As we delve into the captivating realm of wearable technology, one intriguing innovation that mesmerizes the world is the vibrant display that graces the esteemed Apple Watch. While it may seem like mere sorcery, the secret behind this mesmerizing spectacle lies within the enigmatic OLED technology.
Step into a world where colors come alive, where brightness dances with depth, and where every pixel pulsates with energy. The seamless marriage of organic chemistry and cutting-edge technology gives birth to the captivating OLED display, serving as the visual gateway to a world of limitless possibilities.
Behind the scenes, an army of tiny, organic compounds called "organic light-emitting diodes" (or OLEDs) work tirelessly to present vivid imagery to our eyes. These remarkable compounds, brimming with life, emit light as electrons whiz through their intricate network, electrifying our visual experience and bringing forth a symphony of colors.
The fundamentals of OLED panel technology
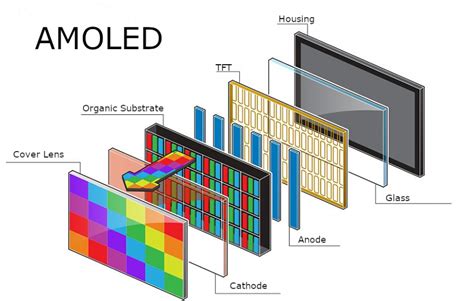
In this section, we will explore the fundamental workings of Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technology and its significance in the display industry. OLED panels are a revolutionary advancement that have reshaped the visual experience in various electronic devices, such as smartphones, televisions, and smartwatches.
Overview:
OLED displays consist of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. These compounds are packed into thin films, which are sandwiched between two electrodes. The electrodes are responsible for supplying electricity to each pixel contained within the panel, illuminating them individually.
Key elements:
One of the key components of an OLED panel is the organic layers, which are made up of organic molecules that contribute to the display's unique characteristics. These layers can be categorized into three main portions - an emissive layer, a conductive layer, and a substrate. The emissive layer emits light when excited by the electric current passing through the conductive layer, resulting in the generation of colors.
Another important element is the electrodes, which are typically made of transparent materials like Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). These electrodes enable the flow of current through the organic layers, helping to create the desired colors and illumination.
Advantages:
OLED technology offers several advantages over traditional display technologies. One significant advantage is its ability to produce true blacks and infinite contrast ratios, as each individual pixel can be turned off completely when required. This enhances the overall visual experience and provides deeper levels of detail.
Furthermore, OLED displays offer wider viewing angles, improved response times, and better energy efficiency compared to alternative display technologies. These advantages make OLED particularly suitable for small devices like the Apple Watch, where vibrant colors, crisp visuals, and power efficiency are crucial.
In conclusion, understanding the fundamental aspects of OLED display technology helps unravel the unique qualities and benefits it brings to electronic devices such as the Apple Watch. By harnessing the emissive properties of organic compounds and utilizing transparent electrodes, OLED panels deliver exceptional visual experiences with enhanced contrast, superior colors, and energy efficiency.
Advantages of OLED Technology on Apple Watch
In the realm of wearable technology, the Apple Watch stands out with its cutting-edge use of Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technology, which sets it apart from traditional LCD displays. The advantages of OLED on the Apple Watch are numerous and contribute to an enhanced user experience.
1. Superior color reproduction: With OLED technology, the Apple Watch can offer vibrant and accurate colors, providing an immersive visual experience. From vivid reds to deep blacks, OLED ensures every hue is rendered with precision, ideal for showcasing colorful watch faces and graphics.
2. Perfect black levels: OLED's self-emissive pixels allow for true blacks by individually controlling each pixel's illumination. This means that when a black image is displayed, these pixels are completely turned off, resulting in unmatched contrast and deep black levels. This not only enhances the overall visual quality but also saves power by not requiring energy to illuminate black pixels.
3. Enhanced viewing angles: OLED displays provide excellent viewing angles, allowing users to comfortably view the Apple Watch from various angles without experiencing significant color or contrast loss. This is particularly advantageous for a wearable device that is frequently glanced at from different positions on the wrist.
4. Energy efficiency: OLED technology's pixel-level control enables power efficiency. As each pixel on the Apple Watch's OLED display emits its light, it eliminates the need for a separate backlight, reducing overall power consumption. This translates into longer battery life, a critical advantage for a device that should ideally last throughout the day.
5. Thinner and lighter design: The use of OLED technology allows for a thinner and lighter design profile on the Apple Watch. Unlike LCD displays, OLED panels do not require a separate backlight, resulting in a slimmer build. Such a design advantage enhances comfort, making the Apple Watch less obtrusive to wear, especially during physical activities.
In summary, the implementation of OLED technology on the Apple Watch offers significant advantages such as superior color reproduction, perfect black levels, enhanced viewing angles, energy efficiency, and a thinner and lighter design. These benefits contribute to an immersive and visually appealing experience, while also improving the device's functionality and practicality for users.
Understanding the pixel structure of OLED display
The pixel structure of an OLED display is a key component that contributes to its outstanding image quality and functionality. By delving into the specifics of how pixels are structured in an OLED display, we can gain a deeper understanding of the technology behind this innovative type of screen.
At the heart of an OLED display, individual pixels work harmoniously to create a vibrant and visually appealing image. Unlike traditional LCD displays, which rely on a backlight to illuminate the entire screen, OLED displays employ self-emissive organic compounds to generate light directly at the pixel level.
Each pixel in an OLED display consists of several layers, including the anode, organic layer, cathode, and substrate. The organic layer, in particular, plays a crucial role in producing colorful and vivid images. This layer contains different organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them.
The organic layer is further subdivided into three subpixels, commonly referred to as red, green, and blue. These subpixels emit different colors of light and combine to create the wide color gamut and high contrast ratio that OLED displays are known for. By independently controlling the intensity of each subpixel, OLED technology enables precise color reproduction and deep blacks.
Another important aspect of the pixel structure in OLED displays is the pixel density, which refers to the number of pixels per unit area. Higher pixel density results in sharper images and smoother texts, as it allows for more detail to be displayed on the screen. Apple Watch utilizes a high pixel density to deliver crisp visuals and enhance user experience.
In summary, understanding the pixel structure of OLED displays provides insights into the intricate mechanisms that contribute to their exceptional image quality. The use of self-emissive organic compounds, the subdivision of pixels into red, green, and blue subpixels, and the pixel density all play integral roles in creating the stunning visuals that OLED displays, including those on the Apple Watch, are renowned for.
The Significance of Organic Compounds in OLED Technology
Organic compounds play a crucial role in the innovative OLED technology utilized in devices such as the Apple Watch. These compounds serve as the building blocks for the creation of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), which are at the heart of the functioning of OLED displays. By understanding the importance of organic compounds in OLED technology, we can gain insight into the impressive display capabilities of devices like the Apple Watch.
The incorporation of organic compounds in OLED displays enables the production of vibrant and high-quality images. OLEDs consist of multiple layers, with the organic compounds serving as emissive and conductive materials. When an electric current is applied, the organic layers emit light, resulting in the vivid and colorful visuals displayed on devices like the Apple Watch.
Organic compounds used in OLED technology offer several advantages over alternative display technologies. Firstly, they have the ability to emit light independently, eliminating the need for a separate backlighting system. This enables OLED displays to achieve true black levels and enhances the contrast ratio, leading to a more immersive viewing experience. Additionally, organic compounds are inherently flexible, allowing for the creation of bendable and curved OLED displays, which can be seamlessly integrated into sleek and compact devices like the Apple Watch.
Furthermore, the use of organic compounds in OLED technology contributes to energy efficiency. OLED displays do not require a constant power supply to maintain image quality, as they produce light only when needed. This results in lower energy consumption and extends the battery life of devices equipped with OLED displays, such as the Apple Watch.
In conclusion, the role of organic compounds in OLED technology is fundamental to the exceptional display performance of devices like the Apple Watch. Their ability to emit light, flexibility, and energy efficiency make OLED displays stand out among other display technologies. By harnessing the potential of organic compounds, OLED technology continues to shape the future of visual displays in consumer electronics.
Differences in Backlighting between OLED and LCD Displays
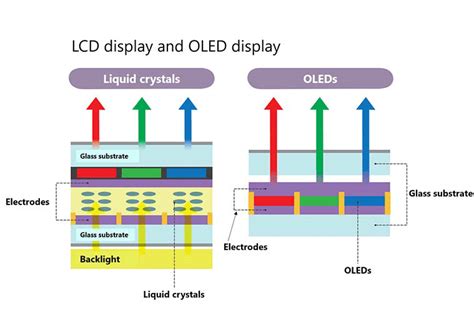
In the realm of display technology, one key aspect that sets OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) displays apart from each other is the approach they take to provide illumination. While both types of displays offer vibrant visuals, their backlighting mechanisms differ significantly.
When it comes to OLED displays, they do not rely on a separate backlighting component, unlike their LCD counterparts. Instead, each individual pixel in an OLED display emits light independently. This means that every pixel acts as a tiny light source, resulting in high contrast ratios and deep blacks that lend a sense of depth and realism to the visuals.
On the other hand, LCD displays use a backlight panel that shines light through a series of color filters and liquid crystals to generate images. The backlight panel is located at the back of the display, and the liquid crystals manipulate the light's intensity and color before it reaches the viewer. This process ensures that the pixels on an LCD display are able to display different colors by blocking or allowing specific wavelengths of light.
Due to their illumination method, OLED displays offer several advantages over LCD displays, including better energy efficiency, wider viewing angles, and faster response times. The lack of a backlight in OLED displays also allows for thinner and more flexible designs. However, it's worth mentioning that LCD displays can still excel in certain areas, such as brightness levels and cost-effectiveness in larger screen sizes.
Exploring the Color Reproduction Capabilities of OLED Display
In this section, we will delve into the impressive color reproduction capabilities offered by the OLED display technology found in the Apple Watch. Through its innovative use of organic light-emitting diodes, the display exhibits exceptional color accuracy and vibrancy.
One of the key advantages of OLED display technology is its ability to produce deep blacks and infinite contrast ratios. The individual pixels in an OLED display emit light independently, allowing for precise control over the brightness and color of each pixel. This results in rich and true blacks, as the pixels can be entirely turned off in order to achieve pure darkness.
Furthermore, OLED technology enables a wide color gamut, encompassing a vast range of colors that can be reproduced on the display. This allows for vibrant and lifelike visuals, enhancing the overall viewing experience on the Apple Watch. Colors appear more vivid and saturated, creating a more immersive and realistic display.
Additionally, OLED displays offer excellent color accuracy, ensuring that the colors depicted on the screen closely match the original source. With their ability to accurately reproduce colors across a wide range, OLED displays are ideal for tasks that require precise color representation, such as photo editing or viewing multimedia content.
Thanks to the individual pixel control and high color fidelity, the OLED display on the Apple Watch can provide stunning visuals that showcase the finest details and nuances. Whether it's displaying vibrant watch faces, vivid app icons, or intricate graphics, the OLED technology contributes to a visually captivating user experience on the Apple Watch.
In conclusion, the OLED display on the Apple Watch exemplifies remarkable color reproduction capabilities. Its ability to offer deep blacks, vibrant colors, and accurate color representation enhances the overall visual appeal and immersive experience of using the device.
FAQ
What is an OLED display?
An OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) display is a type of display technology that uses organic compounds to produce light when an electric current is applied.
How does an OLED display work on the Apple Watch?
The OLED display on the Apple Watch works by using tiny organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is passed through them. These compounds are arranged in individual pixels, which can be controlled to produce different colors and brightness levels.
What are the advantages of an OLED display on the Apple Watch?
OLED displays offer several advantages on the Apple Watch, such as vibrant colors, deep blacks, wide viewing angles, and energy efficiency. They also allow for thinner and lighter device designs due to their flexibility and lack of backlight.
Do OLED displays have any drawbacks on the Apple Watch?
While OLED displays have many advantages, they do have a few drawbacks. One of the main concerns is the potential for burn-in, where static images displayed for a long period can leave a permanent mark on the screen. However, Apple has implemented measures to minimize this issue on the Apple Watch.
How does the OLED display on the Apple Watch compare to other smartwatches?
The OLED display on the Apple Watch is highly regarded and often considered one of the best in the smartwatch market. Its color accuracy, brightness, and overall picture quality are highly praised by users and reviewers alike.
How does an OLED display work on the Apple Watch?
The OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) display on the Apple Watch uses a layer of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. This means that each individual pixel on the screen emits its own light, allowing for high contrast, deep blacks, and vibrant colors.
What are the advantages of using an OLED display on the Apple Watch?
OLED displays offer several advantages for the Apple Watch. They provide better power efficiency compared to traditional LCDs as each pixel can be lit individually, conserving energy when displaying dark content. Additionally, OLED displays produce deeper blacks and higher contrast, resulting in sharper and more vibrant visuals on the Apple Watch screen.




