Discover the seamless process of configuring a robust system to allocate IP addresses dynamically with utmost precision and efficiency. This comprehensive guide will take you on a journey through the intricacies of establishing a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server on your Windows-based operating system, ensuring uninterrupted network connectivity without the hassle of manual configuration.
Unlock the potential of your network infrastructure as we delve into the detailed steps involved in setting up a DHCP server, bestowing your network with the power of automatic IP address assignment. Eliminate the complexities of managing IP address allocations manually, streamlining your network administration tasks and empowering your organization's IT department with enhanced control and agility.
Unleash the inherent capabilities of your Windows Server as you join us in exploring the ins and outs of configuring a DHCP server. From understanding the underlying principles of dynamic IP address allocation to implementing a scalable solution tailored to your organization's specific needs, this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap, forcing the boundaries of what your network infrastructure can truly achieve.
Dive into the vast sea of IP address management, equipped with the knowledge to effortlessly configure a DHCP server on your Windows-based system. Maximize the potential of your network, ensuring seamless connectivity, reduced administrative overhead, and the flexibility to adapt effortlessly to changes. Embark on this immersive journey towards efficient network management, where technology merges with simplicity, resulting in an unparalleled user experience.
Understanding the Functionality of a DHCP Server
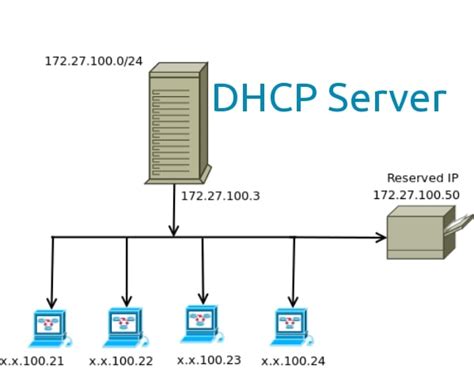
A DHCP server is a vital component in computer networking that enables the automatic assignment of IP addresses and network configuration settings to client devices within a network. This server operates as a central hub that efficiently manages the distribution of network resources to various devices, ensuring smooth communication and seamless connectivity.
The operation of a DHCP server revolves around the concept of leasing. When a client device joins a network, it sends a DHCP discovery message, seeking an available IP address. The DHCP server responds with an offer, providing an IP address and other configuration details, such as subnet mask, DNS servers, and default gateway. The client device then requests the offered IP address, which the server acknowledges and assigns as a lease for a specific duration.
By dynamically allocating IP addresses, a DHCP server eliminates the need for manual configuration, making it ideal for large-scale networks. It simplifies the administration process by providing a centralized platform for managing IP address assignment, reducing human errors and ensuring efficiency. Additionally, a DHCP server enables the easy scalability of networks, accommodating new devices without the hassle of manual IP address allocation.
A DHCP server utilizes a pool of available IP addresses, which can be customized based on the network's requirements. It keeps track of assigned addresses and their lease durations, ensuring that IP addresses are efficiently managed and avoid conflicts. This table-like organization of IP addresses and lease information ensures efficient delivery of network resources to client devices, promoting a smooth and seamless network experience.
| Advantages of a DHCP Server | Disadvantages of a DHCP Server |
|---|---|
|
|
Setting Up a Windows Server
In this section, we will explore the process of configuring and preparing a Windows Server for various tasks and functionalities. We will delve into the fundamental steps required to establish a stable and reliable server environment.
Ensuring the smooth operation of a Windows Server involves a series of crucial actions that lay the foundation for an efficient and secure system. By carefully organizing the server, configuring the necessary services, and implementing appropriate security measures, you can optimize the server's performance and enhance productivity.
Throughout this section, we will cover various aspects of setting up a Windows Server, including fundamental configurations, network settings, user management, and system optimization. By following these guidelines, you will be able to establish a robust server environment tailored to your specific requirements.
Key steps:
- Initial Setup: Explore the necessary initial configurations required to ensure a smooth server deployment.
- Network Configuration: Configure network settings and establish connectivity to enable communication within the server environment.
- User Management: Learn how to create and manage user accounts with different privileges to ensure secure access to server resources.
- Service Configuration: Configure essential services and applications on your Windows Server to support various functionalities.
- System Optimization: Implement optimization techniques to enhance server performance, reliability, and security.
By following these step-by-step instructions, you will be equipped with the necessary knowledge to set up a functional Windows Server. Establishing an efficient server environment is essential for organizations to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and maximize productivity.
Configuration of DHCP Role on the Microsoft Server Platform
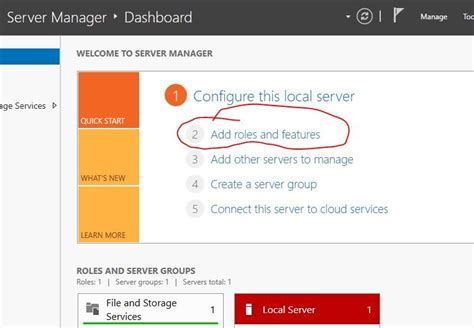
Introduction: This section aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the process involved in configuring the DHCP role on the Microsoft Server platform. By utilizing this role, administrators can effectively manage and allocate IP addresses dynamically within a network, ensuring efficient connectivity for all connected devices.
Role of DHCP: The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) plays a vital role in simplifying the network administration process by automating the assignment of IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other network parameters to client devices. Through the DHCP role, network administrators can streamline IP address assignment, minimize manual configuration efforts, and enhance network efficiency.
Overview of Configuration Steps: Configuring the DHCP role on the Microsoft Server platform involves a series of well-defined steps to ensure smooth operation. This section will guide you through each step, highlighting the significance of individual settings and options available within the DHCP configuration process.
Exploration of DHCP Configuration Options: This subsection will delve into the various configuration options available within the DHCP role, such as scope configuration, reservation setup, lease duration adjustment, DNS and WINS integration, and much more. Understanding the functionalities and customization aspects of these configuration options is crucial for creating a DHCP server tailored to your specific network requirements.
Best Practices for DHCP Role Configuration: In this segment, we will discuss the best practices that system administrators should adhere to when configuring the DHCP role. Whether it involves segregating scopes, implementing redundancy, or securing the DHCP server, following these recommendations can ensure a robust and reliable DHCP infrastructure.
Verification and Troubleshooting: Verifying the successful configuration of the DHCP role is vital for ensuring the correct functioning of the network. This subsection will guide you on how to verify the DHCP server's operation, troubleshoot common configuration issues, and interpret DHCP server logs to diagnose potential problems.
Conclusion: This section concludes the segment on configuring the DHCP role on the Microsoft Server platform. By following the step-by-step guidelines and understanding the various customization options, network administrators can effectively set up and manage a DHCP server that optimizes IP address assignment and enhances overall network performance.
Managing DHCP Server Configuration
In this section, we will explore the process of configuring the essential settings for the DHCP server. These settings enable the server to allocate dynamic IP addresses, assign network configuration parameters, and manage the allocation of IP addresses efficiently within the network.
Firstly, we will examine the configuration options to define the IP address range. This range determines the pool of available IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to network devices. Additionally, we will discuss the subnet mask, which defines the network's size and aids in organizing IP addresses into logical groupings.
Next, we will delve into the configuration of lease duration, which specifies the length of time that the DHCP server will allocate an IP address to a client. By setting an appropriate lease duration, network administrators can ensure efficient usage of IP addresses and maintain a balance between address availability and efficient address allocation.
Additionally, we will explore the configuration of DNS (Domain Name System) and WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) servers. These servers play a vital role in translating domain names into IP addresses and resolving names within the network. Proper configuration of DNS and WINS servers within the DHCP server settings ensures seamless communication and accessibility within the network.
Lastly, we will discuss the utilization of reservation options provided by the DHCP server. These options allow network administrators to assign specific IP addresses to particular devices based on their MAC addresses. By leveraging reservations, organizations can ensure that critical network devices always receive the same IP address, simplifying network management and troubleshooting.
By carefully configuring these DHCP server settings, network administrators can establish a robust and efficient network infrastructure that dynamically allocates and manages IP addresses, resolves domain names, and ensures optimal network performance.
Configuring IP Address Range and Lease Duration
In the process of establishing a network connection, it is crucial to determine the range of available IP addresses and the duration for which these addresses will be assigned. This section delves into the configuration of the IP address range and lease duration, providing essential factors to consider.
Defining IP Address Range: The IP address range refers to the range of possible IP addresses that can be allocated by the DHCP server. This range is typically defined as a starting IP address and an ending IP address. By specifying a specific range, the DHCP server ensures that the assigned IP addresses fall within the defined limits.
Setting Lease Duration: The lease duration specifies the length of time for which the DHCP server assigns a particular IP address to a client device. It determines how long the client device can retain the assigned IP address without the need for renewal. Lease durations can be set for different time intervals, such as hours, days, weeks, or even longer periods, depending on the network requirements.
Choosing Optimal IP Address Range: Selecting the appropriate IP address range is crucial to prevent IP address conflicts and ensure efficient allocation. Considerations include the number of network devices, potential growth, and the subnet mask used within the network. It is advisable to assign a range that is large enough to accommodate the current and future devices while avoiding unnecessary wastage of IP addresses.
Optimizing Lease Durations: The lease duration should be carefully chosen to balance network efficiency and IP address availability. Shorter lease durations allow for quick reallocation of IP addresses and adaptability to changing network conditions. On the other hand, longer lease durations reduce administrative overhead and ensure consistent IP address assignment for devices with stable connections.
Considering Network Requirements: When configuring the IP address range and lease duration, it is crucial to consider the specific needs of the network. Factors such as the number of users, device mobility, and network security requirements play a vital role in determining the optimal settings. Regular assessments of these requirements ensure that the DHCP server is effectively meeting the network's demands.
By understanding the process of configuring the IP address range and lease duration, network administrators can establish a DHCP server that efficiently manages and allocates IP addresses within the network.
Managing DHCP Network Configuration
In this section, we will explore the process of creating a customized network configuration using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) on a Windows Server. By creating a DHCP scope and configuring the relevant options, you can efficiently allocate IP addresses and provide specific network settings to clients within your network.
Defining DHCP Scope
To start, we will define a DHCP scope, which determines the range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to clients. This includes specifying the starting and ending IP addresses, as well as the subnet mask and default gateway for the network.
For optimal network management, it is essential to carefully plan and allocate IP addresses within the scope, ensuring that they do not overlap with any existing static or reserved IP addresses.
Configuring DHCP Options
Additionally, we will explore the configuration of DHCP options, which provide clients with specific network settings such as DNS servers, domain names, and time servers. These options can be customized based on the requirements of your network infrastructure.
By properly configuring DHCP options, you can streamline the process of network configuration for clients, eliminating the need for manual configuration and ensuring consistent settings across the network.
Managing Network Configurations and DNS Parameters
Configuring a dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) server involves specifying network parameters and setting up domain name system (DNS) settings. This section will provide detailed instructions on managing network configurations and DNS parameters to ensure seamless communication within your network.
Firstly, it is crucial to define the network parameters, such as the IP address range, subnet mask, and default gateway. These settings are essential for proper network segmentation and efficient routing of data packets. By configuring these parameters accurately, you can ensure that each device on your network receives a unique IP address and can connect to other devices seamlessly.
In addition to network configurations, setting up DNS parameters is vital for name resolution within your network. The DNS settings determine how domain names are translated into IP addresses, enabling users to access websites, servers, and other network resources through user-friendly domain names. By properly configuring DNS settings, you can ensure that your network's devices can communicate with each other using human-readable domain names.
When specifying network parameters, it is important to consider factors such as network scalability, security, and compatibility with existing network infrastructure. Likewise, while setting up DNS settings, you need to define primary and secondary DNS servers, configure forward and reverse lookup zones, and ensure proper DNS record management.
By understanding the importance of managing network configurations and DNS parameters, you can effectively set up a DHCP server that enhances network performance, simplifies network administration, and provides a reliable and efficient network infrastructure for your organization.
configure DHCP Server on windows server 2016
configure DHCP Server on windows server 2016 来自Angkor Sokhom 53,968次观看 8年前 9分钟56秒钟
FAQ
How do I set up a DHCP server on Windows Server?
To set up a DHCP server on Windows Server, you need to follow several steps. First, open the Server Manager and click on "Add Roles and Features". Then, select the DHCP Server role and proceed with the installation. Once installed, open the DHCP console and right-click on "IPv4" or "IPv6" and select "New Scope". Follow the wizard to configure the scope settings. Finally, authorize the DHCP server in Active Directory. Detailed instructions can be found in the article.
What are the benefits of setting up a DHCP server on Windows Server?
There are several benefits of setting up a DHCP server on Windows Server. Firstly, it simplifies the network administration process by automatically assigning IP addresses to devices. This eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration, saving time and reducing the chance of configuration errors. Secondly, a DHCP server allows for centralized management and configuration of IP addresses, making it easier to make changes or updates to the network. Additionally, DHCP provides options for automatic DNS registration and other advanced settings that enhance network functionality.
Can I configure multiple DHCP servers on Windows Server?
Yes, it is possible to configure multiple DHCP servers on Windows Server. However, it is important to ensure that each DHCP server has non-overlapping scope ranges to avoid IP address conflicts. By setting up multiple DHCP servers, you can achieve redundancy and load balancing, allowing for uninterrupted DHCP service in case one server fails. It is recommended to use DHCP failover feature available in Windows Server to achieve this. The article provides step-by-step instructions on how to configure multiple DHCP servers.




