In today's digital age, where wireless technology and Bluetooth reign supreme, it's easy to overlook the humble yet essential audio connectors that have been a staple in our devices for decades. These small, unassuming jacks play a crucial role in delivering high-quality sound directly to our ears, allowing us to enjoy music, podcasts, and phone calls with clarity and precision.
So, what exactly goes on inside these unassuming metal plugs that connect our headphones to our devices? The answer lies in the intricate design and engineering that allows electrical signals to pass through seamlessly, transforming them into the captivating sounds we experience.
At the heart of an audio connector is a series of electrical contacts, meticulously designed to transmit audio signals from the source to the headphones. These contacts, typically made of conductive materials like gold or copper, create a connection that allows the transfer of electrical energy in the form of sound waves.
Furthermore, within the convoluted pathways of the connector, you'll find a labyrinth of wires and insulation materials that work together to prevent audio interference, ensuring the purity of the signals being transmitted. This delicate dance of conductivity and insulation is what separates a high-quality audio connector from a subpar one, ultimately influencing the overall audio experience.
The Evolution of Audio Connection Technology
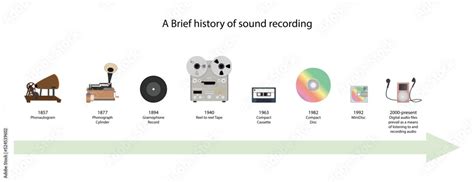
Over the years, the way we connect our audio devices to headphones has undergone a fascinating transformation. This section explores the rich history and evolution surrounding the technology behind the humble audio jack.
In the early days, when audio devices started emerging, users were limited to using large and bulky connectors to listen to their favorite music or audio content. However, as technology progressed, smaller and more convenient solutions were developed, resulting in the birth of the headphone jack.
The concept of the headphone jack as we know it today originated from the need for a standardized connection method that allows users to easily connect their headphones to various audio devices like radios, televisions, and eventually portable devices such as Walkmans and smartphones.
Throughout the years, headphone jacks have evolved, reflecting advancements in technology and user demands. Initially, simple mono jacks were commonly used for basic audio output. As stereo audio became more prevalent, the introduction of stereo headphone jacks allowed users to enjoy a more immersive audio experience.
As portable devices became more compact, the desire for smaller audio connectors emerged. This paved the way for the development of mini-jacks, which revolutionized the way headphones were connected to devices. The mini-jack, also known as the 3.5mm jack, quickly became the global standard for audio connection, offering compatibility across a wide range of devices.
However, in recent years, the rise of wireless audio technology and the demand for slimmer devices have led to the emergence of new connection methods. Manufacturers have started phasing out the traditional 3.5mm headphone jack in favor of wireless Bluetooth connectivity or USB-C ports for audio output.
Despite the emergence of alternative connection options, the headphone jack remains an enduring symbol of audio connectivity and convenience. Its history and evolution showcase not only technological advancements but also the ever-changing demands and preferences of users in the realm of audio enjoyment.
Anatomy of a Headphone Jack: Exploring the Parts
In this section, we will delve into the intricate components that make up a headphone jack, shedding light on the inner workings without getting too technical. Understanding the anatomy of a headphone jack is crucial for both users and enthusiasts, enabling a deeper appreciation of the technology and enhancing the overall audio experience.
At the core of a headphone jack is the audio connector, a small but essential component responsible for establishing a connection between the headphones and the device. It acts as a gateway, transmitting audio signals seamlessly. The connector comprises several key parts, each playing a vital role in ensuring clear sound reproduction.
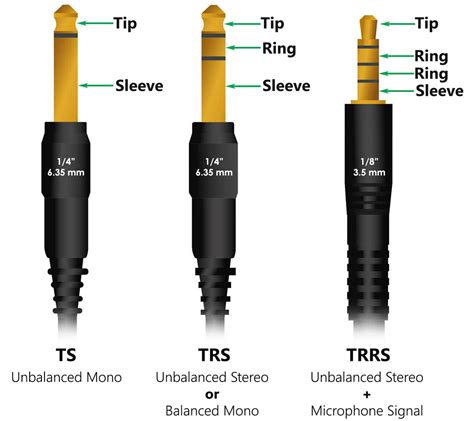
1. Tip: The tip, usually distinguished by its black or silver color, is responsible for delivering the left audio channel to the headphones. It serves as the primary point of contact, making a secure connection with the corresponding terminals inside the jack.
2. Ring: Surrounding the tip is the ring, identified by its insulating color. The ring is responsible for transmitting the right audio channel, allowing for stereo sound. Together with the tip, it completes the audio connection to the headphones.
3. Sleeve: The sleeve, commonly found at the base of the connector, acts as a protective layer and provides stability to the jack. It also serves as the ground conductor, ensuring a balanced audio output and minimizing interference or static noise.
4. Reinforcement Collar: Some headphone jacks come with a reinforcement collar, which adds durability and strength to the connector. It provides extra support, preventing bending or breaking of the jack when subjected to regular use or accidental tugs.
5. Contact Terminals: Inside the headphone jack, tiny contact terminals establish electrical connections with the corresponding parts of the audio cable. These terminals ensure reliable signal transmission and help maintain audio quality throughout the connection.
6. Insulation: Insulation materials, such as rubber or plastic, help to separate and protect the different components of the headphone jack. They prevent electrical interference and ensure that the audio signals remain isolated, leading to clearer and more accurate sound reproduction.
7. Gold Plating: Some higher-end headphone jacks feature gold plating on the connectors and contact terminals. Apart from the aesthetic appeal, gold plating enhances conductivity and reduces the risk of corrosion, resulting in improved signal transmission and extended longevity.
By examining the various parts of a headphone jack, we gain a deeper understanding of its construction and functionality. This knowledge can help us make informed decisions when selecting headphones, understanding compatibility, and troubleshooting any audio issues that may arise. Ultimately, exploring the anatomy of a headphone jack empowers us to fully appreciate the technology behind this fundamental audio component.
Unraveling the Mechanics of Audio Output Connectors

Discovering the underlying principles behind the operation of audio output connectors provides valuable insight into the transmission of sound signals. In this section, we will explore the intricate workings of these small yet significant components, shedding light on their role in delivering high-quality audio experiences.
At their core, headphone jacks function as connectors that establish a physical and electrical connection between audio devices and headphones or speakers. They serve as a conduit through which audio signals can be transferred, enabling the conversion of electrical impulses into audible sound waves.
One crucial element of headphone jacks is their versatility, as they can support various audio equipment, including headphones, earbuds, and external speakers. This flexibility arises from their standardized design, allowing for compatibility across different devices and platforms.
The simplicity of the headphone jack design belies the complexity of its inner workings. A typical headphone jack consists of three conductive surfaces, commonly referred to as the tip, ring, and sleeve. Each of these surfaces plays a distinct role in the transmission of audio signals.
| Conductive Surface | Function |
|---|---|
| Tip | The tip carries the left audio channel signal, ensuring the delivery of stereo sound. |
| Ring | The ring carries the right audio channel signal, contributing to the immersive audio experience. |
| Sleeve | The sleeve acts as the common ground for both audio channels, maintaining audio fidelity and eliminating noise. |
By understanding the distinct functions of these conductive surfaces, one can grasp the intricate interplay that enables the seamless transmission of audio signals through headphone jacks.
It is worth noting that advancements in technology have led to the emergence of alternative audio connectivity options such as USB-C and wireless solutions. However, the headphone jack continues to be a prevalent and reliable means of audio output, offering universal compatibility and accessibility.
With a newfound understanding of how headphone jacks operate, the next time you plug in your headphones or connect your device to external speakers, you can appreciate the intricate mechanics that bring your audio to life.
Different Types of Audio Connectors and their Applications
When it comes to connecting audio devices, there are various types of connectors available that serve different purposes. These connectors enable the transmission of sound signals from one device to another without any loss in quality. Understanding the different types of audio connectors can help you choose the right one for your specific needs and enhance your audio experience.
1. 3.5mm Jack:
- The 3.5mm jack, also known as the mini jack or TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) connector, is one of the most commonly used audio connectors.
- It is predominantly found in portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and audio players.
- The 3.5mm jack is typically used for connecting headphones, earphones, and external speakers.
2. 6.35mm Jack:
- The 6.35mm jack, also known as the quarter-inch jack or TRS connector, is a larger version of the 3.5mm jack.
- It is commonly used in professional audio equipment, musical instruments, and audio interfaces.
- The 6.35mm jack provides a more robust connection and is capable of handling higher audio output levels.
3. RCA Connector:
- The RCA connector, also known as the phono connector, is a type of electrical connector commonly used for analog audio and video signals.
- It features two or three connectors, usually color-coded as red and white for audio and yellow for video.
- RCA connectors are widely used in home entertainment systems, including TVs, DVD players, and audio receivers.
4. XLR Connector:
- The XLR connector is a professional audio connector commonly used in the music and entertainment industry.
- It is designed for balanced audio signals, reducing noise and interference.
- XLR connectors are typically found in microphones, mixing boards, and professional audio equipment.
5. Optical Connector (Toslink):
- The optical connector, also known as Toslink, uses fiber optics to transmit digital audio signals.
- It provides a high-quality, noise-free audio transmission and is commonly used in home theater systems and audio consoles.
- Optical connectors are compatible with devices that support digital audio, such as TVs, soundbars, and gaming consoles.
By understanding the different types of audio connectors and their applications, you can easily identify the appropriate connector for your audio needs and ensure optimal sound quality and compatibility.
Issues and Solutions for Headphone Jacks

In this section, we will discuss common problems that can arise with headphone jacks and provide troubleshooting tips to help resolve them. Whether you experience connectivity issues, sound distortions, or compatibility problems, we have got you covered.
1. Connectivity Problems: One of the most common issues with headphone jacks is a loss of connectivity. This can manifest as intermittent sound or a complete lack of audio output. To troubleshoot this problem, start by checking the physical connection between your headphones and the device. Ensure that the plug is securely inserted into the jack.
2. Sound Distortions: Another frequent issue with headphone jacks is sound distortions, such as crackling noises, static, or uneven audio. To address this problem, first, try adjusting the headphone plug within the jack to ensure a stable connection. If the issue persists, inspect the headphone cable for any damages or fraying and consider replacing it if necessary.
3. Compatibility Troubles: Sometimes, headphone jacks may not be compatible with certain devices or accessories. This can prevent the headphones from working as expected or even cause damage to the device. To troubleshoot compatibility issues, check if the headphones are designed to work with the specific device you are using. Additionally, verify that all audio settings on the device are correctly configured.
4. External Interference: External factors, such as electromagnetic interference or nearby electronic devices, can also cause problems with headphone jacks. If you notice buzzing sounds or disturbances while using your headphones, try moving away from potential sources of interference, such as Wi-Fi routers or other devices emitting strong electromagnetic fields.
5. Cleaning and Maintenance: Over time, dust, lint, or debris may accumulate within the headphone jack, leading to connectivity issues or sound problems. Regularly clean the jack using a soft, dry brush or a cotton swab to remove any obstructions. Be gentle to avoid damaging the delicate components inside the jack.
6. Professional Assistance: If the troubleshooting tips mentioned above do not resolve your headphone jack issues, it may be necessary to seek professional assistance. Consider contacting the manufacturer's customer support or consulting with an audio technician who can provide specialized diagnostics and repairs.
By understanding these common issues and following the troubleshooting tips, you can overcome challenges you may encounter with your headphone jack. Remember to approach the troubleshooting process systematically and consider seeking expert guidance when needed.
How I Repaired A Hydraulic Jack.
How I Repaired A Hydraulic Jack. מאת AJ Restorations 2,823,044 צפיות לפני שנתיים 14 דקות, 23 שניות
FAQ
How does a headphone jack work?
A headphone jack works by connecting the audio signals from the device to the headphones. The jack consists of multiple metal rings and connectors that transmit the electrical signals to the headphones, allowing you to hear the audio from the device.
Are headphone jacks universal?
No, headphone jacks are not universal. There are different types and sizes of headphone jacks, such as the 3.5mm jack commonly found in smartphones and computers, and the larger 6.35mm jack used in professional audio equipment. It is important to use the correct type of headphone jack for your device.
Can I use an adapter to connect headphones with a different jack size?
Yes, you can use an adapter to connect headphones with a different jack size. For example, if you have headphones with a 3.5mm jack and want to connect them to a device with a 6.35mm jack, you can use a 3.5mm to 6.35mm adapter. This allows you to use your headphones with devices that have a different jack size.







