When it comes to exploring the depths of modern technology, one cannot overlook the intricate mechanisms that govern our beloved Windows 10 operating system. Delving into the essence of these mechanisms, it becomes increasingly apparent that the functionality of the GUID Partition Table (GPT) plays a pivotal role in the seamless operation of our digital realm.
In essence, GPT encapsulates the foundation upon which our Windows 10 system is built. It harmonizes the complex interplay of various components, enabling efficient data organization, storage, and retrieval for optimal system performance. This fundamental pillar empowers users to navigate their digital realms effortlessly, while providing a sturdy structure for the countless applications and functionalities that the Windows 10 system offers.
Dynamic. This single word encapsulates the very essence of GPT in the Windows 10 ecosystem. It breathes life into our digital experiences, acting as the driving force behind the smooth sailing of our daily operations. Steeped in its ability to adapt effortlessly to the ever-changing landscape of technological development, GPT functions as an indispensable guardian, ensuring the seamless integration of hardware, software, and user interaction.
Mastering the intricacies of GPT is essential for both the tech-savvy and the casual users of Windows 10 alike. By unraveling the inner workings of GPT, one can unlock a deeper understanding of the mechanisms at play and harness its full potential. From the initial partitioning process to the allocation of precious storage space, the functionalities of GPT have a profound impact on system efficiency, data security, and performance optimization - and it is this realm that we are poised to explore.
GPT: An Overview
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of the widely used GPT (GUID Partition Table) in the context of Windows 10. We will explore the key components and functioning of GPT and gain a comprehensive understanding of its significance in the Windows operating system.
- Introduction to GPT
- Understanding the Architecture
- Benefits of GPT
- GPT and Windows Compatibility
- Considerations and Best Practices
GPT, an abbreviation for GUID Partition Table, is a crucial component in the Windows 10 operating system. It serves as an essential framework for disk partitioning, organizing data, and managing drives. By comprehending the fundamentals of GPT, users can make informed decisions regarding disk management and optimize the performance of their systems.
For a foundational understanding of GPT, it is necessary to comprehend its underlying architecture. GPT utilizes a globally unique identifier (GUID) to assign a unique identifier to each partition on a disk. This approach allows for more flexibility and scalability compared to its predecessor, the Master Boot Record (MBR). Furthermore, GPT introduces protective MBR, primary GPT headers, partition entries, and CRC32 checksums to enhance stability and reliability.
GPT brings several significant advantages over MBR, making it the preferred partitioning scheme in modern Windows systems. Increased partition size limit, support for larger storage devices, improved data integrity through redundancy, and enhanced error detection and recovery mechanisms are some of the noteworthy benefits. Understanding these advantages empowers users to fully utilize the capabilities of GPT for their disk management needs.
Windows 10 seamlessly integrates with GPT, ensuring optimal compatibility and performance. The operating system includes the necessary tools and utilities to create, modify, and manage GPT partitions effortlessly. By exploring the intricacies of GPT integration with Windows, users can harness the full potential of this partitioning scheme and maximize the efficiency of their systems.
To leverage GPT effectively, it is essential to be aware of some key considerations and adhere to best practices. This section will cover important aspects such as disk initialization, partitioning guidelines, coexistence with legacy systems, and compatibility with firmware standards. Following these recommendations will help users avoid potential issues and ensure smooth operation when utilizing GPT in Windows 10.
The Advantages of GPT in Windows 10
In this section, we will explore the various benefits that come with the adoption of the GUID Partition Table (GPT) in Microsoft's operating system, Windows 10. By implementing GPT, Windows 10 provides users with a more reliable and efficient disk partitioning system, resulting in improved performance and enhanced overall functionality.
- Enhanced Disk Capacity: GPT supports larger disk capacities compared to the older Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme used in legacy systems. This allows users to utilize the full potential of modern high-capacity storage devices.
- Improved Data Protection: GPT offers better data integrity and protection mechanisms, such as redundant partition tables and cyclic redundancy checks, ensuring that critical information remains intact even in the event of disk errors or failures.
- Flexible Partitioning Options: With GPT, users can create up to 128 primary partitions, providing greater flexibility in organizing and managing their disk space. Additionally, GPT supports dynamic resizing of partitions without the need to reformat or reinstall the operating system.
- Efficient Boot Process: GPT supports the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) boot mode, which allows for faster boot times and a more streamlined startup process. This enables users to quickly access their system and reduces downtime.
- Compatibility with Modern Technologies: GPT is compatible with advanced technologies, such as Secure Boot and BitLocker Drive Encryption, ensuring a higher level of security for sensitive data stored on Windows 10 systems.
By leveraging the benefits of GPT in Windows 10, users can experience improved disk management capabilities, enhanced data protection, and optimized system performance. This makes GPT a valuable feature for both personal and professional users, providing a reliable foundation for data storage and system operations within the Windows operating system.
GPT vs MBR: Exploring the Distinctions
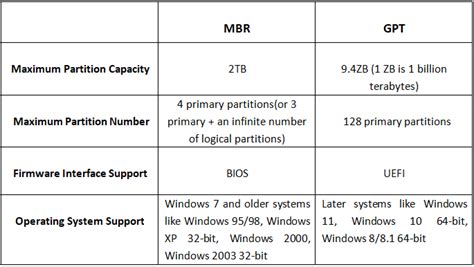
Delving into the realm of system partitions and disk management in modern operating systems, it becomes essential to comprehend the divergences between the two prominent partitioning schemes - GPT and MBR. This section aims to shed light on the dissimilarities between GPT (GUID Partition Table) and MBR (Master Boot Record), providing a comprehensive understanding of their distinctive features and the impact they have on one's Windows 10 experience.
GPT: A New Paradigm in Disk Partitioning
The GPT, also known as GUID Partition Table, represents a contemporary partitioning scheme that brings forth various advancements compared to its predecessor, the MBR. GPT introduces the utilization of globally unique identifiers, allowing for an extensive number of partitions on a single drive and surpassing the limitations imposed by MBR's four primary partitions. This innovation expands the capacity of storage devices, enabling more efficient utilization of disk space in Windows 10 systems.
Furthermore, GPT incorporates a protective MBR that acts as a shield against compatibility issues with legacy systems, facilitating seamless data interchange between GPT and MBR disks. With its support for larger disk sizes and redundancy features, GPT paves the way for enhanced reliability, data integrity, and potential fault tolerance in Windows 10 environments.
MBR: Long-standing Legacy with Limitations
In contrast, the MBR, or Master Boot Record, has been a longstanding standard for partitioning disks in previous iterations of Windows. However, MBR possesses certain limitations that hinder its effectiveness in today's advanced computing landscape. One such limitation is its restricted support for a mere four primary partitions, a constraint that restricts the overall flexibility and scalability of disk partitions.
Additionally, MBR utilizes a bootstrapping process, which limits its ability to handle larger disk sizes effectively. With these limitations and the rapid evolution of storage technologies, MBR's significance has diminished in modern Windows 10 systems, giving way to the ascendancy of the GPT partitioning scheme.
Conclusion
By gaining insight into the differences between GPT and MBR partitioning schemes, one can make informed decisions when it comes to disk management and system configurations in Windows 10. While GPT introduces innovative features and empowers users with increased flexibility and reliability, MBR continues to exist as a legacy option, albeit with its inherent limitations. Thus, understanding the contrasting aspects of GPT and MBR becomes crucial for optimizing system performance and ensuring seamless operations in the Windows 10 ecosystem.
Converting MBR to GPT: A Step-by-Step Guide for Windows 10
In this section, we will explore the process of converting the Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme to the Guid Partition Table (GPT) in the Windows 10 operating system. By understanding how to transform your disk from MBR to GPT, you can optimize your system for more advanced features and improve overall disk performance.
Before delving into the conversion process, it is important to comprehend the key differences between MBR and GPT. MBR, also known as the Master Boot Record, has been the standard partitioning scheme for many years. However, GPT, or Guid Partition Table, provides several advantages such as support for larger disk sizes, improved data redundancy, and compatibility with modern systems.
To convert your MBR disk to GPT in Windows 10, you will need to use the built-in Disk Management tool. This utility allows you to manage your disk partitions and perform various operations. The conversion process involves backing up your data, deleting all existing partitions on the disk, and then initializing it as GPT.
Here are the step-by-step instructions to convert MBR to GPT in Windows 10 using Disk Management:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Launch Disk Management |
| 2 | Backup Your Data |
| 3 | Delete Existing Partitions |
| 4 | Initialize Disk as GPT |
| 5 | Create New Partitions |
| 6 | Restore Data |
It is crucial to follow these steps carefully to avoid any data loss during the conversion process. Additionally, it is recommended to create a full backup of your disk before proceeding.
Once you have successfully converted your disk from MBR to GPT, you can take advantage of the enhanced capabilities provided by the GPT partitioning scheme. These may include compatibility with newer hardware, support for larger drives, and improved data resiliency.
In summary, understanding how to convert MBR to GPT in Windows 10 allows you to unlock the benefits of the GPT partitioning scheme and optimize your system's disk performance. By following the step-by-step guide outlined above, you can easily transform your disk and reap the advantages offered by GPT.
Utilizing GPT for UEFI Boot in Windows 10

Achieving efficient and reliable booting is a crucial aspect of any operating system. In the context of Windows 10, the usage of GPT (GUID Partition Table) for UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) booting offers a cutting-edge solution for enhancing system performance and functionality.
By employing GPT for UEFI boot in Windows 10, users can take advantage of its advanced features to ensure a more streamlined and secure boot process. Here, we will delve into the key aspects of utilizing GPT for UEFI boot and explore the benefits it brings to the Windows 10 environment.
- Compatibility: GPT for UEFI boot is designed to work seamlessly with modern UEFI firmware, enabling compatibility with a wide range of hardware configurations.
- Increased Partition Capacity: Unlike its predecessor MBR (Master Boot Record), GPT allows for the creation of up to 128 partitions, providing enhanced flexibility in managing storage space.
- Protection Against Data Corruption: GPT incorporates a backup partition table that helps prevent data loss in the event of primary table corruption, ensuring system stability.
- Secure Boot: UEFI coupled with GPT enables the implementation of Secure Boot, safeguarding the boot process against malicious software and unauthorized operating systems.
- Efficient Disk Management: The GPT disk layout simplifies disk management tasks, including resizing partitions and dynamic disk configurations, resulting in improved overall disk utilization.
With GPT for UEFI boot in Windows 10, users can experience a more robust and secure boot process while taking advantage of the numerous features it offers. By understanding and utilizing this functionality, Windows 10 can deliver a seamless and efficient experience for both personal and enterprise users.
GPT Partitioning: Optimal Practices and Recommendations
In this segment, we delve into the realm of GPT partitioning, exploring the most effective approaches and guidelines for its implementation. Without getting into intricate technicalities, we present a comprehensive overview of the best practices surrounding GPT partitioning, offering valuable insights for Windows 10 users.
Within the realm of disk management, GPT partitioning stands as an essential aspect for optimizing storage utilization and ensuring efficient data organization. By understanding the fundamental strategies and principles underlying GPT partitioning, users can leverage its potential to enhance performance and streamline operations.
1. Establishing a Logical Structure:
When implementing GPT partitioning, it is crucial to establish a logical structure that caters to the specific requirements of the system. By carefully planning the allocation of partitions, users can effectively segregate data, auxiliary files, and operating system resources, optimizing storage usage and facilitating streamlined access.
2. Overcoming Capacity Limitations:
Unlike its predecessor, MBR, GPT partitioning circumvents the limitations associated with storage capacity. To make the most of this advantage, it is recommended to allocate appropriate partition sizes, considering the present and future data growth requirements. By setting realistic sizes for each partition, users can avoid fragmenting data and prevent premature partition exhaustion.
3. Ensuring System Compatibility:
While GPT partitioning offers numerous benefits, it is essential to ensure that the system and its components are compatible with this partitioning scheme. Before proceeding with GPT partitioning, it is recommended to verify the firmware and hardware compatibility, enabling a smooth transition to this advanced disk management technology.
4. Harnessing Data Protection Mechanisms:
GPT partitioning incorporates robust mechanisms for data protection, including the replication of critical system data across multiple partitions. To further enhance the resilience of the system, users are encouraged to implement regular backups, leveraging the inherent redundancy offered by GPT partitioning.
5. Proper Maintenance and Upkeep:
GPT partitioning necessitates regular maintenance and upkeep to ensure optimal performance and reliability. It is advised to periodically review the partitioning scheme, eliminating obsolete partitions and reallocating resources as required. Additionally, conducting routine disk integrity checks and keeping up with software updates are vital for maintaining a healthy GPT partitioned system.
In conclusion, adhering to the best practices and guidelines outlined above can significantly contribute to an efficient and robust GPT partitioning experience. By understanding and implementing these recommendations, users can harness the full potential of GPT partitioning, enhancing storage management and optimizing system performance on Windows 10.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with GPT in Microsoft Windows
In this section, we will explore the commonly encountered problems and potential solutions related to the usage of GPT (GUID Partition Table) in the Windows operating system. Understanding and addressing these issues can help ensure the smooth functioning and optimal performance of GPT in Windows 10.
1. Compatibility with Legacy Systems
- GPT may face compatibility issues when used with older systems or operating systems that do not support this newer partitioning scheme.
- To address this, ensure that the system meets the minimum requirements for GPT usage, including having a UEFI-based firmware and a compatible operating system.
2. Partitioning Error Messages
- Users may encounter error messages related to partitioning when attempting to initialize or format GPT disks.
- To troubleshoot such issues, verify the disk integrity, ensure that the disk is not write-protected, and use disk management tools to diagnose and repair the partitioning errors.
3. Booting and System Recovery
- GPT disks can face difficulties in booting or being recognized by the system during the recovery process.
- To overcome these challenges, check the system's firmware settings, enable the UEFI boot mode, and ensure that the required system partitions are properly configured and active.
4. Disk Cloning and Backup
- Cloning or backing up GPT disks may encounter compatibility issues with certain disk cloning or backup software.
- To overcome this, select a reliable and GPT-compatible disk cloning or backup tool that supports proper partition alignment and GPT-specific features.
5. Data Recovery
- In case of data loss or accidental deletion on GPT disks, traditional data recovery methods may not be effective.
- To recover lost data, utilize specialized GPT data recovery tools or seek professional assistance to ensure safe and efficient recovery without compromising the integrity of the partitioned data.
By understanding and addressing these common issues and troubleshooting steps, users can maximize the utilization of GPT in Windows 10, ensuring a stable and reliable storage system for their data and operating system.
FAQ
What is GPT in Windows 10 and what functionality does it provide?
GPT stands for GUID Partition Table, and it is a partitioning scheme used in Windows 10. It provides multiple advantages over the older Master Boot Record (MBR) scheme, including support for larger disk capacities, improved data integrity, and support for more partitions.
Can I convert an MBR disk to GPT in Windows 10 without losing data?
Yes, Windows 10 provides a built-in tool called "MBR2GPT" that allows you to convert an MBR disk to GPT without data loss. However, it is recommended to backup your important data before performing the process, as unexpected errors can sometimes occur.
Does GPT require UEFI to work in Windows 10?
While GPT is fully compatible with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), it can also work with BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). However, if you want to boot from a GPT disk in Windows 10, your system must have UEFI firmware instead of BIOS firmware.




