In the realm of communication, our voice holds a certain kind of power. Its intonations, vibrations, and nuances convey our thoughts, our emotions, and our very essence. But what happens when the very sound of our voice is projected back to us, echoing in our ears through a pair of remarkable devices?
Imagine being in a world where speaking is not merely a one-way street; where the intricate mechanism of a peculiar contraption allows our voice to travel within us, reverberating and shaping our perception. It is within this surreal soundscape, with its labyrinthine pathways and myriad echoes, that we venture.
This enigma revolves around the invisible tether that connects us to the intricate web of technology. Through the artistry of a microphone and the marvel of headphones, there exists a peculiar synergy that alters not only our physical experience but also our psychological understanding of ourselves. It is a phenomenon that captivates the curious mind, beckoning us to explore the profound effects of this mystical connection.
Understanding the Phenomenon of Auditory Self-Perception while Monitoring Vocal Output
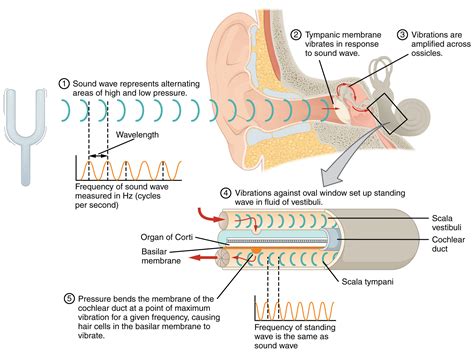
The auditory experience of perceiving one's own voice through headphones while utilizing a sound capture device has intrigued researchers and individuals alike. This phenomenon, characterized by the ability to hear oneself in real-time, represents a complex interaction between acquired sound waves and the intricate workings of the human auditory system.
Exploring the intricacies of this phenomenon is essential for unraveling the underlying mechanisms involved and shedding light on the subjective experiences and potential implications it holds. By examining the intricate relationship between sound production, auditory perception, and the technology facilitating vocal monitoring, a comprehensive understanding of this phenomenon can be attained.
| Table: Key Concepts in Understanding the Phenomenon | |
| Term | Description |
| Self-monitoring | The act of listening to one's own voice as it is recorded or transmitted through a microphone |
| Auditory feedback | The process of perceiving one's own voice through headphones or other auditory devices |
| Sound capture device | Equipment such as microphones or headsets used to capture and transmit sound waves |
| Acoustic perception | The interpretation and processing of sound waves by the human auditory system |
| Subjective experience | The individual's unique perception and interpretation of auditory sensations |
| Implications | The potential effects and applications of auditory self-perception on vocal performance and communication |
By gaining a deeper understanding of the factors influencing auditory self-perception, researchers can uncover insights into how individuals perceive and adjust their vocal output based on real-time feedback. This knowledge has the potential to benefit various domains, including vocal training, language learning, public speaking, and audio recording.
Furthermore, understanding the complex interplay between technology, such as microphones and headphones, and the subjective experience of hearing oneself can facilitate the development of improved audio devices and sound processing algorithms. This may lead to enhanced audio quality, reduced latency, and improved user experiences in various contexts.
In conclusion, comprehending the phenomenon of hearing oneself in headphones represents a fascinating area of research. By delving into the underlying mechanisms, exploring subjective experiences, and considering potential implications, we can unlock new insights and pave the way for advancements in vocal monitoring technology and auditory self-perception.
The Phenomenon of Acoustic Feedback in Sound Systems
In the realm of audio systems, there exists a fascinating phenomenon known as acoustic feedback. This occurrence occurs when audio from an output source, such as a microphone, is fed back into the system and subsequently returned as amplified sound through the speakers. The result is a continuous loop of sound that can impact the overall quality and performance of the audio system.
Acoustic feedback can be a double-edged sword, offering both advantages and challenges in audio production. On one hand, it allows individuals to monitor their own audio without relying solely on external playback devices. This self-monitoring capability is commonly facilitated through the use of headphones, where the user can hear their own voice as it is picked up by the microphone and processed through the system. This feature is particularly useful in scenarios such as live performances or recording sessions where real-time audio monitoring is vital.
However, the concept of acoustic feedback introduces several potential complications. One of the main challenges lies in the control and prevention of unwanted audio loops or "howling" that may arise from the feedback. This can result in an unpleasant screeching sound that disrupts the intended audio output and causes discomfort to both listeners and performers. Effective feedback management techniques, such as proper microphone placement and sound system configuration, must be employed to mitigate these issues.
Furthermore, the phenomenon of feedback can also have implications for the overall sound quality and intelligibility of audio systems. When the loop of sound generated by the feedback becomes too strong or prolonged, it can overshadow the intended audio signal, leading to muffled or distorted sound reproduction. This can compromise the clarity and impact of the audio, making it difficult for listeners to fully comprehend the intended message or enjoy the experience.
In conclusion, understanding the concept of acoustic feedback is essential for audio professionals and enthusiasts alike. It is crucial to strike a balance between harnessing the advantages of self-monitoring through headphones and managing the potential challenges associated with feedback loops. Through careful optimization of sound systems and the implementation of effective feedback control techniques, it is possible to achieve high-quality audio reproduction while minimizing the negative effects of acoustic feedback.
How Microphones Capture Sound

Discovering the process of how sound is captured by microphones can provide a deeper understanding of the technology behind these devices. By examining the mechanics and principles involved, we can explore the intricate ways in which microphones transform sound into electrical signals.
A fundamental concept in microphone technology is the conversion of sound waves into electrical energy. This process, known as transduction, involves the microphone's ability to transform acoustic vibrations into electrical signals that can be recorded or transmitted. Various types of microphones utilize different transduction mechanisms, such as dynamic, condenser, ribbon, or carbon microphones, each having its unique way of capturing sound.
One of the most common transduction methods employed by microphones is the use of diaphragms. Diaphragms act as the "ears" of a microphone, vibrating in response to sound waves and converting these vibrations into electrical signals. These diaphragms can take on different forms, including ribbons, capsules, or condenser plates, depending on the type of microphone.
- Dynamic microphones, for example, employ a diaphragm attached to a coil that moves within a magnetic field, generating electrical signals
- Condenser microphones, on the other hand, employ a diaphragm and a fixed plate separated by a small air gap, creating a capacitor that converts sound waves into electrical signals
- Ribbon microphones use a thin strip of metal as the diaphragm, which vibrates in response to sound waves, generating electrical signals through electromagnetic induction
- Carbon microphones rely on the carbon granules' resistance to vibration, which alters the electrical current passing through them, resulting in sound conversion
Microphones also utilize various pickup patterns, determining the directionality of sound capture. Common pickup patterns include omnidirectional, unidirectional (cardioid, supercardioid, hypercardioid), and bidirectional. These pickup patterns play a crucial role in capturing sound in specific situations, whether it's for recording vocals, instruments, or in live sound reinforcement.
Understanding how microphones capture sound opens up a world of possibilities for audio engineers, performers, and enthusiasts alike. By delving into the intricacies of transduction mechanisms and pickup patterns, we gain a deeper appreciation for the technology that allows us to express ourselves through sound.
The Role of Headphones in Monitoring
In the realm of audio production, the significance of headphones in the monitoring process cannot be overstated. These devices play a vital role in capturing and assessing sound, offering a unique auditory experience to the user. By providing a direct and isolated channel to listen to recorded audio, headphones enable professionals to detect and analyze even the subtlest nuances in sound quality, ensuring optimal output in various artistic and technical endeavors.
Enhanced Sensory Perception:
Just as a painter relies on their eyes to meticulously observe the colors and details of their artwork, audio professionals depend on their ears in the same manner. Headphones enhance this sensory perception by delivering an accurate and precise representation of the audio being recorded or played back. By isolating the sound, headphones eliminate external distractions and allow for a concentrated focus on the intricacies of the audio signals, including tonal balance, frequency response, stereo imaging, and spatial characteristics.
Improved Audio Precision:
Headphones provide a controlled listening environment where fine adjustments can be made to achieve the desired audio precision. As opposed to speakers, which introduce variables such as room acoustics and ambient noise, headphones present a more consistent and reliable sonic reference. This reliability facilitates tasks like mixing and mastering, where minute adjustments are necessary to ensure the overall clarity, dynamics, and coherence of the audio content.
Critical Listening and Evaluation:
When it comes to critical listening and evaluation, headphones are indispensable tools. The isolated auditory environment they create allows for meticulous examination and scrutiny of every audio element, including individual instrument or vocal tracks in a mix. By discerning the details that might be missed with other monitoring methods, headphones enable professionals to identify and rectify any imperfections or inconsistencies, leading to a higher-quality end product.
Portable and Versatile Monitoring:
The use of headphones in monitoring extends beyond the studio. With their portable nature, headphones offer the convenience of evaluating audio in various locations and environments. This makes them invaluable during live performances, field recordings, and mobile production setups. Their versatility and capability to provide a consistent monitoring experience across different contexts make headphones an essential companion for audio professionals on the go.
In conclusion, headphones are an integral part of the monitoring process in audio production. They provide an enhanced auditory experience, improve audio precision, facilitate critical listening and evaluation, and offer portability and versatility. These qualities, when harnessed effectively, contribute to the creation of high-quality audio content across a multitude of industries and artistic endeavors.
Exploring the Sound Routing in a Recording Setup
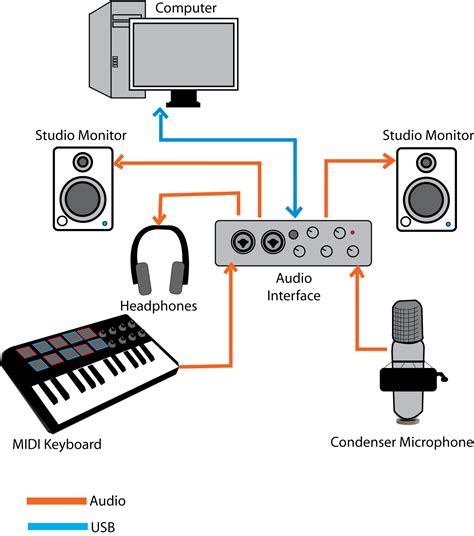
Understanding the intricate process of sound routing is essential when it comes to working with recording setups. In this section, we will delve into the fascinating world of how audio signals are directed and manipulated within a recording environment.
Audiophiles and sound engineers alike are constantly seeking to optimize the sound quality and ensure all audio components work harmoniously together. To achieve this, a comprehensive understanding of the sound routing process is crucial.
Sound routing refers to the path that an audio signal takes from the source (such as a microphone) to different destinations, including headphones, speakers, and recording devices. It involves the manipulation of the audio signal through various stages, allowing for monitoring, mixing, and recording purposes.
The sound routing process typically starts with the microphone, which converts sound waves into electrical signals. These signals then travel through various components, including a mixer or audio interface, where further adjustments and enhancements can be made.
One vital aspect of sound routing is monitoring. This allows the recording artist or sound engineer to listen to the audio in real-time, precisely as it will be heard by the audience. Headphones play a significant role in this, providing isolated audio playback while preventing any audio leakage.
Moreover, sound routing enables signal processing, where various effects and adjustments can be applied to modify the audio signal. This can include equalization, compression, and reverb, among others. Understanding how these effects are routed and applied is fundamental for achieving the desired sound aesthetic.
By exploring the intricacies of sound routing in a recording setup, we gain valuable insights into the technical aspects that contribute to high-quality audio production. It allows us to comprehend the importance of proper signal flow and how different components work together, ultimately resulting in exceptional sound recording and reproduction.
Possible Causes of Hearing My Voice in the Headset
There are various factors that could result in the occurrence of hearing one's own voice in the headphones while speaking into a microphone. This section will explore some potential causes of this phenomenon, investigating the underlying reasons without directly referencing the specific terms.
- Audio Feedback: When using audio equipment, it's essential to ensure proper configuration and settings to avoid audio feedback. This can occur when sound from the headphones is picked up by the microphone and sent back as a loop, resulting in hearing one's voice.
- Signal Leakage: Another potential cause could be signal leakage within the audio system. If there is an issue with the isolation or shielding of the equipment, it is possible for the sound from the headphones to leak into the microphone, leading to the unintended self-auditory experience.
- Monitoring Setup: The way the monitoring system is set up can also contribute to hearing oneself in the headphones. If the monitoring level is too high or if the microphone does not have proper monitoring settings, it can result in the voice being excessively transmitted back to the headphones.
- Microphone Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the microphone could play a role in this phenomenon. If the microphone is too sensitive or improperly adjusted, it may pick up sound from the headphones and amplify it, causing the voice to be heard in the headphones.
- Acoustic Reflections: The environment in which the recording or speaking is taking place can impact the occurrence. If there are reflective surfaces or inadequate soundproofing, the sound from the headphones can reflect off these surfaces and reach the microphone, resulting in the perception of one's own voice.
It is important to consider these potential causes when encountering the experience of hearing oneself in the headphones. By identifying and addressing the underlying factors, it becomes possible to resolve this issue and ensure optimal audio monitoring during microphone usage.
Minimizing or Eliminating the Feedback Effect: Effective Strategies to Reduce Audio Disturbances

In this section, we will explore various techniques and methods that can be employed to minimize or completely eliminate the undesirable feedback effect experienced while using a microphone and headphones. By employing these strategies, you can significantly improve the audio quality and enhance your overall recording or communication experience.
1. Adjusting the microphone and headphone positioning
One way to combat the feedback effect is to carefully position your microphone and headphones. Experiment with their placement to find the optimal distance and angle that minimizes acoustic reflections and potential audio disturbances.
2. Utilizing directional microphones
Consider using a directional or cardioid microphone for better control over audio pickup patterns. These microphones are designed to capture sound mainly from the front, reducing the likelihood of capturing and amplifying unwanted noise or feedback from the headphones.
3. Implementing noise reduction techniques
Employing noise reduction techniques, such as using pop filters or foam windscreens, can help minimize ambient noise and prevent it from being picked up by the microphone. This, in turn, reduces the chances of feedback occurring.
4. Employing audio ducking or sidechain compression
Utilizing audio ducking or sidechain compression can be an effective way to automatically reduce the volume of your headphones when speaking into the microphone. This technique lowers the chances of audio feedback by creating an audio balance between your voice and the audio output.
5. Ensuring proper grounding and cable management
Proper grounding and cable management are essential to minimize the risk of audio interference and feedback. Ensure that all audio equipment is properly grounded and that cables are routed away from potential sources of interference, such as power cables or electromagnetic devices.
6. Conducting sound checks and adjusting gain levels
Before recording or using a microphone, conduct sound checks to ensure the optimal gain levels are set. Adjusting the gain levels can help prevent audio distortion and feedback caused by excessively high microphone sensitivity.
By following these strategies, you can minimize or eliminate the feedback effect, resulting in clearer and more impactful audio recordings or communications.
Proper Techniques for Positioning Your Headphones and Microphone
Ensuring optimal sound quality and clarity during vocal recordings involves more than simply speaking into a microphone and listening through headphones. Proper positioning of both the microphone and headphones is crucial in order to attain the desired audio outcome.
- Microphone Positioning: The placement of the microphone greatly affects the sound that is captured. Experiment with different distances and angles to find the best position for your voice. An ideal position is where the microphone is neither too close to nor too far from your mouth. This helps to minimize distortion and unwanted background noise.
- Headphone Positioning: The way headphones sit on your head can greatly impact your ability to hear and monitor your own voice. Position the headphones comfortably so that they fully cover your ears without exerting too much pressure. This ensures proper sound isolation and allows you to accurately gauge your vocal performance.
- Adjusting Volume Levels: Pay close attention to the volume levels of both the microphone and the headphones. Avoid setting the microphone input level too high, as it can result in clipping and distortion. Adjust the headphone volume to a comfortable level that allows you to hear yourself clearly without causing discomfort.
- Using Pop Filters: Pop filters are essential accessories that can enhance the audio quality of vocal recordings. Placing a pop filter between your mouth and the microphone helps to reduce plosive sounds caused by pronunciation of certain letters. This prevents distortion and ensures a smoother, more professional sound.
- Considering Room Acoustics: The environment in which you record can significantly affect the sound captured by the microphone. Keep in mind the acoustic properties of the room and experiment with placement options to minimize reverberations and echoes. Soundproofing techniques such as using foam panels or a reflection filter can also improve recording quality.
By implementing these proper techniques for positioning your headphones and microphone, you can optimize the sound quality of your vocal recordings. Experimenting with different positions and considering the overall acoustic environment will help you achieve the desired audio results. Remember that finding the perfect positioning may require some trial and error, but the end result will be well worth the effort.
Pro Tips for Resolving the Issue
When encountering the problem of hearing your own voice through the headphones while using a microphone, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to resolve the issue. By following these pro tips, you can effectively address the problem and restore the normal functionality of your audio setup.
To begin, check the connections between your microphone, headphones, and audio interface. Ensure that all cables are securely plugged in and that there are no loose connections. Oftentimes, a loose or faulty cable can cause audio feedback and result in the issue at hand.
Next, examine the settings on your audio device and software. Make sure that the input and output settings are properly configured. Adjust the volume levels to an appropriate level and confirm that any effects or filters are not causing the problem. It is also helpful to update your audio drivers or firmware to the latest version, as outdated software can sometimes lead to audio malfunctions.
If the problem persists, try using a different microphone or headphones. This can help determine if the issue lies with the specific equipment you are using. Additionally, testing your setup on another device can provide insight into whether the problem is related to your computer or audio interface.
An important step in troubleshooting is to rule out any external factors that may be causing interference. Check for nearby devices that may emit electromagnetic waves, such as smartphones or Wi-Fi routers. Moving away from these sources of interference or adjusting their positions can help eliminate any unwanted audio feedback.
Lastly, consider seeking professional assistance if the above steps do not resolve the issue. An audio technician or expert can provide further guidance and determine if there are any hardware problems that need to be addressed.
- Check all cable connections and ensure they are secure
- Verify and adjust the settings on your audio device and software
- Update your audio drivers or firmware
- Test with different microphones or headphones
- Try your setup on another device
- Avoid interference from nearby devices
- Consider seeking professional assistance if needed
The Significance of Effective Communication with Sound Technicians and Producers
Effective communication plays a crucial role in achieving harmonious collaborations between musicians, vocalists, and sound engineers or producers. It is paramount to establish a shared understanding and create a seamless workflow throughout the recording process.
1. Clear Artistic Direction: The ability to effectively communicate one's creative vision to sound technicians and producers ensures that the desired outcome is achieved. Accurate articulation of artistic intentions, musical style, and emotional nuances enables the team to accurately capture and enhance the desired sound.
2. Efficient Problem Solving: Establishing open lines of communication allows for seamless problem-solving during recording sessions. When faced with technical issues or artistic challenges, promptly conveying concerns ensures that potential obstacles are overcome efficiently, minimizing time wastage and frustration.
3. Collaborative Decision Making: Encouraging open dialogue and active participation of sound technicians and producers fosters a collaborative environment. Effective communication facilitates the exchange of ideas, leading to well-informed decisions regarding microphone placement, sound effects, mixing techniques, and overall production choices.
4. Optimum Sound Capture: Communication between artists and sound engineers helps to capture the desired sound accurately. Clear instructions regarding preferred vocal or instrumental tones, desired reverberation levels, and specific effects contribute to achieving a high-quality recording.
5. Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Regular and constructive feedback should be communicated between all parties involved. This enables the sound engineer or producer to make necessary adjustments and improvements during the recording and post-production phases, ensuring the final product aligns with the artist's creative vision.
6. Creating Trust and Rapport: Building trust and rapport through effective communication helps establish a strong working relationship. Trust allows artists to be vulnerable, facilitating experimentation and exploration of new sonic territories, resulting in unique and innovative productions.
Effective communication with sound engineers and producers not only leads to a successful recording session but also fosters a collaborative environment where the shared goal of creating outstanding music is achieved. Emphasizing the importance of communication ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same artistic vision.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why do I hear myself when I speak into a microphone?
When you speak into a microphone, the sound waves from your voice are converted into electrical signals by the microphone. These electrical signals are then amplified and sent to the headphones. This allows you to hear your own voice in real-time, which can help you monitor your volume and tone while speaking.
Is it normal to hear myself in the headphones when using a microphone?
Yes, it is completely normal to hear yourself in the headphones when using a microphone. This feature is known as "monitoring" and it allows you to hear your own voice as you speak, which can be useful for adjusting your performance and ensuring the audio quality is adequate.
Can I turn off the feature that allows me to hear myself in the headphones?
Yes, most professional audio equipment allows you to adjust the monitoring level or completely turn it off. This can be done using the controls on the microphone, audio interface, or mixer. However, it is important to note that hearing your own voice while speaking can provide valuable feedback and help you deliver a better performance, so it is generally recommended to use at least a low level of monitoring.




