With the constant advancements in technology, the integration of radio functionality into smartphones using headphones has become a widespread and influential feature. This innovative technology enables users to efficiently access and enjoy their favorite radio stations, podcasts, and audio content directly through their mobile devices, accompanied by the convenience of portable headphones.
When it comes to comprehending the mechanics behind this system, it is crucial to unravel the intricacies within. By employing a combination of digital signals and wireless communication protocols, smartphones with headphone capability are able to tune into frequencies and transmit signals, essentially turning these portable devices into personal radios. This seamless integration allows users to have a comprehensive audio experience without relying on additional devices or clunky, external radio equipment.
The incorporation of radio functionality onto mobile phones with headphones offers a myriad of benefits. On one hand, it presents users with a vast selection of radio stations, granting access to diverse content from all corners of the globe. Furthermore, this integration enables users to stay connected and informed, regardless of their location, ensuring that opportunities for entertainment, news, and educational content are never out of reach.
To achieve such seamless functionality, smartphones with headphone compatibility utilize antennas to capture radio waves, which are then converted into audio signals that can be accessed through the connected headphones. Additionally, devices often implement advanced algorithms and circuitry to enhance signal quality and minimize interference, guaranteeing a crisp and uninterrupted listening experience.
In conclusion, the integration of radio functionality into mobile phones through the use of headphones has revolutionized the way individuals access and benefit from audio content. This innovation combines convenience, versatility, and portability, elevating the listening experience to new heights. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and benefits of this technology, individuals can fully appreciate the value it brings to their everyday lives.
Transmission and Reception of Radio Signals via Headphones
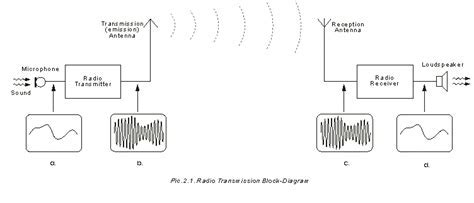
This section explores the fascinating process through which radio signals are transmitted and received on a mobile phone equipped with headphones. Understanding this technology will shed light on how audio signals are converted into electromagnetic waves and then back into sound for our listening pleasure.
- The Generation of Radio Signals
- Transmission of Radio Signals
- Reception of Radio Signals
- Transformation into Audio Signals
The conversion of audio signals into radio waves is made possible through a device called a radio transmitter. This transmitter takes the electrical audio signals produced by the phone and amplifies them to generate electromagnetic waves with specific frequencies. These radio waves carry the encoded audio information that will ultimately be heard through our headphones.
Once the audio signals have been converted to radio waves, they are transmitted wirelessly through the air. This is achieved by the radio transmitter emitting the radio waves into the surrounding space using an antenna. These waves travel through the air, carrying the audio information, until they reach a receiving device.
To receive the transmitted radio signals, a mobile phone relies on its built-in radio receiver. This receiver, typically integrated into the phone's circuitry, picks up the radio waves that are in range and captures them using its antenna. The radio receiver then decodes the radio waves, extracting the audio information from them.
Once the audio information has been retrieved from the radio waves, the mobile phone's circuitry processes and decodes it to reproduce the original audio signals. These electrical signals are then sent to the headphone jack, where the headphones are connected. The headphones act as transducers, converting the electrical signals into sound waves that can be perceived by our ears.
In summary, the transmission and reception of radio signals on a phone with headphones involve the conversion of audio signals into electromagnetic waves, wireless transmission of these waves, their reception by the phone's radio receiver, and finally, the transformation of the received signals into audio that can be heard through the headphones.
Understanding the Basics of Radio Technology
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental principles underlying the functioning of radio technology. By gaining a better understanding of these core concepts, we can appreciate the intricate workings behind radio communication on phones with headphones.
Radio technology is a wireless communication method that allows the transmission and reception of signals over a large distance. It is an integral part of mobile phones, enabling various functionalities such as voice calls, data transfer, and even entertainment options like listening to radio stations through headphones.
One essential aspect of radio technology is the use of electromagnetic waves, which are a form of energy that travel through space. These waves vary in frequency and wavelength, with each frequency corresponding to a specific radio band. Different radio bands cater to different applications, such as AM (Amplitude Modulation) and FM (Frequency Modulation) broadcasts.
The transmission process begins with the creation of radio signals, achieved through a process called modulation. Modulation involves combining the original audio input, such as the voice of a person speaking, with a specific radio frequency. This effectively encodes the audio information onto the electromagnetic waves, allowing it to be transmitted wirelessly.
On the receiving end, a radio receiver or the phone with headphones extracts the radio signals from the electromagnetic waves. This is done through a process known as demodulation, which separates the audio information from the carrier frequency. The demodulated signals are then amplified and converted into audible sound waves, allowing us to hear the transmitted audio through the headphones.
Radio technology has greatly evolved over the years, with advancements in signal processing, antenna design, and frequency allocation. These advancements have made it possible for us to enjoy a seamless and immersive audio experience on our phones through radio signals and headphones.
| Key Points |
|---|
| 1. Radio technology enables wireless communication on phones with headphones. |
| 2. Electromagnetic waves are used to transmit radio signals. |
| 3. Modulation encodes audio information onto radio waves. |
| 4. Demodulation extracts the audio information from radio signals. |
| 5. Advancements in technology have improved the audio experience on phones. |
The Role of the Antenna in Receiving Radio Signals
When it comes to receiving radio signals on a phone with headphones, one crucial component plays a vital role: the antenna. The antenna serves as the essential link between the electromagnetic waves carrying the radio signals and the phone's audio system, allowing users to enjoy their favorite radio stations or content with the convenience of headphones.
Without an antenna, the phone would be unable to capture and convert the electromagnetic waves into meaningful audio signals. The antenna works by picking up these waves, which are transmitted wirelessly through the air, and converting them into electrical signals that can be processed by the phone's internal circuitry.
The effectiveness of the antenna in receiving radio signals depends on various factors, including its design, size, and placement within the phone. Different phone models may employ different types of antennas, such as internal or external ones, to optimize reception capabilities.
- Internal antennas: These antennas are integrated into the internal structure of the phone, carefully positioned to receive signals efficiently. They provide a compact and streamlined design, ensuring convenience and minimizing interference.
- External antennas: Some phone models may feature an external antenna, typically retractable or detachable, which can be extended or adjusted to enhance signal reception. External antennas often offer improved reception in situations where internal antennas may struggle, such as in areas with weak signal coverage.
Regardless of the antenna type, it is important to note that the overall performance of radio reception can also be influenced by external factors. Obstructions like buildings, trees, or even physical barriers can potentially weaken signal strength, leading to a poorer listening experience.
In conclusion, the antenna plays a crucial role in enabling the phone to receive radio signals when using headphones. Its design and placement within the phone, along with external factors, contribute to the overall reception quality, ensuring that users can enjoy their favorite radio content seamlessly.
How Headphones Convert Radio Signals into Audio
In this section, we will explore the fascinating process by which headphones transform radio signals into the audible sound we can enjoy. Through the utilization of innovative technology, headphones have the ability to convert the radio waves received by the phone into high-quality audio that can be easily heard and appreciated.
One of the key components responsible for this transformation is the headphone's built-in receiver. This receiver works in conjunction with the radio antenna in the phone to capture the incoming radio signals. As the radio waves pass through the receiver, they are converted into electrical signals that can be understood and processed by the audio system of the headphones.
The conversion of radio signals into audible sound involves several intricate steps. Once the electrical signals are generated, they are carefully amplified by an amplifier within the headphones. This amplification process ensures that the audio produced is loud enough to be heard clearly by the listener.
After amplification, the electrical signals are further processed by a decoder or demodulator. This essential component in the headphones decodes the electrical signals and provides the necessary separation between different audio frequencies. By separating and enhancing various frequencies, the decoder ensures that the sound we perceive is clear, balanced, and effectively represents the original audio content.
Finally, the decoded electrical signals are delivered to the headphone's speakers, also known as drivers. These speakers are designed to convert the electrical signals into sound waves that can be perceived by our ears. The drivers consist of diaphragms that vibrate rapidly in response to the electrical signals, producing the audio that we can finally hear and enjoy.
Overall, the process through which headphones convert radio signals into audio is a complex and sophisticated one. Thanks to the careful interplay between the receiver, amplifier, decoder, and speakers, headphones are able to deliver high-quality sound from the radio waves received by our phones. Understanding this transformation allows us to appreciate the impressive technology that enables us to enjoy our favorite radio stations through our headphones.
Exploring the Different Types of Wireless Frequency Bands
The world of wireless communication is constantly evolving, and radio frequencies play a crucial role in ensuring seamless connectivity. Understanding the different types of radio frequency bands is essential in comprehending how phones with headphones are able to receive radio signals.
Wireless communication operates within specific frequency bands, which determine the range and capabilities of devices. These frequency bands are categorized into different types, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Let's explore some of the most commonly used radio frequency bands.
- Very Low Frequency (VLF): VLF bands range from 3 to 30 kilohertz and are primarily used for long-range communication. They are ideal for submarine communication and radio navigation systems.
- Low Frequency (LF): LF bands range from 30 to 300 kilohertz and are used for various purposes, including AM radio broadcasting and aircraft communication.
- Medium Frequency (MF): MF bands range from 300 to 3000 kilohertz and are commonly used for AM radio broadcasting and maritime communication.
- High Frequency (HF): HF bands range from 3 to 30 megahertz and are known for their long-range capabilities. They are often used for international broadcasting and amateur radio.
- Very High Frequency (VHF): VHF bands range from 30 to 300 megahertz and are widely used for FM radio broadcasting, television transmission, and air traffic control.
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF): UHF bands range from 300 to 3000 megahertz and are commonly used for television broadcasting, mobile communication, and satellite communication.
- Super High Frequency (SHF): SHF bands range from 3 to 30 gigahertz and are utilized in various applications, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and radar systems.
- Extremely High Frequency (EHF): EHF bands range from 30 to 300 gigahertz and are primarily used for satellite communication, remote sensing, and research purposes.
Each of these frequency bands has its own advantages and limitations, and their selection depends on the specific requirements of the communication system. By exploring the different types of radio frequency bands, we gain a deeper understanding of how phones with headphones are able to receive and transmit radio signals effectively.
Factors Influencing the Quality of Radio Signal Reception
In order to understand the factors that can affect the quality of radio signal reception on a phone with headphones, it is important to consider the various elements that contribute to the transmission and reception of radio waves. Several factors exist that can influence the strength and clarity of the radio signal, ultimately impacting the overall listening experience.
1. Distance from the Broadcasting Station: The proximity of the phone to the broadcasting station can greatly affect the quality of the radio signal received. The closer the phone is to the station, the stronger and clearer the signal is likely to be. Conversely, if the phone is located far away from the station or is obstructed by structures or geographical features, the signal strength may weaken, resulting in reduced audio quality.
2. Atmospheric Conditions: Atmospheric conditions can also play a significant role in radio signal reception. Factors such as weather patterns, temperature changes, and atmospheric interference can weaken or disrupt the signal. For example, rain, snow, or extreme heat can cause signal degradation, resulting in static or loss of signal.
3. Headphone or Antenna Quality: The quality of the headphones, particularly the built-in antenna, can impact the reception of radio signals. Headphones with better antennas are generally able to capture and transmit radio waves more effectively, resulting in improved signal reception and audio quality. Poorly designed or low-quality headphones may struggle to pick up weaker signals, leading to a degraded listening experience.
4. Phone and Headphone Compatibility: The compatibility between the phone and headphones can also influence the quality of radio signal reception. Certain phones or headphones may be designed with specific features or technologies that enhance radio signal reception. Using compatible devices can help optimize the reception and transmission of radio waves, thereby improving the overall audio quality.
5. Interference from Other Electronic Devices: Interference from other electronic devices can disrupt the radio signal and impact its clarity. Devices such as smartphones, Wi-Fi routers, or even nearby electrical appliances can emit radio frequency (RF) signals that interfere with the reception. Minimizing the proximity of such devices or using shielding technologies can help reduce interference and enhance radio signal reception.
By considering these factors and taking necessary precautions to optimize radio signal reception, users can ensure a high-quality listening experience when using their phones with headphones. Understanding the potential limitations and the impact of various factors can help individuals troubleshoot any issues and make informed choices to enjoy an uninterrupted radio experience.
The Impact of Signal Strength on Radio Performance
When it comes to the functioning of radio on a mobile device with headphones, one essential factor that significantly affects its performance is the signal strength. The quality and reliability of the radio transmission depend on the strength of the signal received by the device.
Signal strength refers to the power of the radio frequency signal that is received by the device. It is measured in units such as dBm (decibels related to milliwatts) and provides an indication of how strong or weak the radio signals are in a particular location. A stronger signal generally results in better radio performance, while a weaker signal can lead to issues like sound distortion or even complete signal loss.
The impact of signal strength on radio performance can be observed in various aspects. Firstly, a stronger signal allows for clearer and more stable reception of radio signals, eliminating or minimizing issues such as static, crackling sounds, or interference. This enhances the overall listening experience, ensuring that the audio content transmitted via radio remains crisp and undistorted.
Moreover, a stronger signal also improves the range over which the radio can function effectively. This means that even in areas with weaker signal coverage, a device with a stronger signal can still receive radio transmissions, while one with a weaker signal might struggle or fail to pick up any signals at all. This can be particularly relevant when using the radio feature on a mobile device while moving between different areas or in locations with obstacles that can impede signal reception, such as buildings or dense vegetation.
It is important to note that signal strength is influenced by various factors. These include the proximity to the radio transmitter, the presence of physical barriers, such as walls or tall structures, and environmental conditions like weather or electromagnetic interference. Therefore, it is not uncommon for signal strength to fluctuate, resulting in intermittent or variable radio performance, especially in areas with less optimal conditions for signal transmission.
In conclusion, signal strength plays a crucial role in determining the performance of radio on a mobile device with headphones. A stronger signal provides better audio quality, improved range, and overall enhanced radio experience. Understanding the impact of signal strength can help users optimize their listening experience and be aware of potential limitations in areas with weaker signal coverage.
Advancements in Wireless Technology for Enhanced Phone Audio Experience
The evolution of radio technology has revolutionized the way we listen to audio on our phones. With the integration of advanced wireless features and enhancements, the listening experience when using headphones has reached unprecedented levels of convenience and quality.
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in radio technology, allowing for seamless connectivity and improved audio performance. One notable development is the emergence of Bluetooth, a wireless communication standard that enables phones to establish a reliable and efficient connection with headphones.
Bluetooth technology eliminates the need for wired connections, providing users with the freedom to move around without being tethered to their devices. This wireless solution enables a more comfortable and convenient listening experience as users can enjoy their favorite audio content without the hassle of tangled cords.
Moreover, Bluetooth technology has continually improved in terms of audio transmission quality. With the introduction of codecs like aptX and LDAC, users can now experience higher fidelity sound with minimal latency. These codecs employ advanced compression algorithms, preserving audio details and minimizing data loss during transmission, resulting in an enhanced listening experience that closely resembles wired connections.
Another significant advancement is the integration of noise-canceling technology in both headphones and smartphones. This feature utilizes advanced algorithms to analyze and counteract ambient noise, ensuring that users can immerse themselves in their audio content without disruptions from external sounds. Noise-canceling technology, coupled with wireless capabilities, offers a truly immersive and captivating listening experience.
Furthermore, advancements in radio technology have also led to the development of smart audio features. Today, many smartphones and headphones offer intelligent voice assistants that can be accessed through voice commands. These voice assistants provide a hands-free experience, enabling users to control their audio playback, manage phone calls, and access various applications without the need to physically interact with their devices.
In conclusion, the continuous advancements in radio technology have greatly improved the audio listening experience when using headphones with mobile phones. The integration of wireless connectivity, enhanced audio codecs, noise-canceling technology, and intelligent voice assistants have collectively contributed to a more convenient, immersive, and satisfying audio experience.
FAQ
How does radio work on a phone with headphones?
Radio on a phone with headphones works by utilizing the phone's built-in FM receiver. The headphones act as an antenna to capture the radio signals. The signals are then converted into audio and transmitted to the headphones, allowing you to listen to FM radio stations on your phone.
Do all phones support radio with headphones?
No, not all phones support radio with headphones. The ability to use FM radio on a phone depends on the phone model and its hardware. Some smartphones come with an FM receiver chip, while others do not. It is important to check the specifications of your phone or consult the phone manufacturer to determine if your phone supports FM radio with headphones.
Can I use any type of headphones for radio on my phone?
Most smartphones that support radio with headphones use the headphone cord as the antenna, so it is recommended to use wired headphones for this purpose. Wireless headphones or Bluetooth earphones may not work effectively as they do not have a physical connection to the phone's FM receiver. It's always best to check the phone's manual or consult the manufacturer to ensure compatibility with your headphones.




