Efficiency, organization, and seamless collaboration - these three pillars lie at the very core of every successful business. And when it comes to creating a secure and interconnected network infrastructure that fosters these values, mastering the art of configuring a productive Windows domain is essential.
Picture a digital ecosystem where information flows effortlessly across departments and devices, ensuring that decision-makers, employees, and clients are always on the same page. This is precisely what a well-configured Windows domain enables - a centralized platform that fuels productivity, streamlines operations, and enhances communication in a secure environment.
Unlocking the full potential of a Windows domain configuration is a journey that requires a deep understanding of its intricacies and nuances. It involves setting up user accounts, managing group policies, establishing trust relationships, and harnessing the power of Active Directory. By carefully navigating through each step, businesses can harness the true power of their Windows domain, propelling their operations to new heights.
Understanding the Essence of a Windows Domain

In the realm of computer networks, a Windows Domain embodies a powerful framework that establishes a network of interconnected devices, enabling efficient communication, centralized administration, and enhanced security. This intricate system serves as the backbone of an organization's IT infrastructure, providing a structured environment for resource sharing, user authentication, and access control.
Within a Windows Domain, various components harmoniously collaborate to form a cohesive ecosystem. The domain controller acts as the authoritative entity, authenticating and authorizing users, managing security policies, and maintaining a database of network objects. Meanwhile, client devices, referred to as member computers, join the domain to participate in the network and benefit from the centralized management capabilities offered by the domain controller.
By establishing a Windows Domain, organizations can streamline their network administration efforts. They can define comprehensive sets of policies, permissions, and restrictions for different user groups, ensuring secure and efficient access to shared resources such as files, printers, and applications. Additionally, domain-wide settings can be configured, eliminating the need for individually managing each device, leading to consistent configurations, simplified software distribution, and centralized updates.
Advantages of Implementing Windows Domain Configuration
Implementing the Windows Domain Configuration offers numerous benefits that contribute to an enhanced network management and improved overall productivity. By centralizing user and computer accounts, it simplifies the administration process and streamlines access control. This approach provides a secure foundation for data sharing, centralized resource management, and seamless collaboration across the network.
One of the major advantages of Windows Domain Configuration is its ability to provide a centralized authentication system. Instead of individually managing usernames and passwords on each computer, a domain controller authenticates users and grants access to network resources. This improves security by enforcing password policies, enabling multi-factor authentication, and allowing for more efficient user provisioning and deprovisioning processes.
Another notable benefit is the ease of network management that Windows Domain Configuration brings. With a domain controller, administrators can effortlessly manage user accounts, group policies, and permissions from a single location. This simplifies the task of adding or removing users, applying software updates, and implementing security measures, increasing efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
Windows Domain Configuration also fosters better collaboration among users. By centralizing data storage and sharing, users can easily access shared folders and files, facilitating seamless collaboration and efficient information exchange. This feature enables teams to work collectively on projects and improves productivity by eliminating redundancies and minimizing data duplication.
Furthermore, Windows Domain Configuration supports the implementation of group policies, allowing administrators to enforce specific settings and restrictions across the network. This ensures consistency in system configurations, enhances security measures, and assists with compliance requirements. Group policies enable administrators to control various aspects of network behavior, such as restricting access to specific websites or enforcing software installation policies.
In conclusion, the implementation of Windows Domain Configuration brings numerous benefits to network management, security, collaboration, and overall efficiency. By centralizing user accounts, authentication, and resource management, it provides a secure and streamlined environment that enhances productivity and simplifies administration tasks.
Establishing a Windows Network Environment

Creating a Windows network ecosystem involves configuring various components to enable communication and collaboration among connected devices. A well-planned network setup reinforces data security, simplifies administration tasks, and enhances overall productivity.
When setting up a Windows domain configuration, several essential steps need to be followed to ensure smooth operation and seamless integration within the network. These steps involve establishing a hierarchical structure, defining user roles, configuring security protocols, and implementing appropriate file sharing and access permissions. By carefully orchestrating these elements, administrators can create a cohesive network environment that facilitates effective resource management and user collaboration.
- Designing the Network Hierarchy: Creating an organized structure by grouping devices and users based on their roles and responsibilities, allowing for efficient management and control.
- Defining User Roles and Permissions: Assigning specific access rights to users based on their job requirements, ensuring secure usage and data protection.
- Implementing Network Security Measures: Establishing robust security protocols such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard against potential threats and unauthorized access.
- Configuring File Sharing and Access Permissions: Enabling seamless data exchange and collaboration across the network while maintaining appropriate access controls to protect sensitive information.
- Centralizing User and System Management: Streamlining administrative tasks by implementing centralized management tools, simplifying user account creation, password resets, and device configuration.
- Integrating External Services and Applications: Facilitating integration with external services to enhance functionality, such as email servers, cloud storage, or third-party applications, expanding the network's capabilities.
- Enforcing Network Policies and Monitoring: Establishing policies to regulate network usage, monitor performance, and detect anomalies to proactively address potential issues and ensure a stable network environment.
By following these steps and best practices, administrators can successfully configure a Windows domain that allows for efficient resource utilization, simplified management, and secure collaboration within the network.
Step 1: Prepare the Network Foundation
In the initial phase of configuring a Windows domain, it is crucial to lay a strong groundwork for the network infrastructure. This preparatory step ensures that the entire network is ready to support the successful implementation of the domain.
During this stage, it is essential to evaluate and optimize the network components necessary for the domain configuration, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. Identifying and addressing any potential weaknesses or limitations in these devices will help establish a robust and efficient network infrastructure.
Moreover, it is vital to ensure network connectivity between all the devices that will be part of the domain. This involves verifying the availability of necessary network protocols, like TCP/IP, and setting up IP addressing schemes to facilitate smooth communication among the various domains, servers, and client computers.
Another crucial aspect of preparing the network foundation is securing the network infrastructure. This involves implementing appropriate security measures, such as configuring strong passwords, enabling firewalls, and implementing encryption protocols. These measures should be designed to protect the network from unauthorized access, malware, and potential security threats.
Lastly, it is important to document the network infrastructure, including network diagrams, IP addresses, and configuration details. This documentation serves as a valuable reference point for future troubleshooting, maintenance, and expansion of the domain.
By carefully preparing the network foundation, businesses can ensure a stable and secure environment for setting up their Windows domain configuration.
Setting Up Active Directory: Step 2
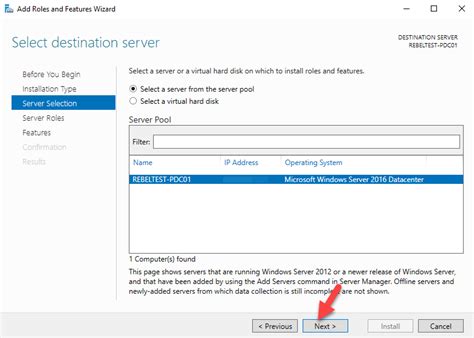
Implementing and Configuring Active Directory: Step 2 in Windows Domain Setup
In this section, we will focus on the second crucial step in the process of setting up a Windows Domain Configuration. Step 2 entails the installation and configuration of Active Directory, a fundamental component in managing and organizing resources within a network infrastructure.
Active Directory serves as a centralized database that stores information about network users, groups, computers, and shared resources. This step is essential as it enables administrators to manage access rights, security policies, and efficiently distribute resources across the network.
As part of the installation process, we will discuss the prerequisites and considerations before proceeding with the installation. Additionally, we will guide you through the steps required to configure Active Directory, including domain controller promotion and defining the domain structure.
By following this step-by-step guide, you will be able to successfully set up and configure Active Directory, bringing you one step closer to establishing a robust and secure Windows Domain Configuration.
Step 3: Establish User and Group Accounts within the Network
In this stage, we will focus on creating user and group accounts within the established Windows domain configuration. As the network administrator, it is essential to define and manage these accounts effectively to ensure proper access control and organizational structure.
User Management: With user accounts, you can provide individual network access to employees or authorized individuals. By defining their user accounts, you can assign specific permissions, privileges, and access levels according to their roles or responsibilities within the organization.
Group Management: By organizing users into groups, you can streamline access control and facilitate efficient management across the Windows domain. Group accounts allow you to assign permissions, policies, and resources to multiple users simultaneously, simplifying administration tasks and ensuring consistency throughout the network.
Creating User Accounts: To create a user account, navigate to the Active Directory Users and Computers console, locate the relevant Organizational Unit (OU), and select the "New User" option. Enter the required user information, such as username, full name, and password, and configure additional settings as necessary. This process ensures that each user has a unique identifier and login credentials within the Windows domain.
Creating Group Accounts: To create a group account, access the Active Directory Users and Computers console and choose the appropriate OU. Select the "New Group" option, provide a name and description for the group, and specify the group type (e.g., security or distribution). Afterwards, add the desired users to the group, either individually or by using filtering criteria, to establish the group's membership.
Note: It is crucial to align the user and group accounts with the organizational structure and access requirements. Regularly review and manage these accounts to ensure security and compliance within the Windows domain configuration.
Step 4: Customize Group Policy Configuration
Once the foundational setup of your Windows network environment is complete, it is essential to configure the Group Policy settings to ensure consistent and secure management of your domain. This step focuses on customizing the policies that govern various aspects of your network, allowing you to enforce specific rules, restrictions, and preferences across all connected devices.
Group Policy settings provide a centralized approach to managing the behavior and configuration of multiple computers and users in a Windows domain. By leveraging these settings, administrators can streamline administrative tasks, control access to resources, deploy software, enforce security measures, and maintain a standardized environment.
To configure Group Policy settings, you will utilize the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), a powerful tool that provides a comprehensive interface for managing policies. Within the GPMC, you will navigate through different policy categories, such as User Configuration and Computer Configuration, to define and customize specific settings.
Commonly customized Group Policy settings include password requirements, software installation and updates, Internet Explorer settings, folder redirection, printer management, network drive mappings, and security configurations such as firewalls and Windows Defender settings.
Group Policy settings can be applied at various levels within your domain hierarchy, allowing for different settings based on organizational units, groups, or individual users. By strategically designing these policies, administrators can efficiently manage and control the behavior of their network, ensuring compliance with company guidelines and enhancing overall system security.
Remember, when configuring Group Policy settings, it is crucial to test and validate the changes before deploying them to your entire domain. Utilize the GPMC's simulation mode to assess the impact of policy changes and identify any potential conflicts or issues that may arise.
In conclusion, configuring Group Policy settings is a paramount step in establishing an efficiently managed Windows domain. By customizing these settings, you can enforce consistent rules, streamline administrative tasks, and enhance the security and functionality of your network environment.
| Tips for Configuring Group Policy Settings: |
|---|
| 1. Regularly review and update your Group Policy settings to meet evolving security requirements and organizational needs. |
| 2. Before making changes, thoroughly document your existing Group Policy configurations to ensure a smooth transition and easier troubleshooting. |
| 3. Utilize Group Policy Preferences to grant additional customization options to users while still maintaining centralized control. |
| 4. Create separate Group Policy Objects (GPOs) for different configurations to facilitate easy management and troubleshooting. |
| 5. Regularly test newly configured Group Policy settings in a controlled environment before deploying them broadly. |
| 6. Leverage Group Policy modeling and Group Policy Results tools to analyze the impact and scope of your policies. |
Troubleshooting the Setup of a Windows Domain
In this section, we will explore the common issues that may arise during the configuration of a Windows domain, and how to effectively troubleshoot them. Understanding how to resolve these problems will ensure a smooth deployment and management of your domain infrastructure.
Identifying Connectivity Problems: One of the key challenges when setting up a Windows domain is ensuring connectivity between network devices. This step involves verifying network cables, switch configurations, and network adapter settings. With proper troubleshooting techniques, you can identify and resolve connectivity issues, enabling smooth communication within the domain.
Resolving Active Directory Replication Issues: Active Directory replication is vital for maintaining a consistent domain environment. However, replication errors can occur due to various factors such as network disconnections, DNS problems, or inconsistencies in the replicated data. By understanding the common replication issues and their resolution methods, you can ensure a reliable and up-to-date Active Directory infrastructure.
Addressing DNS Configuration Errors: DNS plays a critical role in Windows domain configuration as it facilitates name resolution and helps clients locate domain resources. Misconfigured DNS settings can lead to various domain-related problems, including authentication failures or inability to join the domain. This section will guide you through troubleshooting common DNS configuration errors and provide solutions to ensure seamless domain functionality.
Troubleshooting Group Policy Application: Group Policy is a powerful tool for managing and controlling user and computer configurations within a Windows domain. However, improper settings or conflicts can prevent the effective application of Group Policy, resulting in unexpected results. By understanding the common issues with Group Policy application and utilizing appropriate troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure that the desired policies are efficiently applied throughout the domain.
Resolving Security-related Challenges: Windows domain configuration involves implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data and infrastructure. However, issues related to permissions, access controls, or authentication can compromise the overall security of the domain. This section will cover troubleshooting methods to address common security-related challenges and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of your domain.
Note: As you troubleshoot Windows domain configuration, it is important to document the steps taken and the solutions applied. This documentation will serve as a valuable resource for future reference and assist in troubleshooting similar issues that may arise.
Resolving Common Challenges in Establishing and Managing a Windows Domain Environment

In the process of organizing an interconnected network of computers using the Windows operating system, there are various obstacles that one may encounter. This section aims to address and provide solutions to some of the most frequently encountered issues in configuring and maintaining a Windows domain setup.
1. Authentication and Access Problems
One common challenge that administrators often face in a Windows domain environment is difficulties with user authentication and access rights. This can result in users being unable to log in or access specific resources on the network. To resolve this, it is essential to ensure that the Active Directory credentials are properly synchronized across all domain controllers and that correct permissions are assigned to users and groups.
2. DNS Configuration and Name Resolution Errors
In a Windows domain, the Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in resolving domain and hostnames to IP addresses. Issues with DNS configuration can lead to problems with name resolution, causing network services and applications to malfunction. To overcome this challenge, it is vital to verify the DNS settings, configure forward and reverse lookup zones correctly, and ensure that all DNS servers within the domain are properly registered.
3. Group Policy Troubles
Group Policy is a powerful tool for managing and configuring various aspects of a Windows domain environment. However, misconfigurations or conflicts in Group Policy settings can result in unexpected behavior, inconsistent configurations, or failure to apply updates across the network. To address this, administrators should review and analyze Group Policy settings, ensure proper inheritance and precedence, and regularly test the impact of policy changes on different user groups and organizational units.
4. Replication and Synchronization Failures
In multi-domain or multi-site Windows domain configurations, replication and synchronization between domain controllers are crucial for maintaining a consistent and up-to-date directory database. Failures in replication can lead to inconsistencies, replication delays, or even data loss. To resolve such issues, administrators should monitor replication health, troubleshoot connectivity problems, and check for any DNS or firewall issues that may interfere with replication processes.
5. Security and Permissions Challenges
Establishing proper security measures and managing permissions is vital for safeguarding sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access in a Windows domain environment. However, misconfigurations or inadequate security settings can expose the network to potential risks. To mitigate these challenges, administrators should regularly review and update security policies, conduct proper access control and permission audits, and implement proper security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption.
By understanding and addressing these common challenges in configuring and managing a Windows domain environment, administrators can ensure a stable, secure, and efficient network infrastructure.
Tips for Efficient Management of a Windows Domain
Enhance your productivity: Discover effective strategies to optimize your workflow and streamline daily operations within your Windows Domain environment. By implementing these tips, you can improve the overall efficiency and organization of your domain management tasks.
Stay organized: Maintain a structured approach by categorizing and labeling your resources, such as users, groups, and organizational units. Utilize naming conventions and logical hierarchies to ensure easy navigation and quick access to essential components within your domain.
Implement security measures: Safeguard your Windows Domain by implementing robust security practices. Enforce strong password policies, regularly update and patch systems, and utilize appropriate access controls to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Automate administrative tasks: Simplify your daily administrative tasks by leveraging automation tools and scripts. Implementing automation not only reduces potential human errors but also frees up your time to focus on more critical tasks that require your expertise.
Regularly monitor and update: Stay proactive by consistently monitoring the health and performance of your Windows Domain infrastructure. Regularly review event logs, monitor resource usage, and apply necessary updates and patches to ensure optimal performance and secure operations.
Train and empower your team: Invest in your team's skills and knowledge by providing regular training sessions and resources to keep them updated on the latest domain management practices. Empowering your team members will foster a collaborative and efficient working environment.
Backup and disaster recovery strategies: Develop robust backup and disaster recovery plans to prevent data loss or system failures. Regularly perform backups of critical data and test your recovery procedures to ensure quick and seamless restoration in case of any unplanned events.
Continuously evaluate and optimize: Regularly assess your domain configuration, processes, and workflows to identify areas for improvement. Implement continuous improvement strategies to optimize and refine your domain management practices, allowing for better performance and efficiency over time.
Keep up with industry trends: Stay informed about the latest technologies, trends, and best practices related to Windows Domain management. Continuous learning and adaptation will help you stay at the forefront of domain management, ensuring you can effectively address evolving challenges and pursue innovation.
Collaborate and network: Engage with other domain administrators and IT professionals through networking events, forums, and online communities. Establishing connections with peers will enable knowledge sharing, problem-solving, and access to valuable insights from others' experiences.
Note: Implementing these tips will not only streamline your Windows Domain management processes but also contribute to a secure, efficient, and well-organized environment for your organization.
Setup Active Directory, Domain Controller, Configure DNS, DHCP and Join Computers to Domain
Setup Active Directory, Domain Controller, Configure DNS, DHCP and Join Computers to Domain 作成者: Kindson The Tech Pro 121,272 回視聴 3 年前 40 分
Active Directory: Episode 2 - Joining a computer to a domain
Active Directory: Episode 2 - Joining a computer to a domain 作成者: Professor Andrew 32,597 回視聴 3 年前 18 分
FAQ
What is Windows Domain Configuration?
Windows Domain Configuration is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows multiple computers to be connected and managed centrally under a single domain. It enables administrators to control user access, security policies, and network resources efficiently.
How can I set up Windows Domain Configuration?
To set up Windows Domain Configuration, you need to have a Windows Server installed. Then, you can follow step-by-step guidelines provided by Microsoft to configure active directory, promote the server to a domain controller, and connect client computers to the domain.
What are the benefits of setting up Windows Domain Configuration?
Setting up Windows Domain Configuration offers several benefits. It centralizes user administration, simplifies security management, allows for efficient resource sharing, enhances network performance, provides better data security, and simplifies the deployment of software updates and configurations.
Can I set up Windows Domain Configuration on non-Windows operating systems?
No, Windows Domain Configuration is a feature specific to Microsoft Windows operating systems. It cannot be directly set up on non-Windows systems. However, some cross-platform solutions exist that can provide similar functionalities across different operating systems.
What happens if the domain controller in Windows Domain Configuration fails?
If the domain controller fails in a Windows Domain Configuration setup, it can cause disruption in user access, security policies, and resource management. To minimize the impact, it is crucial to have backup domain controllers and a proper disaster recovery plan in place to restore the functionality swiftly.
What is Windows Domain Configuration?
Windows Domain Configuration is the process of setting up and managing a centralized network environment using Windows Server and Active Directory. It allows administrators to manage user accounts, security settings, and resources in a more organized and secure manner.




