNS-related issues effectively, ensuring seamless access to network resources and optimal performance of the network infrastructure.
Various Approaches for Eliminating a Records in Windows Server Configuration
When administering a Windows Server, it is essential to understand how to modify the Domain Name System (DNS) configuration effectively. One crucial task in DNS management involves removing specific entry records from the server. This section presents an overview of the common techniques and methods utilized to eliminate unwanted DNS entries on a Windows Server system.
1. Manual Removal:
Manually removing a DNS entry involves accessing the DNS management console, locating the target record, and deleting it directly. This approach provides a straightforward and immediate solution for removing unwanted records from the server's configuration. However, caution must be exercised to ensure that the correct records are selected for deletion.
2. Command-line Interface (CLI) Removal:
For those comfortable working with the Windows command prompt, utilizing the Command-line Interface (CLI) can provide an efficient method for removing DNS entries. By executing specific commands, it is possible to directly modify the server's DNS configuration and eliminate unwanted records. This technique is particularly useful when dealing with multiple entries that need removal or for automation purposes.
3. PowerShell Scripting:
PowerShell scripting offers a powerful toolset for managing DNS entries on a Windows Server environment. By creating scripts that leverage PowerShell cmdlets specifically designed for DNS management, it becomes possible to remove entries quickly and accurately. This approach is ideal for administrators who prefer automation and want to perform bulk removals or recurring tasks.
4. Third-Party Tools:
Third-party tools provide an alternative approach for removing DNS entries, offering additional features and functionality beyond the standard Windows Server capabilities. These tools often provide a user-friendly interface, allowing administrators to easily navigate, identify, and delete specific records. Some tools also offer advanced options, such as automated scanning for obsolete or duplicate entries.
DNS entry removal is a crucial aspect of server administration, ensuring that the DNS configuration remains accurate and up to date. By utilizing the various methods mentioned above, administrators can choose the approach that best meets their requirements, whether it be a manual removal, CLI commands, PowerShell scripting, or the use of third-party tools.
Remember to exercise caution and validate the removal actions to avoid unintended consequences, such as disrupting critical services or impacting network connectivity.
Best Practices and Recommendations for Removal of Domain Name System (DNS) Records
Efficient management of DNS records is crucial for maintaining a stable and secure network infrastructure. In this section, we will explore some best practices and recommendations for removing DNS entries in a Windows environment, keeping in mind the significance of accurate and up-to-date DNS configurations.
- Perform Regular DNS Audits: It is essential to conduct regular audits of your DNS records to identify and remove any outdated or unnecessary entries. This proactive approach ensures that your DNS infrastructure remains streamlined and efficient, reducing the risk of potential vulnerabilities or resource wastage.
- Verify DNS Record Ownership: Before removing any DNS entry, ensure that you have the necessary permissions and authority to make changes to the specific record. This practice minimizes the chances of accidental deletion or unauthorized modifications.
- Backup DNS Configuration: Prior to removing any DNS entry, it is highly recommended to create a backup of the existing DNS configuration. This backup serves as a safety net and allows for easy restoration in case of any unexpected issues or mistakes.
- Document Changes: Maintaining thorough documentation of all DNS record removals is essential for maintaining an organized and easily traceable network infrastructure. Proper documentation enables efficient troubleshooting and helps in understanding the history of DNS modifications.
- Monitor DNS Changes: Implementing a monitoring system for DNS changes allows for real-time tracking of any modifications made to the DNS records. This helps in promptly identifying any unauthorized or potentially malicious changes and taking corrective actions.
- Verify DNS Propagation: After removing a DNS entry, it is recommended to verify the propagation of the changes by testing the resolution of the corresponding domain or hostname. This ensures that the removal has been successfully propagated throughout the network and avoids any potential disruptions.
- Periodic Review of DNS Records: Regularly review and reevaluate your DNS records to eliminate any obsolete or redundant entries. This practice helps in optimizing network performance and mitigating security risks.
By following these best practices and recommendations, you can ensure the accurate and efficient removal of DNS entries in a Windows network environment, contributing to the overall stability and security of your infrastructure.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Can I remove multiple DNS entries at once on Windows Server?
No, the DNS Manager on Windows Server does not provide a built-in option to remove multiple DNS entries at once. Each DNS entry needs to be removed individually by following the steps mentioned in the answer to the first question.
Is it possible to restore a deleted DNS entry on Windows Server?
No, once a DNS entry is deleted from the Windows Server, it cannot be directly restored. However, if you have a backup or a previous zone file, you can import it to restore the DNS entry. It is recommended to regularly backup your DNS data to avoid permanent loss of important records.
What is a DNS entry?
A DNS entry, also known as a DNS record, is a mapping between a domain name and an IP address. It allows computers to communicate with each other over the internet using user-friendly domain names instead of numerical IP addresses.
Why would I need to remove a DNS entry on a Windows Server?
There can be several reasons why you might need to remove a DNS entry on a Windows Server. Some common reasons include updating IP addresses, decommissioning a server, or resolving issues with incorrect or outdated DNS records.




