When it comes to achieving seamless synchronization on your Windows device, there are crucial steps you can take to ensure a flawless experience. By fine-tuning your settings and optimizing your system, you can unlock the full potential of your device's synchronization capabilities.
Enhancing the harmonious flow of data across your Windows device is an art that requires attention to detail and careful configuration. With a few simple adjustments, you can establish a reliable and efficient sync system that empowers you to effortlessly manage your files and information.
Think of your Windows device as a symphony, where different components play their unique parts in creating a synchronized masterpiece. By harnessing the power of your device's settings, you can orchestrate a seamless sync process that harmonizes all your favorite applications, files, and data.
Imagine a world where all your devices work as one, effortlessly exchanging information and staying up-to-date without any hitches. With the right adjustments and configuration, you can transform your Windows device into a well-oiled synchronization machine, allowing you to seamlessly transition between workstations and devices. So, why settle for anything less than perfect sync when you have the opportunity to optimize your Windows experience to its fullest potential?
Deciding on the Appropriate Windows Edition for Synchronization
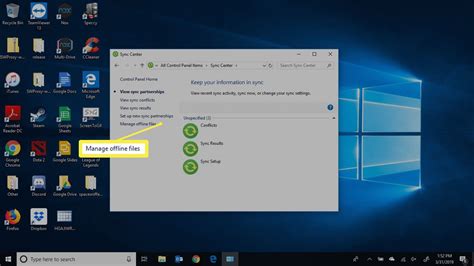
When it comes to ensuring efficient synchronization within a computer system, selecting the ideal version of the Windows operating system is crucial. Various factors need to be considered for choosing the right edition that aligns with the synchronization requirements.
- Take Account of Synchronization Needs: First and foremost, it is essential to deeply understand the synchronization needs of the system. Whether it is data synchronization, file synchronization, or synchronization between multiple devices, evaluating these requirements will guide the selection process.
- Evaluate Performance and Reliability: Different Windows editions offer varying levels of performance and reliability. The choice of an operating system with robust performance metrics and a reputation for stability ensures smooth synchronization processes without interruptions.
- Consider Compatibility and Scalability: Compatibility with existing hardware and software solutions is paramount for effective synchronization. Assessing the compatibility of different Windows versions with the existing infrastructure and determining the scalability options they provide is crucial for long-term synchronization success.
- Security and Data Protection: Synchronization involves the transfer of sensitive data between devices or systems. Prioritizing security features and data protection mechanisms offered by different Windows editions is vital to safeguard against potential threats or vulnerabilities.
- Support and Updates: Regular updates and dedicated technical support are essential for maintaining a synchronized system. Considering the level and frequency of updates provided by different Windows editions, as well as the available support channels, helps in making an informed decision.
By carefully analyzing and considering these factors, it is possible to choose the most suitable Windows edition for synchronization that meets the specific needs of the system. The right selection lays the foundation for a well-integrated and efficient synchronization system, facilitating smooth data flow and seamless collaboration.
Determining compatibility and system requirements
Before implementing the synchronization system, it is crucial to assess the compatibility of your current setup and ensure that your system fulfills the necessary requirements. This section will guide you through the process of determining the compatibility and system requirements, allowing for a seamless setup process.
Evaluating compatibility:
First and foremost, it is essential to evaluate whether your system components, including hardware and software, are compatible with the synchronization system. This assessment will help identify any potential conflicts or limitations that may hinder the system's effectiveness.
Hardware compatibility:
Review the hardware specifications required by the synchronization system, considering factors such as processor speed, memory capacity, and storage space. Ensure that your hardware meets or exceeds these requirements to guarantee optimal performance during synchronization.
Software compatibility:
Assess the compatibility of your existing software with the synchronization system. Verify whether the required software versions are supported and check for any potential conflicts. Additionally, consider ensuring that necessary drivers or updates are installed to eliminate any compatibility issues.
Determining system requirements:
Once you have assessed compatibility, it is important to determine the specific system requirements for setting up the synchronization system. This step will help you prepare your system adequately and ensure a smooth implementation process.
Operating system:
Verify the compatibility of your operating system with the synchronization system. Determine the minimum supported version and ensure that your system meets this requirement. Additionally, consider any specific system configurations or settings that may be necessary for ideal synchronization performance.
Network requirements:
Examine the network requirements for the synchronization system, including network speed, bandwidth, and stability. Ensure that your network infrastructure can support the anticipated synchronization load and consider any additional measures, such as optimizing network settings, if required.
User access and permissions:
Identify the user access and permission levels needed for the synchronization system. Determine whether specific user accounts or elevated privileges are required to ensure seamless operation. Plan and configure user access accordingly to prevent any disruptions during the setup and usage of the synchronization system.
By thoroughly evaluating compatibility and determining system requirements, you can establish a solid foundation for setting up the synchronization system. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks and ensure the smooth operation of the system, enhancing productivity and efficiency in your workflow.
Configuring Firewall on your Device for Synchronization
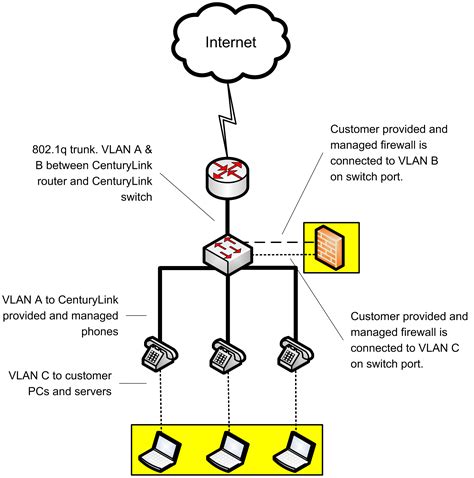
When it comes to synchronizing data between devices, ensuring that your firewall is properly configured is essential. The firewall acts as a security measure, controlling the network traffic and protecting your system from unauthorized access.
In order to optimize the synchronization process and allow for seamless data transfer, here are some key steps to configure your firewall:
- Identify the firewall software or built-in firewall on your device
- Access the firewall settings and locate the configuration options
- Enable or create a rule to allow incoming and outgoing synchronization traffic
- Specify the synchronization software or application as an exception to the firewall rules
- Adjust the firewall settings to allow the specific synchronization ports or protocols
- Consider enabling logging for synchronization-related activities
- Regularly update and review the firewall rules to ensure continued compatibility and security
By carefully configuring your firewall for synchronization purposes, you can optimize the efficiency and security of your data transfer. Remember to consult the documentation or support resources of your specific firewall software for detailed instructions and best practices.
Enabling Necessary Network Traffic
In the process of configuring a comprehensive synchronization system, it is essential to ensure that the appropriate network traffic is allowed. This involves enabling the transmission of vital data across the network infrastructure, allowing seamless communication between devices and systems.
To facilitate the smooth operation of the synchronization system, it is crucial to establish the necessary network settings that allow the flow of information. This includes configuring firewall rules, defining access control policies, and permitting specific protocols and port numbers for communication.
- Configuring Firewall: One of the first steps is to configure the firewall settings to enable the required network traffic. This involves identifying the necessary ports, protocols, and IP addresses that the synchronization system utilizes, and creating rules to allow communication through the firewall.
- Defining Access Control Policies: To ensure secure and authorized access, access control policies need to be defined. These policies outline which devices or users are permitted to connect to the synchronization system, and what level of access they have.
- Permitting Protocols and Port Numbers: Different synchronization systems rely on specific protocols and port numbers for data transmission. It is essential to identify these requirements and permit the respective protocols and port numbers to avoid any communication interruptions.
- Monitoring and Fine-tuning: Once the necessary network traffic has been enabled, continuous monitoring and fine-tuning of the network settings are required. This ensures optimal performance and security of the synchronization system, as well as the ability to adapt to any changes in the network environment.
By enabling the necessary network traffic, organizations can create a robust and efficient synchronization system that allows devices and systems to seamlessly communicate and exchange data. Implementing the appropriate configurations and regularly monitoring the network settings are crucial to maintaining the reliability and security of the synchronization system.
Installing and Configuring Synchronization Software
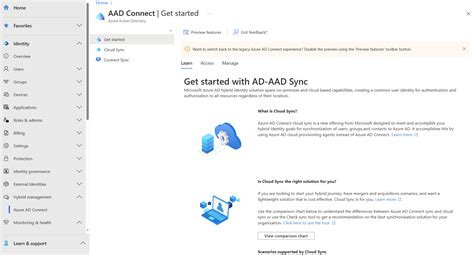
In this section, we will explore the process of setting up and configuring synchronization software to ensure effective data synchronization across different devices and systems. By utilizing specialized software, users can seamlessly synchronize their data, files, and settings, enabling convenient access and consistent updates across multiple platforms.
1. Selecting the Appropriate Synchronization Software:
- Researching and assessing various synchronization software options
- Identifying software compatibility with different operating systems and devices
- Evaluating available features for data synchronization and file management
2. Downloading and Installing the Synchronization Software:
- Accessing the official website or trusted sources to download the software
- Verifying system requirements and ensuring compatibility
- Initiating the software installation process
3. Configuring Initial Settings:
- Launching the synchronization software on the device
- Completing the initial setup and registration process
- Creating a user account or logging in with existing credentials
4. Setting up Synchronization Preferences:
- Configuring synchronization options such as automatic or manual syncing
- Selecting the preferred synchronization method (e.g., cloud-based, local network)
- Choosing specific folders or data types for synchronization
5. Adding Devices for Synchronization:
- Linking additional devices to the synchronization software
- Verifying the device's connection and ensuring proper authorization
- Configuring sync settings for each connected device
6. Resolving Synchronization Conflicts:
- Understanding common synchronization conflicts (e.g., conflicting file versions)
- Implementing conflict resolution strategies provided by the software
- Manually resolving conflicts and ensuring data integrity
7. Testing and Verifying Synchronization:
- Performing test synchronization to validate successful setup
- Verifying synchronized data, files, and settings across devices
- Troubleshooting and resolving any synchronization issues
By following the steps mentioned above and configuring the synchronization software correctly, users can enjoy the benefits of effortless data synchronization, improved productivity, and enhanced collaboration.
Choosing the appropriate software and configuring the synchronization process
In this section, we will cover the essential steps to consider when selecting suitable software and setting up the synchronization process for your desired system. Finding the right software solution is crucial to ensure efficient data exchange and integration between various devices and platforms.
To begin, thoroughly evaluate the available software options that align with your specific requirements and use case. Consider factors such as compatibility, scalability, ease of use, and the range of synchronization features offered. It is essential to select software that can seamlessly connect and synchronize data across different operating systems and devices, creating a smooth and efficient synchronization process.
Once you have chosen the appropriate software, the next step is to configure the synchronization process. Start by identifying the data sources that need to be synchronized and determine the frequency and priority level of each synchronization task. Create a comprehensive plan that outlines the synchronization workflow, including the mapping of data fields, filters, and any necessary transformations.
- Define the synchronization intervals and establish a schedule that ensures data is updated and synchronized in a timely manner.
- Configure the software settings to enable automatic synchronization or set up triggers based on specific events or conditions.
- Implement appropriate security measures to protect sensitive data during the synchronization process, such as data encryption or user authentication.
- Regularly monitor and analyze the synchronization process to identify any potential issues or bottlenecks. Set up alerts or notifications to quickly address any problems that may arise.
Remember that proper software selection and meticulous configuration are essential for successful synchronization. By choosing the right software and carefully setting up the synchronization process, you can ensure seamless data exchange and integration, improving overall system efficiency and productivity.
Exploring Synchronization Protocols: Windows Unveiled

The realm of operating systems is ever-evolving, with Windows being at the forefront of innovation. Amidst the intricacies and complexities of synchronization protocols lies the key to harmonious interplay between diverse devices and applications.
In this article, we delve into the inner workings of synchronization protocols in the Windows ecosystem, unraveling their significance and impact. Understanding how these protocols function is vital for streamlining data exchange, ensuring seamless collaboration, and fostering optimal system performance.
The Essence of Synchronization
Synchronization, in the context of Windows, refers to the careful orchestration of data transfer and the establishment of consistency across interconnected systems. It facilitates the sharing and updating of information, empowering users to access real-time data effortlessly.
Compatibility, Efficiency, and Reliability
Windows synchronization protocols are designed to embrace compatibility by employing standardized methods that cater to various devices and platforms. These protocols strive for efficiency by minimizing data redundancy, optimizing network utilization, and reducing latency. Moreover, they promote reliability by offering robust error and conflict resolution mechanisms, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of synchronized data.
Understanding the Supported Protocols
Windows encompasses an array of synchronization protocols tailored to meet diverse requirements in different scenarios. From the venerable SMB protocol for file sharing to more advanced protocols like SyncML for mobile device synchronization, Microsoft has crafted a versatile toolbox of standards to empower users with seamless synchronization capabilities.
Examining Protocol Components
In our exploration, we analyze the key components that underpin synchronization protocols. These include the synchronization engine, conflict resolution mechanisms, data compression techniques, and encryption algorithms. Understanding how these pieces fit together enables users to optimize their synchronization setup and address potential performance bottlenecks.
Embracing Synchronization: Benefits and Beyond
Mastering synchronization protocols empowers Windows users to unlock a myriad of benefits. Enhanced collaboration, data availability, and streamlined workflows are just a few advantages that become attainable through the proper implementation and configuration of synchronization protocols.
Conclusion
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of synchronization protocols in Windows, users can harness the full potential of their operating system. With the ability to synchronize seamlessly across diverse devices and applications, Windows users can embrace productivity, efficiency, and innovation like never before.
Exploring different communication protocols and their benefits
This section aims to delve into the various communication protocols available for synchronizing systems on different Windows environments. By understanding the unique advantages of each protocol, you can make informed decisions when setting up synchronization systems.
When it comes to synchronizing systems, the choice of communication protocol plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient data exchange and seamless integration. Different protocols offer distinct features and benefits that cater to specific synchronization requirements. By exploring these protocols, you can optimize the performance, security, and reliability of your Windows synchronization system.
One popular communication protocol is the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Known for its reliability, TCP guarantees that data packets are received in the intended order without any loss or corruption. This protocol ensures error-free communication by employing various mechanisms, such as acknowledgment, retransmission, and flow control. By using TCP, you can ensure the integrity of your synchronization data, providing a stable foundation for your Windows environment.
Another commonly used protocol is the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Unlike TCP, UDP sacrifices reliability for speed and efficiency. It enables rapid data transmission by sending packets without waiting for acknowledgment or retransmissions. UDP is well-suited for scenarios where real-time updates and quick synchronization are critical, such as multimedia streaming or online gaming. Although it may be susceptible to packet loss or corruption, the speed advantages of UDP make it an attractive option in certain Windows synchronization setups.
Furthermore, the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and its secure variant, HTTPS, offer versatility and compatibility for synchronization systems. HTTP provides a standardized way of exchanging data between web servers and clients. It allows synchronization processes to leverage the existing infrastructure of servers and browsers, simplifying integration and development. HTTPS adds an additional layer of security through encryption, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your synchronized data. Utilizing HTTP or HTTPS protocols can provide seamless communication in a Windows environment that heavily relies on web-based technologies.
Additionally, other communication protocols like the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), and Remote Procedure Call (RPC) have their own strengths and applications in specific synchronization scenarios. FTP facilitates the secure transfer of files, making it ideal for large-scale data synchronization. SMTP enables email-based communication, which can be utilized for lightweight synchronization operations. RPC allows processes on different systems to communicate with each other, supporting distributed synchronization across Windows networks.
Overall, understanding the strengths and benefits of various communication protocols empowers you to choose the most suitable option for your Windows synchronization system. By considering factors such as reliability, speed, security, compatibility, and scalability, you can create a well-rounded and efficient synchronization environment tailored to your specific needs.
Establishing User Accounts and Permissions for Data Sync
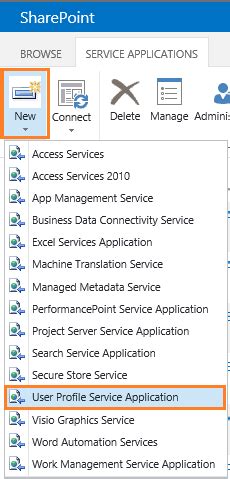
In this section, we will discuss the process of creating user accounts and defining their permissions to facilitate seamless data synchronization within a Windows environment.
User accounts play a crucial role in ensuring that data synchronization operates smoothly and securely. When setting up user accounts, it is important to carefully configure various permissions and access levels to maintain data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
| Account Name | Access Level | Permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Admin | Superuser | Full access to all synchronization settings and files |
| Manager | Team Leader | Access to manage synchronization settings for assigned teams |
| Employee | Standard User | Read and write access to specific synchronized folders |
It is essential to define the appropriate access levels and permissions for each user account based on their role and responsibilities within the synchronization system. Administrators have ultimate control and can manage settings and files, while managers oversee specific teams and can modify synchronization settings for their assigned teams. Employees have access to specific synchronized folders for reading and writing data.
By carefully defining user accounts and their corresponding permissions, organizations can ensure that data synchronization is efficient, secure, and tailored to meet the unique requirements of their workflow.
Establishing User Access and Permissions
In order to ensure efficient and secure synchronization within the Windows environment, it is essential to configure appropriate access levels and privileges for system users. By setting up specific access levels and assigning corresponding privileges, organizations can control and regulate the actions and operations performed by different individuals within the system.
Defining User Roles:
One key aspect of setting up access levels and privileges is defining user roles within the synchronization system. User roles are essential for categorizing individuals based on their responsibilities and tasks within the organization. By clearly defining these roles, organizations can ensure that each user is granted appropriate permissions based on their specific requirements and job responsibilities.
Granting Access Levels:
Once user roles have been identified, it is important to assign access levels to each role. Access levels determine the extent of privileges and permissions a user can have within the system. They dictate the actions that users are allowed to perform, such as creating, modifying, or deleting files or accessing certain features or settings. By carefully determining access levels, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and maintain data integrity within the synchronization system.
Configuring Permissions:
Permissions further refine the access granted to users by specifying the specific operations and actions they can perform within the assigned access levels. These permissions can include read, write, modify, delete, or execute privileges, among others. By setting up permissions accurately, organizations can ensure that users have the necessary access required to fulfill their responsibilities while maintaining data security and preventing unauthorized modifications.
Regular Review and Maintenance:
Establishing access levels and assigning privileges is not a one-time task. It is crucial for organizations to regularly review and revise user access and permissions to accommodate any changes in user roles, responsibilities, or security requirements. By consistently monitoring and updating access privileges, organizations can maintain an appropriate level of control and security within their synchronization system.
In conclusion, setting up access levels and privileges plays a vital role in establishing an efficient and secure synchronization system within the Windows environment. By defining user roles, assigning appropriate access levels, configuring permissions, and regularly reviewing and updating access privileges, organizations can ensure that their system operates smoothly and securely, with each user having the necessary level of access to fulfill their responsibilities while safeguarding sensitive data.
Configuring synchronization options and settings
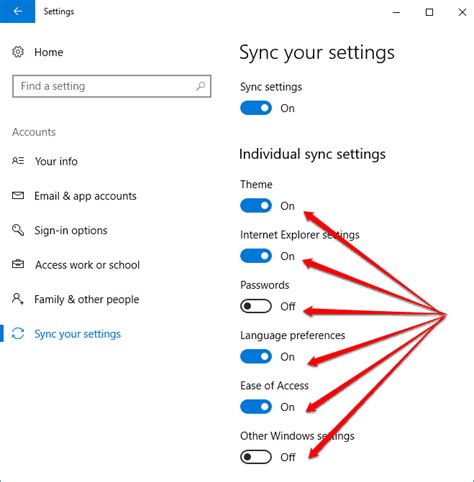
In this section, we will explore the various options and settings available for customizing and fine-tuning the synchronization capabilities of your Windows operating system. By adjusting these parameters, you can ensure that your files, data, and settings are efficiently synchronized across different devices and platforms.
1. Synchronization frequency
- Choosing the appropriate synchronization frequency is vital to strike a balance between real-time updates and system resources utilization. You can adjust the synchronization interval based on your needs, be it continuous synchronization for instantaneous updates or scheduled synchronization at specific time intervals like hourly, daily, or weekly.
- customizing
- preferences
- deciding
- interval
2. Selective file and folder synchronization
- Not all files and folders require immediate synchronization. By selectively choosing which files and folders to synchronize, you can optimize the synchronization process and prioritize the most important data for seamless integration across devices and platforms.
- choosing
- prioritizing
- relevant
- essential
3. Conflict resolution strategies
- When multiple devices are synchronizing data simultaneously, conflicts may arise when changes are made to the same file or folder. Configuring conflict resolution strategies allows you to define rules for handling conflicts, such as prioritizing the most recent updates or manually reviewing and merging conflicting changes.
- resolving
- handling
- addressing
- managing
4. Bandwidth management
- To optimize the synchronization process and minimize the impact on network bandwidth, you can configure bandwidth limits for synchronization activities. By setting restrictions on upload and download speeds, you can prevent excessive data usage and ensure a seamless synchronization experience without compromising overall network performance.
- optimizing
- restricting
- minimizing
- consumption
Configuring Sync Settings: Customizing frequency, file types, and exclusions
In this section, we will explore how to personalize your sync settings to meet your specific needs. By customizing the frequency of synchronization, determining the types of files to include or exclude, and specifying specific file exclusions, you can tailor the synchronization process to optimize efficiency and minimize resource usage.
1. Adjusting the Synchronization Frequency
To ensure that your files are always up to date, it is crucial to set an appropriate synchronization frequency. By modifying the interval at which synchronization occurs, you can balance the desire for real-time updates with the impact on system performance. We will guide you through the steps to optimize the synchronization frequency to suit your requirements.
2. Defining File Types for Synchronization
Not all files may need to be synchronized across devices. By specifying the file types that should be included or excluded from synchronization, you can refine the sync process and conserve resources and storage space. We will show you how to customize the file types to be synchronized, ensuring that only relevant files are shared between devices.
3. Configuring File Exclusions
In some cases, there may be specific files or folders that you do not want to include in the synchronization process. By configuring file exclusions, you can avoid unnecessary synchronization of sensitive, large, or temporary files, saving time and resources. We will walk you through how to exclude specific files or directories from synchronization, delivering greater control over the sync process.
By customizing the synchronization frequency, file types, and exclusions, you can optimize the synchronization system to meet your specific needs, striking a balance between real-time updates and resource efficiency.
FAQ
What is synchronization system in Windows?
Windows synchronization system is a feature that allows data synchronization between multiple devices or applications to ensure that they have the most up-to-date and consistent data.
How can I set up synchronization system in Windows?
To set up synchronization system in Windows, you can use the built-in Sync Center. Open Sync Center from the Control Panel, click on "Set up new sync partnerships" and follow the prompts to configure synchronization for your desired files or folders.
Can I synchronize my Windows settings across multiple devices?
Yes, you can synchronize your Windows settings across multiple devices using the Microsoft account sync feature. Simply sign in to each device with the same Microsoft account, go to Settings > Accounts > Sync your settings, and turn on the desired settings to synchronize.
What precautions should I take before setting up synchronization in Windows?
Before setting up synchronization in Windows, it is important to back up your data to prevent any potential data loss. Additionally, ensure that you have a stable internet connection and sufficient storage space on all devices involved in the synchronization process.
What are the benefits of using synchronization system in Windows?
The synchronization system in Windows offers several benefits such as seamless access to updated files or folders across multiple devices, increased productivity through automatic synchronization, and the ability to work offline and have changes synchronized when a connection is restored.
What is the purpose of setting up Windows for Synchronization System?
The purpose of setting up Windows for Synchronization System is to enable synchronization between different devices and ensure that all data is up to date and consistent across all devices.
What are the steps involved in setting up Windows for Synchronization System?
The steps involved in setting up Windows for Synchronization System may vary depending on the specific synchronization system being used. However, the general steps usually involve configuring synchronization settings, selecting the folders or files to be synchronized, and initiating the synchronization process.




