When it comes to safeguarding your valuable data, nothing is more crucial than having a reliable backup strategy in place. Whether you are an individual user or a small business owner, the significance of a comprehensive data backup system cannot be overstated. By implementing a robust backup solution, you can mitigate the risks associated with unexpected data loss, hardware failures, and security breaches.
Today, we delve into the realm of system data protection and explore the intricacies of setting up Windows' efficient data backup feature. By following our step-by-step guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to establish a solid backup routine tailored to your needs, without relying on costly third-party solutions.
Unforeseen circumstances can strike at any given moment, be it malicious software infiltrating your system or an accidental file deletion. Without a reliable backup solution, you are left to deal with the devastating consequences of data loss. However, by taking advantage of Windows' built-in backup capabilities, you can effortlessly create a protective safety net for your critical files and folders.
Join us as we unravel the intricacies of Windows Server Backup and empower you to secure your system data effectively!
A step-by-step guide to setting up an efficient data backup system
Creating a reliable and effective data backup system is essential for any organization's smooth functioning. This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of configuring a robust data backup solution on your Windows Server, ensuring the safety and integrity of your crucial information.
- Gather the necessary hardware and software: Before beginning the configuration process, ensure that you have the required hardware components such as external storage devices or network-attached storage (NAS) systems. Additionally, make sure that your Windows Server operating system is up to date.
- Assess your backup requirements: Analyze your organization's data storage needs and determine the frequency and type of backups required. Consider factors such as the size of your data, the rate of data change, and the retention period.
- Select the appropriate backup method: Windows Server offers various backup options, including full, incremental, and differential backups. Evaluate your specific needs and choose the most suitable method to optimize both storage space and time.
- Configure backup settings: Access the Windows Server Backup utility and set up a backup schedule that aligns with your business requirements. Define the source data, destination location, and any specific exclusions or inclusions.
- Implement a disaster recovery plan: To ensure complete preparedness, develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan. Regularly test your backup system and keep multiple copies of your backups in different locations for enhanced security.
- Monitor and maintain the backup system: Continuously monitor the backup operation to identify any potential issues or failures. Regularly review the backup logs and perform maintenance tasks, such as cleaning up outdated backups or upgrading storage devices.
By following this step-by-step guide, you will be able to configure a robust and efficient data backup system on your Windows Server, safeguarding your organization's critical information from potential loss or corruption.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Windows Server Backup
In this section, we will explore the underlying principles and essential concepts of Windows Server Backup. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals, you will be better equipped to effectively utilize this powerful data protection tool.
Defining the Essence: Windows Server Backup is a vital solution for safeguarding critical data on Windows-based servers. It offers a comprehensive set of functionalities that enable the creation and maintenance of reliable backups, ensuring the continuous availability of essential information.
Key Components: To grasp the essence of Windows Server Backup, it is important to familiarize yourself with its primary components. These include the backup schedule, which determines the frequency and timing of backup operations, and the backup storage location, where the backed-up data is stored securely.
Working Principles: Windows Server Backup operates based on the principle of creating a full backup followed by incremental backups. Initially, a complete snapshot is taken to capture all the data. Subsequently, incremental backups record only the changes made since the last full or incremental backup, significantly reducing the time and storage required.
Ensuring Data Integrity: Data integrity is a paramount aspect of any backup strategy. Windows Server Backup implements various mechanisms to guarantee the reliability and consistency of backed-up data, including the utilization of shadow copies and the validation of backups for errors or corruption.
Utilization and Benefits: Understanding the basics of Windows Server Backup empowers you to leverage its capabilities to successfully protect vital data. By implementing a reliable backup strategy, you can minimize the risk of data loss, enhance business continuity, and ensure the swift restoration of critical information in the event of system failures or disasters.
By delving into the core concepts and principles of Windows Server Backup, you can harness its potential to safeguard your valuable data effectively.
Exploring the features and advantages of Windows Server Backup

In this section, we will delve into the various attributes and benefits offered by the Windows Server Backup tool for efficient data protection and recovery. By understanding the capabilities of this powerful feature, users can enhance their backup and restore strategies while ensuring the reliability and integrity of their Windows environment.
- Comprehensive Data Protection: Windows Server Backup provides a robust solution to safeguard critical information, including files, folders, applications, and system settings. This comprehensive approach ensures that every aspect of your Windows server environment is protected from unexpected data loss or corruption.
- Flexible Scheduling Options: With a range of scheduling options, users can easily configure Windows Server Backup to perform regular backups based on their specific requirements. Whether it is daily, weekly, or monthly backups, the tool offers flexibility to accommodate diverse business needs.
- Incremental and Differential Backups: Windows Server Backup offers the choice between incremental and differential backups, allowing users to optimize storage utilization and minimize backup time. Incremental backups capture only changes made since the last backup, while differential backups save changes made since the last full backup.
- Bare Metal Recovery: One of the standout features of Windows Server Backup is its ability to perform bare metal recovery. This means that in the event of a system failure or disaster, the tool can restore not only individual files but also the entire Windows server environment, including the operating system, system state, and application settings.
- Integration with Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS): Windows Server Backup seamlessly integrates with VSS, allowing for the creation of shadow copies of selected volumes. These shadow copies provide a point-in-time snapshot of the data, ensuring consistency and accuracy during the backup process, even when files are in use.
By harnessing the features and advantages offered by Windows Server Backup, IT administrators can implement a comprehensive backup strategy that addresses their specific needs. From robust data protection and flexible scheduling options to bare metal recovery capabilities, this tool provides a reliable and efficient solution for safeguarding critical data and ensuring the continuity of Windows server environments.
Preparing Your System for Windows Server Backup
In this section, we will discuss the necessary steps that need to be taken to ensure your system is ready for Windows Server Backup. These preparations are essential to ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of the backup process.
| 1. Verify System Compatibility |
| Before proceeding with the configuration of Windows Server Backup, it is crucial to verify that your system meets the necessary requirements. This includes checking hardware compatibility, disk space availability, and the supported operating system version. |
| 2. Install the Required Services |
| Ensure that all the relevant services required for Windows Server Backup are installed and running properly. This may include services such as Volume Shadow Copy, Block-Level Backup Engine, and Windows Server Backup Service. |
| 3. Allocate Sufficient Storage Space |
| Before starting the backup process, make sure you have allocated enough storage space to accommodate the backup data. Analyze your storage needs and ensure that the designated backup location has adequate free space. |
| 4. Check Backup Media Availability |
| If you are using external backup media such as external hard drives or network shares, it is essential to verify their availability and connectivity to your system. Ensure that the media is properly connected and accessible. |
| 5. Test System Reliability |
| Perform system tests to ensure the overall reliability and stability of your system. This can include checking for hardware issues, analyzing system logs, and running diagnostic tools to identify any potential problems that may interfere with the backup process. |
By following these preparations, you can ensure that your system is fully prepared and optimized for the Windows Server Backup process. Taking the time to verify compatibility, install required services, allocate sufficient storage space, check backup media availability, and test system reliability will help in avoiding any potential issues and ensure a successful backup operation.
Ensuring system compatibility and meeting prerequisites
In order to successfully implement and utilize the backup functionality within your operating environment, it is imperative to ensure that your system meets the necessary requirements and prerequisites. By guaranteeing compatibility and preparing your system accordingly, you can maximize the effectiveness and reliability of the Windows backup solution.
To begin, it is essential to verify that your hardware and software components align with the recommended specifications for Windows Server Backup. This includes evaluating the compatibility of your server's processor, memory, and storage capabilities. Additionally, you must assess the version and edition of Windows you are running to ensure compatibility with the backup feature.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider any necessary updates or patches that may be required for your operating system and related software. Keeping your system up to date with the latest service packs and security updates is paramount to guaranteeing a seamless and efficient backup process.
Another factor to be mindful of is the availability and allocation of sufficient storage space for storing backup copies. Adequate disk space is necessary to accommodate the size of the intended backups and ensure their successful completion. It is recommended to have a dedicated disk or partition solely for backups, minimizing the risk of data fragmentation and improving performance.
Lastly, prior to configuring Windows Server Backup, it is advisable to validate that the necessary privileges and permissions are in place. Ensuring that the user account being used has the appropriate administrative rights and access permissions will prevent any potential issues during the backup process.
Setting up Windows Server Backup
When it comes to ensuring the security and integrity of your data, installing a reliable backup solution is paramount. In this section, we will explore the process of setting up Windows Server Backup, a robust tool designed to safeguard your important files and folders.
Step 1: Launching Windows Server Backup
To begin the installation process, open the Windows Server Backup application, which can be accessed through the Start menu or by searching for "Windows Server Backup" in the search bar. Once launched, you will be presented with the main interface of the application.
Step 2: Selecting the Backup Destination
Before you can begin creating backups, you need to specify where the backup files will be stored. Click on the "Backup Schedule" option in the navigation pane, followed by "Configure Backup" in the Actions pane. Here, you can choose between various backup destinations, such as an external hard drive, a network share, or even a dedicated backup drive.
Step 3: Choosing the Backup Configuration
Once you have selected the backup destination, you can proceed to configure the backup settings. You can choose to create a full server backup, which includes all files and folders on your system, or opt for a custom backup where you can select specific data to be included in the backup. Additionally, you can set a backup schedule, choosing whether the backups should run automatically or on a specified time and date.
Step 4: Confirming the Backup Selections
After selecting the desired backup configuration, review the summary of your selections to ensure they are accurate. If everything appears correct, click on the "Backup" button to initiate the backup process. Windows Server Backup will now begin creating regular backups based on your specified settings, providing you with peace of mind knowing that your data is protected.
Note: It is recommended to periodically test the backups to ensure they can be successfully restored in the event of data loss.
By following these steps, you can easily install and set up Windows Server Backup, giving you a reliable solution for safeguarding your valuable data.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting up Windows Server Backup
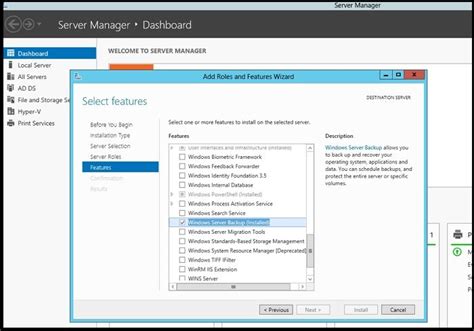
In this section, we will guide you through the installation process of a reliable backup solution for your Windows server environment.
- Preparing for installation
- Verification of system requirements
- Download and installation of necessary software
- Configuration of backup settings
- Testing and validation of backup functionality
Before diving into the installation process, it is important to ensure that your system meets the necessary prerequisites for a successful backup implementation. Verification of system requirements ensures compatibility and prevents any potential issues down the line.
Once you have confirmed your system meets the requirements, you can proceed with downloading and installing the appropriate backup software. This step may involve selecting the specific version and architecture that best suits your server environment.
After the installation is complete, you can begin configuring the backup settings. This includes selecting the data and files you wish to back up, defining the backup schedule, and specifying the storage location for your backups.
Once your backup settings are configured, it is crucial to perform tests and validate the functionality of your backups. This step ensures that your backup solution is working as intended and provides peace of mind knowing that your data is protected.
By following this step-by-step guide, you will be able to successfully install and configure a Windows Server Backup solution tailored to your specific server environment, safeguarding your important data and ensuring business continuity.
Setting up Backup Schedule with Windows Server Backup
In this section, we will explore the process of establishing a backup schedule using Windows Server Backup, ensuring the preservation of vital data and system configurations. By establishing a well-thought-out backup schedule, you can safeguard your important files, applications, and settings, minimizing the risk of data loss and system failures.
Step 1: Defining Backup Frequency
Begin by determining how often you want your backups to occur. Consider the criticality of the data and the frequency of changes made. You can choose to perform daily, weekly, or monthly backups.
Step 2: Selecting Backup Type
Decide on the backup type that suits your requirements. Windows Server Backup provides options for full backups, which capture the entire data set, or incremental backups, which only back up the changes made since the last backup. Consider the trade-offs between storage space usage and restoration time.
Step 3: Configuring Backup Destination
Specify the destination where your backups will be stored. This could be an external hard drive, a network location, or even dedicated backup storage drives. Ensure that the chosen storage solution has ample capacity to accommodate your backup needs.
Step 4: Setting Backup Start Time
Choose a suitable time for your backup process to commence. Consider periods of low system activity to minimize any impact on the server's performance.
Step 5: Verifying Backup Success and Monitoring
Regularly check the backup logs to ensure successful completion of backups and monitor for any errors or warnings. Investigate and resolve any issues promptly to maintain the integrity of your backup schedule.
By following these steps, you can confidently establish a backup schedule tailored to your distinct needs using Windows Server Backup. This proactive approach will help safeguard crucial data, ensuring system reliability and preparedness for any unexpected events.
Creating Automated Backup Schedules for Your Server

In this section, we will discuss the process of setting up automated backup schedules for your server, ensuring that your data remains secure and accessible at all times. By configuring regular backup routines, you can minimize the risk of data loss and simplify the management of your server.
Step 1: Define the Frequency - Determine how often you want your server to perform backups. This could be daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the specific needs of your organization. It is important to strike a balance between the frequency of backups and the impact it may have on server performance.
Step 2: Select the Backup Destination - Choose a reliable location to store your backups. This can be an external hard drive, network attached storage (NAS), or a remote location using cloud backup services. Consider factors such as capacity, accessibility, and redundancy when making this decision.
Step 3: Configure Backup Settings - Define the specific settings for your automated backup schedule. This includes selecting the data and directories to be backed up, setting compression and encryption options, and deciding whether to include system state data and application-specific files. Take into account any regulatory or compliance requirements that your organization may have.
Step 4: Set the Backup Time - Specify the exact time when the automated backup will run. It is advisable to schedule backups during off-peak hours to minimize any impact on server performance. Additionally, consider the availability of resources, such as network bandwidth, during the chosen backup time.
Step 5: Monitor and Test - Regularly monitor and review the backup logs to ensure that the scheduled backups are running successfully. Conduct restore tests periodically to validate the integrity of your backed-up data and verify the effectiveness of your automated backup processes.
By following these steps, you can establish automated backup schedules for your server, promoting data protection and enabling swift recovery in the event of any unforeseen circumstances or system failures.
Selecting Backup Destination in Windows Server Backup
In this section, we will explore the process of choosing the storage location for your backups in the Windows Server Backup tool. The backup destination plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and accessibility of your backup data. By selecting an appropriate backup destination, you can safeguard your important files and ensure they are readily available in case of data loss or system failure.
When configuring the backup destination, Windows Server Backup provides several options to cater to different storage requirements. These options include selecting a local disk, a network shared folder, or a dedicated external hard drive. Each choice has its own advantages and considerations, allowing users to tailor their backup strategy to meet their specific needs.
| Backup Destination Options | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Local Disk | Provides fast backup and recovery times. Ideal for small-scale environments. |
| Network Shared Folder | Allows for centralized backup storage and easy accessibility across multiple devices. |
| External Hard Drive | Offers portability and offline storage for added data protection. Suitable for off-site backups. |
Before selecting a backup destination, it is crucial to evaluate your storage requirements, available resources, and recovery objectives. Additionally, considering factors such as security, reliability, and scalability can help you choose the most suitable backup destination.
Once you have determined the appropriate backup destination option for your needs, Windows Server Backup provides a straightforward interface to guide you through the selection process. By following the provided prompts and ensuring proper permissions and connectivity, you can successfully configure Windows Server Backup to store your backups in the desired destination. This ensures the safety and accessibility of your important data, giving you peace of mind in the event of data loss or system failure.
Choosing the Appropriate Storage Location for Safeguarding Your Critical Data

When it comes to securing your important data, one of the key considerations is selecting an optimal storage location for your server backups. The storage location you choose can greatly impact the accessibility, security, and recoverability of your backed-up information. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the available options and make an informed decision that aligns with your specific backup needs.
Firstly, it is essential to assess the level of security required for your server backups. Depending on the sensitivity and confidentiality of your data, you may opt for an on-premises storage solution, such as local disk drives or network-attached storage (NAS) devices. On-premises storage provides direct control over your data and minimizes potential risks associated with external access. Alternatively, you might consider utilizing cloud storage, which offers advanced security measures like encryption and multi-factor authentication, ensuring that your backups remain protected even in the event of local hardware failures or disasters.
Another factor to consider is the scalability and accessibility of your chosen storage location. If you anticipate a continuous growth of data volume over time, opting for a scalable solution is vital. Cloud-based storage options often provide virtually limitless capacity, allowing you to expand your backup storage as your needs evolve. Moreover, cloud storage ensures easy accessibility from any location with an internet connection, enabling seamless data recovery and backup management.
Furthermore, the geographic location of your storage choice plays a significant role in disaster recovery scenarios. Consider selecting a geographically distant location for storing your backups to minimize the risk of losing data in case of a localized disaster, such as fire or flood. This redundancy strategy enhances the overall resilience of your backup system and guarantees swift recovery without compromising critical information.
In conclusion, choosing the right storage location for your server backups is crucial for maintaining the security, accessibility, and recoverability of your important data. By evaluating factors such as security requirements, scalability, accessibility, and geographic redundancy, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your organization's specific backup needs and ensures the protection of your critical information.
Customizing Backup Options for Windows Server Backup
When it comes to tailoring the settings and preferences for your Windows Server Backup, there are a multitude of options available to suit your specific needs. By customizing the backup options, you can optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of your backup process, ensuring the safety and security of your important data.
- Configuring Backup Schedule: You have the flexibility to specify the frequency and timing of your backups, whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly. Additionally, you can choose to run backups at specific times or during specific intervals to avoid any disruptions to your workflow.
- Selecting Backup Type: Depending on your requirements, Windows Server Backup offers different backup types, such as full, differential, or incremental backups. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, allowing you to decide the level of data protection needed and the duration of the backup process.
- Customizing File and Folder Exclusions: To efficiently utilize storage space and reduce backup times, you can exclude certain files or folders that are not critical for your backup. This enables you to prioritize important data and avoid unnecessary duplication.
- Setting Backup Compression: Compressing your backup files can significantly reduce storage space requirements and improve backup speed. By choosing an appropriate compression level, you can strike a balance between storage efficiency and backup performance.
- Enabling VSS and Additional Options: Windows Server Backup leverages Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to create consistent backups of open and locked files. Enabling VSS ensures the integrity of your backups and allows for seamless restores. Furthermore, you can explore additional options such as custom notifications and logging to enhance your backup management capabilities.
By customizing these backup options in Windows Server Backup, you can tailor the backup process to meet your specific needs and ensure the safeguarding of your valuable data. Take advantage of the flexibility and features available to optimize your backup strategy and minimize any potential data loss risks.
FAQ
What is Windows Server Backup in Windows and why should I configure it?
Windows Server Backup is a feature in Windows that allows you to backup and restore your server data. Configuring it is important because it helps in ensuring the safety and availability of your data in case of any unforeseen events or data loss.
How can I configure Windows Server Backup in Windows?
To configure Windows Server Backup in Windows, you need to go to the "Server Manager" and then select "Add Roles and Features" option. From there, you can follow the on-screen instructions to enable and configure the Windows Server Backup feature.
Can I schedule backups using Windows Server Backup?
Yes, you can schedule backups using Windows Server Backup. After configuring the backup settings, you can set a specific date, time, and frequency for the backups to automatically take place. This ensures that your data is backed up regularly without manual intervention.
Does Windows Server Backup support backup encryption?
Yes, Windows Server Backup supports backup encryption. You can choose to enable encryption while configuring the backup settings. This adds an extra layer of security to your backups, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the backed-up data.
Can I restore individual files from a Windows Server Backup?
Yes, you can restore individual files from a Windows Server Backup. The backup utility allows you to browse and select specific files or folders that you want to restore, making it easy to recover specific data without needing to restore the entire backup.
What is Windows Server Backup?
Windows Server Backup is a feature in Windows Server that allows users to perform backups and recovery of their server's data.




