Imagine immersing yourself in a world where listening is not just about hearing, but about feeling. Picture a place where every sound, every syllable, reaches your ears with crystal clarity, stirring your emotions and awakening your senses. Today, we delve into the realm of audio innovation and discover a groundbreaking technique that will revolutionize the way you experience sound.
Unleashing the potential of your audio devices, we explore the art of connecting the voice of your world, the source of your expression, to the gateway of your personal auditory journey. By transforming the auditory input from your recording device into a captivating soundscape that resonates through your headphones, we enable you to witness the magic of audio conversion.
Through utilizing intelligent engineering and cutting-edge technology, we pave the way for a seamless connection between your microphone and headphones. You will discover the ability to bridge the gap between your musical aspirations and the crisp, vibrant performance that envelopes your auditory senses, transcending mere utility and into the realm of sheer delight.
Prepare to embark on an extraordinary journey towards unlocking the true potential of your audio experience. Join us as we explore the intricacies of this groundbreaking conversion process, with every syllable encompassing the power to transport you into a realm where your imagination knows no bounds.
Connecting a Mic to Headphones: A Step-by-Step Guide
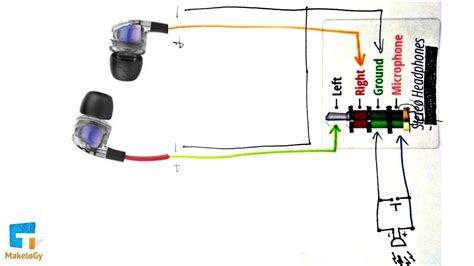
Are you looking to link your microphone to your headphones? In this section, we will guide you through the process step by step, ensuring a smooth connection and optimal audio quality. Follow these instructions closely to ensure successful integration.
- Check the compatibility: Before attempting any connections, make sure that the microphone and headphones are compatible with each other. Refer to the user manuals or the manufacturer's website for information on compatibility.
- Prepare the necessary cables: Identify the appropriate cables required to connect the microphone to the headphones. This may involve an audio adapter or specific connectors depending on the input and output ports of your devices.
- Inspect the ports: Locate the input port on your headphones and the output port on your microphone. Ensure that both ports are clean and free from any obstructions or damage that may affect the connection.
- Connect the cables: Insert one end of the cable into the output port of the microphone and the other end into the input port of the headphones. Make sure the cable connections are secure and tight.
- Adjust the audio levels: Once the microphone and headphones are connected, adjust the audio levels accordingly. Refer to the user manual of each device to understand how to adjust the volume settings properly.
- Test the connection: To confirm the successful connection, perform a test recording using the microphone and listen to the audio playback through the headphones. If the sound quality is clear and without any distortions, the connection is successful.
By following these step-by-step instructions, you can easily connect your microphone to your headphones and enjoy a seamless audio experience. Remember to refer to the user manuals of your devices for specific guidance and troubleshooting tips. Enjoy your newfound ability to use your microphone with your headphones!
Understanding the Fundamentals of Sound Input and Output
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental principles behind the transmission of sound from a source to a receiver. By gaining a better understanding of the basic concepts related to sound input and output, we can explore the process of converting sound captured by a recording device, such as a microphone, into audible sound through a playback device, such as headphones.
- Sound Waves: Exploring the Nature of Sound
- Signal Conversion: From Analog to Digital
- Transducers: Converting Sound Energy
- Amplification and Attenuation: Controlling Sound Levels
- Audio Interfaces: Connecting Devices
- Headphone Design: Delivering High-Quality Sound
In this section, we will examine the basic principles of sound waves and their characteristics, including frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. We will also explore the concept of converting analog sound signals into digital data, which is essential for processing and transmitting sound through various devices.
Additionally, we will discuss transducers, which are responsible for converting sound energy into electrical signals and vice versa. This understanding will be vital as we explore the process of capturing sound with a microphone and reproducing it through headphones.
Moreover, we will touch on the importance of amplification and attenuation in adjusting sound levels to suit personal preferences and optimize audio quality. We will also address the role of audio interfaces in facilitating the connection between different devices, enabling seamless transmission of sound.
Finally, we will explore the design elements and technologies behind headphones, focusing on their ability to deliver high-fidelity sound reproduction and create an immersive audio experience for the listener.
- Sound Input and Output: Explained
- Understanding Sound Frequencies
- The Role of Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- Transducers: Sound Energy in Action
- Controlling Sound Levels with Amplification and Attenuation
- Connecting Devices with Audio Interfaces
- Unraveling the Secrets of Headphone Design
Choosing the Suitable Audio Interface for Your Requirements

When it comes to enhancing your audio capabilities, selecting the proper audio interface is crucial. This section will guide you through the process of identifying the audio interface that best suits your individual needs.
- Consider the Purpose: Determine the specific purpose for which you require an audio interface, such as recording vocals, instruments, or podcasting.
- Connectivity: Evaluate the different types of connections supported by audio interfaces, including USB, Thunderbolt, FireWire, and PCIe, and select one that is compatible with your device.
- Input and Output Options: Assess the number and types of inputs and outputs required for your intended use, such as XLR, quarter-inch, or MIDI inputs, and headphone or line outputs.
- Sample Rate and Bit Depth: Determine the sample rate and bit depth that your projects demand, as this will affect the audio quality and resolution.
- Budget: Establish a budget range and explore audio interfaces within that range, ensuring that you strike a balance between affordability and quality.
- Software Compatibility: Verify that the audio interface is compatible with your preferred recording software, ensuring a smooth integration.
- Portability: If you require a mobile setup, take into consideration the portability and size of the audio interface you choose.
- Additional Features: Research and compare additional features offered by different audio interfaces, such as preamps, built-in effects, and loopback functionality.
By carefully considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can successfully select the ideal audio interface that caters to your specific audio needs. Keep in mind that the right audio interface will enable you to achieve professional and high-quality sound recordings.
Connecting Your Microphone to the Audio Interface
When it comes to integrating your microphone with an audio interface, there are several essential steps to consider. By following these instructions, you can ensure a seamless connection between your microphone and the audio interface, allowing for high-quality sound reproduction.
Step 1: Selecting the appropriate cables
Before connecting your microphone to the audio interface, it is crucial to choose the right cables. It is recommended to use XLR cables for their balanced audio signals, ensuring optimal audio quality. Additionally, consider the length of the cables to avoid any limitations or interference.
Step 2: Identifying the input/output ports
Once you have the correct cables, identify the input and output ports on both the microphone and the audio interface. These ports may vary depending on the specific models, but commonly include XLR, TRS, or even USB connections. Make sure to consult your microphone and audio interface manuals for precise information.
Step 3: Connecting the microphone
Gently connect one end of the XLR cable to the microphone's output port and the other end to the audio interface's input port. Ensure that the connections are secure but do not force the connectors. Taking care of the physical connection will prevent any signal loss or damage.
Step 4: Adjusting the gain
Once the microphone is connected, it is advisable to set the gain levels on the audio interface. The gain controls determine the sensitivity of the microphone, allowing for optimal audio capture. Adjust the gain levels gradually, monitoring the audio output to prevent any distortion or clipping.
Step 5: Testing the audio
After completing the physical and technical connections, test the audio by recording or monitoring the microphone's output. Use headphones connected to the audio interface to perceive the nuances of the captured sound. Adjust the settings as needed to achieve your desired sound quality.
By following these simple steps, you can easily connect your microphone to the audio interface and enjoy high-quality audio reproduction. Remember to consult the respective manuals for your microphone and audio interface for any additional guidelines or specific requirements.
Adjusting the Sound Levels and Monitoring with Headphones

In this section, we will explore the crucial aspect of adjusting the sound levels and monitoring the audio input using headphones. Monitoring the sound is essential to ensure the quality of the recorded audio and make necessary adjustments to achieve the desired output.
- Audio Levels: Adjusting the audio levels properly is vital to avoid distortions and achieve optimum sound quality. By carefully adjusting the input levels, you can ensure that the audio input from the microphone is neither too soft nor too loud. This allows for clear and balanced sound capture that can then be reproduced in the headphones.
- Monitoring with Headphones: Using headphones for monitoring offers several advantages. It enables you to listen to the audio input in real-time, allowing for immediate feedback and adjustments. Headphones also provide a more accurate representation of the sound compared to speakers, as they eliminate the influence of the room's acoustics. Additionally, headphones provide isolation from external noise, improving focus on the recorded audio.
- Techniques for Adjusting Sound Levels: There are different approaches to adjust sound levels effectively. One common technique is to start with the input level set to a lower value and then gradually increase it while speaking or making sounds into the microphone. This approach helps avoid sudden volume spikes and ensures a smoother adjustment process. It is also recommended to monitor the levels on a visual interface, such as a level meter, to have a clear understanding of the input volume.
- Testing with Headphones: After establishing the desired sound levels, it is crucial to test the setup using headphones. Pay close attention to the clarity and balance of the recorded audio. Is the sound crisp and intelligible? Are there any unwanted noises or distortions? Continuously monitor the audio while making adjustments if needed, until achieving satisfactory results.
- Fine-tuning: Once the initial sound levels are set, fine-tuning can be done by making subtle adjustments and listening critically with headphones. This involves evaluating the audio for any nuances, EQ adjustments, or dynamic alterations required to enhance the overall sound quality.
By carefully adjusting the input levels and monitoring the audio with headphones, you can ensure optimal sound quality and accurate representation of the recorded audio. Taking the time to fine-tune and make necessary adjustments will result in a more professional and enjoyable audio experience.
Troubleshooting Common Issues and Enhancing Sound Quality
In this section, we will discuss various common problems that may arise when using microphone and headphone inputs, as well as techniques to improve the overall sound quality without compromising the functionality. By addressing these issues, you can ensure a seamless and enhanced audio experience.
Identifying and Resolving Connectivity Problems:
One of the most frequent issues is related to connectivity. It is essential to check the cables, connectors, and ports for any loose connections or damage. Reconnecting, replacing or repairing faulty components can significantly improve the performance of your audio setup. Troubleshooting tools can also be utilized to diagnose connection problems.
Minimizing Interference and Noise:
Interference and background noise can significantly affect the audio quality. To minimize these issues, it is advisable to keep the microphone and headphones away from potential sources of interference such as other electronic devices or power cables. Additionally, using noise-cancelling technologies or acoustic panels can effectively reduce unwanted noise.
Adjusting Volume and Equalizer Settings:
Proper adjustment of volume and equalizer settings can greatly enhance the sound quality. Experimenting with different levels and EQ presets can help find the perfect balance, ensuring clear, crisp audio without any distortion or imbalance.
Updating Drivers and Software:
Outdated drivers or software can cause compatibility issues and affect the performance of your audio devices. Regularly checking for updates and installing the latest versions can resolve various issues and improve overall functionality.
Optimizing Recording Environment:
The acoustic environment in which you use your microphone can impact sound quality. Reducing echoes and reverberations through the use of sound-absorbing materials, such as foam panels or blankets, can create a more controlled and professional recording environment.
Using High-Quality Accessories:
Investing in high-quality headphones and microphones can significantly enhance sound quality. Choosing devices with better frequency response, impedance, and sensitivity can greatly improve audio reproduction, resulting in clearer and more immersive listening experiences.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning:
Maintaining and cleaning your audio equipment regularly can help prolong its lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate over time, affecting both the functionality and sound quality. Therefore, it is important to follow manufacturer recommendations for cleaning and maintenance routines.
Seeking Professional Help:
If you have tried various troubleshooting techniques and are still experiencing issues with your microphone or headphone input, it may be beneficial to consult a professional audio technician. They can provide expert advice, diagnose more complex problems, and offer tailored solutions based on your specific setup and requirements.
FAQ
What is the purpose of converting microphone input to headphone input?
The purpose is to be able to listen to the sound from a microphone through your headphones, either for monitoring purposes or for recording and listening simultaneously.
What equipment do I need to convert microphone input to headphone input?
You will need an audio interface or a sound card that has both microphone and headphone jacks. Additionally, you will need a cable to connect your microphone to the audio interface and a pair of headphones.
Can I convert microphone input to headphone input without any additional equipment?
No, you need an audio interface or a sound card that supports both microphone and headphone input/output to be able to convert the microphone input to headphone input.
Are there any software solutions to convert microphone input to headphone input?
Yes, there are various software programs available that allow you to route the microphone input to the headphone output. These programs usually come with audio drivers and settings that enable this functionality.
Is it possible to adjust the volume of the microphone input when converting it to headphone input?
Yes, most audio interfaces and sound cards have gain control knobs or sliders that allow you to adjust the volume of the microphone input. Additionally, some software programs also provide volume control options for the microphone input.
How can I convert microphone input to headphone input?
To convert microphone input to headphone input, you will need to use an audio interface or a mixer. These devices allow you to connect your microphone and headphones, and they have the necessary circuitry to convert the input from a microphone to a headphone output. Simply connect your microphone to the appropriate input on the audio interface or mixer, and then connect your headphones to the headphone output. Adjust the input and output levels as needed, and you should be able to hear the microphone input through your headphones.
Do I need any additional equipment to convert microphone input to headphone input?
Yes, to convert microphone input to headphone input, you will need an audio interface or a mixer. These devices act as a bridge between your microphone and headphones, allowing you to convert the microphone input to a headphone output. It is important to choose an audio interface or mixer that has the necessary input and output connections for your microphone and headphones. Additionally, make sure that the device you choose supports the type of microphone and headphones you have (e.g. XLR, USB, 3.5mm, etc.).




