When it comes to computer operating systems, there exists a fascinating variety of choices available to individuals. Two of the most prominent contenders in this realm are the Windows and MacOS operating systems. While each offers its own unique set of features and functionalities, it is their fundamental differences that truly distinguish one from the other.
The Windows operating system, developed by Microsoft, stands as a stalwart of the computing world. Renowned for its widespread compatibility and extensive software support, Windows has become the go-to choice for many users. On the other hand, the MacOS operating system, designed by Apple Inc., has garnered a reputation for its sleek and intuitive interface, as well as its seamless integration with Apple's hardware offerings.
With these key characteristics in mind, exploring the distinctions between Windows and MacOS offers valuable insights into the choices available to consumers. From the subtle nuances of user interface design to the varying levels of customization and control, understanding the unique qualities of each system can empower individuals to make informed decisions based on their personal preferences and needs.
The Architecture of Windows and MacOS Operating Systems

When it comes to understanding the inner workings of the two primary operating systems in the computing world, it is important to delve into the intricate architectural design of both Windows and MacOS. By examining the underlying structures and frameworks of these operating systems, we can gain insights into their functionalities and differences, as well as appreciate the unique approaches each one takes in delivering a seamless user experience.
In order to comprehend the architecture of Windows and MacOS, it is crucial to explore their respective foundational elements. Windows operating system revolves around a modular structure, where different components work independently but coordinate with one another to ensure overall system functionality. On the other hand, MacOS boasts a layered architecture, with distinct layers working in harmony to provide a streamlined and secure operating environment.
- Windows Architecture:
- Kernel: The core component that handles low-level tasks such as memory management, process scheduling, and device drivers.
- File System: Controls how files are stored, organized, and accessed on the disk.
- Hardware Abstraction Layer: Acts as an intermediary layer between the hardware and the operating system, allowing for easier hardware compatibility.
- API: Provides a set of functions and tools for developers to create applications that run on Windows.
- MacOS Architecture:
- Mach Kernel: The central component that manages tasks such as memory management, multi-threading, and inter-process communication.
- System Frameworks: Collections of libraries and interfaces that provide higher-level functionalities and services to applications.
- Core Services Layer: Offers essential system services, including file management, networking, and security.
- Application Layer: The topmost layer where user applications, such as web browsers and media players, interact with the underlying system.
While Windows and MacOS differ in their architectural approaches, they both aim to provide stability, security, and user-friendliness. Understanding the underlying structures of these operating systems not only enhances our knowledge of their unique features but also helps us make informed choices when selecting the most suitable operating system for our computing needs.
Understanding the Core Distinctions in System Architecture
Apprehending the fundamental dissimilarities in the inner framework of the Windows and MacOS operating systems is indispensable for comprehending their divergent functionalities. While both systems carry out comparable tasks, each employs a distinct underlying structure that governs its operations. This section expounds upon the key disparities in their system architectures, shedding light on the distinctive principles that guide their operation.
An In-depth Comparison of Kernel Designs
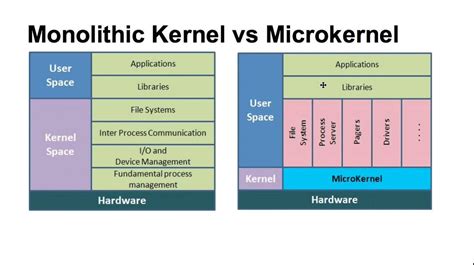
When examining the intricacies of operating systems, it becomes apparent that the design of their kernels plays a crucial role in defining their functionality and performance. In this section, we will delve into a detailed comparison of the kernel designs utilized in the Windows and macOS operating systems, revealing the fundamental differences that shape each system's behavior and capabilities.
- Core Architecture: One notable distinction lies in the core architecture employed by Windows and macOS. Windows utilizes the Hybrid kernel design, which combines elements of both monolithic and microkernel architectures. On the other hand, macOS relies on the XNU kernel, which is a hybrid microkernel architecture.
- Memory Management: The mechanisms for memory management in Windows and macOS exhibit contrasting approaches. Windows adopts a demand-paged virtual memory system, providing flexibility and efficient memory allocation. In contrast, macOS employs a unified memory model, where kernel and application memory is managed as a single entity, resulting in streamlined memory access.
- Device Driver Infrastructure: The handling of device drivers is another area where Windows and macOS diverge. Windows employs a layered architecture known as the Windows Driver Model (WDM), enabling compatibility with a wide range of devices. In contrast, macOS utilizes the I/O Kit framework, which provides a streamlined and object-oriented approach to managing device drivers.
- Security: Both Windows and macOS prioritize security, but their kernel designs yield different approaches. Windows employs a discretionary access control mechanism, allowing users to define permissions for accessing resources. In contrast, macOS utilizes a mandatory access control model known as the XNU security extension framework, which provides enhanced control over resource access.
- Concurrency and Scheduling: The management of tasks and scheduling in Windows and macOS is handled differently due to their kernel designs. Windows utilizes a preemptive multitasking model, where tasks are assigned priorities and scheduled accordingly. macOS, on the other hand, employs a thread-based preemptive multitasking model, providing more fine-grained control over system resources and responsiveness.
By examining the nuances of kernel designs, it becomes evident that Windows and macOS address the challenges of operating system functionality and performance in unique ways. Understanding these differences allows users to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
User Interface: Windows vs. MacOS
In the realm of computer operating systems, Windows and MacOS offer distinct user experiences through their respective user interfaces. While both operating systems aim to provide users with a smooth and intuitive interaction, they achieve this goal in unique ways.
When it comes to the user interface, Windows and MacOS exhibit contrasting design philosophies. Windows presents a more flexible and customizable interface, allowing users to modify various aspects of their desktop environment. On the other hand, MacOS focuses on simplicity and elegance, offering a visually cohesive and polished interface.
- Layout: Windows often adopts a more traditional layout, featuring a Start menu and a taskbar at the bottom of the screen. MacOS, in contrast, emphasizes a top menu bar and a dock for quick access to applications.
- Window Management: Windows offers a range of resizing and snapping options, along with a task view feature, enabling users to multitask efficiently. MacOS, known for its window management system, includes features like Mission Control and Spaces, enhancing productivity and organizational capabilities.
- File System Navigation: Windows typically employs a hierarchical file system navigation, represented by folders, directories, and drives. On the other hand, MacOS adopts a more visual approach with its Finder application, which utilizes a column view for seamless navigation.
- System Menu: Windows integrates a centralized control panel, accessible through the Start menu, where users can access various system settings. Meanwhile, MacOS concentrates these settings within the System Preferences application, allowing for an in-depth configuration of the system.
Ultimately, the user interface of an operating system plays a critical role in shaping the overall user experience. Windows and MacOS differ not only in their visual representation but also in their approach to customization, productivity features, and navigation. Understanding these distinctions can help users make informed decisions when choosing an operating system that best suits their needs and preferences.
Exploring the Distinct Interface Design Approaches
Visual aesthetics play a significant role in shaping the overall user experience when it comes to operating systems. Both Windows and MacOS strive to create a distinguished interface design for their respective platforms, albeit with varying approaches. In this section, we will delve into the unique aspects of interface design offered by Windows and MacOS, focusing on their visual elements, navigational features, and organizational structures.
1. Visual Elements:
- Windows embraces a more versatile and customizable visual approach, allowing users to personalize their desktop backgrounds, icon sizes, and taskbar appearance. The interface reflects a modern and minimalist design, with flat icons and clean lines.
- On the other hand, MacOS opts for a sleek and polished appearance, characterized by smooth gradients, rich textures, and detailed icons. The overall design philosophy embodies elegance and simplicity, creating a visually appealing interface.
2. Navigational Features:
- Windows incorporates a taskbar at the bottom of the screen, providing easy access to frequently-used applications and an intuitive start menu for quick navigation. The taskbar also allows users to switch between open applications effortlessly.
- Contrarily, MacOS places the dock at the bottom of the screen, serving as a central hub for app shortcuts. The dock supports various gestures, such as swipe gestures and Mission Control, enabling users to swiftly navigate through open windows and applications.
3. Organizational Structures:
- Windows organizes files and folders through the File Explorer, utilizing a hierarchical structure. Users can access their files and manage them using a folder system, providing a clear sense of organization and easy retrieval.
- Meanwhile, MacOS adopts a tag-based organizational approach, allowing users to categorize files based on customizable tags rather than relying solely on folders. This system offers a more flexible and intuitive way of organizing and locating files.
As we can see, Windows and MacOS exhibit distinctive interface design strategies, catering to different user preferences. Windows emphasizes customization and versatility, while MacOS takes pride in its elegance and simplicity. Understanding these key differences can help users make an informed decision when selecting an operating system that aligns best with their visual preferences and navigational needs.
FAQ
What is the main difference between Windows and MacOS?
The main difference between Windows and MacOS is the operating system they use. Windows uses Microsoft operating system, while MacOS uses Apple operating system.
Which operating system is more user-friendly, Windows or MacOS?
Both Windows and MacOS have user-friendly interfaces, but MacOS is often considered more user-friendly due to its intuitive design and seamless integration with Apple hardware.
Can I use Windows software on a MacOS computer?
No, you cannot run Windows software directly on a MacOS computer. However, there are virtualization software, such as Parallels Desktop, that allow you to run Windows on a MacOS machine.
Is there a difference in performance between Windows and MacOS?
Performance differences between Windows and MacOS can vary depending on the specific hardware and software configurations. However, MacOS is generally known for its optimized performance on Apple hardware.
Which operating system is more popular, Windows or MacOS?
Windows is more popular worldwide due to its wide adoption by various computer manufacturers. MacOS, on the other hand, is primarily used by Apple devices and has a smaller market share.
What are the main differences between Windows and MacOS operating systems?
The main differences between Windows and MacOS operating systems lie in their user interface, compatibility with software, and hardware requirements. Windows has a more customizable user interface with a Start menu and taskbar, while MacOS offers a cleaner and more streamlined interface. Windows has a wider range of software compatibility, as it supports more applications and games. MacOS, on the other hand, is known for its seamless integration with Apple's hardware and software ecosystem.




