The ever-evolving world of technology continues to bring forth new possibilities and opportunities for users worldwide. One interesting aspect that frequently captures the attention of tech enthusiasts and everyday individuals alike is the idea of running multiple operating systems on a single computer. In this article, we delve into the realm of synergy between two popular and powerful operating systems, exploring the compatibility of Linux and Windows.
Breaking the boundaries of conventional computing, the concept of coexistence between Linux and Windows on a single machine is an intriguing proposition. By harnessing the distinct strengths of these operating systems, users can unlock a world of enhanced productivity, versatility, and customization. The potential benefits and challenges involved in this convergence demand a deep dive into the intricacies of their integration.
Linux, renowned for its robustness, security, and flexibility, serves as the cornerstone of open-source computing. Its diverse distributions offer a wide range of user-friendly interfaces and powerful functionalities, allowing individuals to tailor their Linux environment according to their specific needs. Meanwhile, Windows, the operating system that has dominated the mainstream market, captivates users with its intuitive interface, extensive software compatibility, and extensive support network. The combination of these two behemoths, if achieved harmoniously, could potentially result in an unmatched computing experience.
Comparison of Linux and Windows Operating Systems
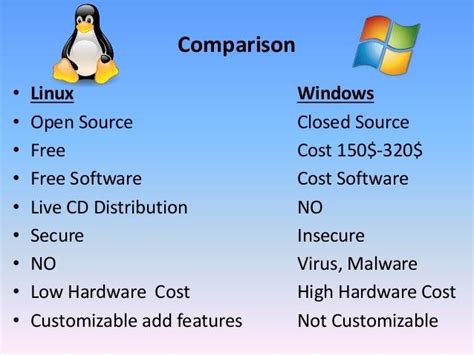
An Examination of Two Prominent Operating Systems
In this section, we will delve into a comprehensive comparison of two widely recognized and popular operating systems. While each possesses its distinctive characteristics, they both provide users with a range of functionalities and features.
The Unique Aspects of Linux and Windows
Linux and Windows are two prominent operating systems that cater to the diverse needs and preferences of computer users. While Linux is an open-source platform, offering immense flexibility and enhanced security, Windows is a proprietary system known for its widespread usage and user-friendly interface.
Operating System Architecture
Both Linux and Windows operating systems are designed based on distinct architectural principles. Linux follows a monolithic kernel model, where the entire operating system is consolidated into a single unit, thereby facilitating efficient resource utilization. In contrast, Windows embraces a hybrid approach, combining elements of both monolithic and microkernel designs, thereby providing a balance between performance and modularity.
Software Compatibility and Availability
When it comes to software compatibility, Windows tends to have an edge due to its extensive market dominance. Numerous commercial applications and games are primarily tailored for Windows, making it a preferred choice for users in certain domains. On the other hand, Linux boasts a vast array of open-source software, offering both stability and customization options for users.
User Interface and User Experience
Windows is widely recognized for its user-friendly interface, featuring a visually appealing design and intuitive navigation. This makes it more accessible to users who may have limited technical expertise. Linux, although often considered less user-friendly, provides a highly customizable interface, offering greater flexibility and control over the system's appearance and behavior.
Security and Reliability
Linux has gained a reputation for its robust security features, owing to the open-source nature of its code. The extensive community-driven development and review process tend to result in quicker identification and resolution of vulnerabilities. While Windows has made significant advancements in security, Linux is often considered a more secure choice. In terms of reliability, both operating systems have matured over time, with minimal instances of system crashes or instability.
Conclusion
Overall, Linux and Windows are two operating systems that offer unique attributes and cater to different user preferences. While Linux provides flexibility, security, and customization options, Windows excels in terms of software compatibility, user-friendliness, and market dominance. The ultimate choice between the two will depend on individual requirements, expertise, and intended use of the operating system.
Compatibility of Linux and Windows Operating Systems on a Single Computer
When it comes to using multiple operating systems on a single computer, there are various factors to consider in ensuring compatibility and seamless functionality between different software environments. In this section, we will explore the compatibility of Linux and Windows operating systems co-existing on the same machine, without compromising the performance or user experience. This article aims to provide valuable insights into the possibilities and challenges faced when running Linux and Windows side by side.
1. Hardware Compatibility:
- Determining whether the hardware components of a computer are compatible with both Linux and Windows operating systems is crucial. It is important to ensure that the devices such as the processor, graphics card, network adapter, and peripherals have suitable drivers available for both operating systems.
- Ensuring compatibility of hardware components can minimize issues such as driver conflicts, system crashes, or performance degradation.
2. Partitioning and Dual Booting:
- Partitioning the hard drive appropriately is necessary to accommodate both Linux and Windows operating systems.
- Setting up a dual boot configuration allows users to choose between Linux and Windows during system startup, providing flexibility in selecting the desired operating system for each session.
- Properly configuring the boot loader is essential for managing the dual boot process and ensuring efficient switching between Linux and Windows.
3. Software Compatibility:
- Compatibility issues may arise when attempting to run certain software applications that were specifically developed for one operating system on the other.
- Emulation or virtualization techniques can be employed to overcome software compatibility challenges. These methods enable running Windows applications within a Linux environment or vice versa.
4. File System Considerations:
- Understanding the differences in file systems used by Linux (e.g., ext4) and Windows (e.g., NTFS) is essential for ensuring seamless data access and sharing between the two operating systems.
- Utilizing compatible file systems and employing appropriate drivers or third-party software can facilitate smooth file exchange and collaboration between Linux and Windows.
5. Security and Updates:
- Implementing robust security measures and keeping both operating systems up to date with the latest patches and updates is crucial in maintaining a secure computing environment.
- Regularly updating antivirus software and performing system scans can help protect against malware threats that may target vulnerabilities in either Linux or Windows.
By taking into account the factors mentioned above and considering the specific requirements and preferences of users, it is indeed possible to achieve compatibility between Linux and Windows operating systems on a single computer. The successful coexistence of these two popular platforms can offer users the benefits of utilizing each operating system's unique features and applications, resulting in an enhanced computing experience.
Methods for Achieving Dual Boot System with Linux and Windows

Dual booting is the practice of installing two different operating systems on a single computer system. In the context of the topic at hand, it involves having both Linux and Windows installed on the same machine, enabling users to choose between the two during system startup.
Several methods exist for setting up a dual boot system with Linux and Windows. One commonly used approach is partitioning the hard drive to create separate sections for each operating system. This involves dividing the disk space into partitions, with one partition dedicated to Linux and another to Windows. By allocating enough space to each operating system, users can ensure that both systems have sufficient resources for optimal performance.
Another approach to achieve dual booting involves the use of a boot loader. A boot loader is a software program that is responsible for loading the operating system during system startup. By configuring the boot loader, users can select which operating system to boot into. Popular boot loaders like GRUB (GRand Unified Bootloader) and LILO (LInux LOader) provide a user-friendly interface for managing dual boot systems.
In addition to partitioning and boot loaders, virtualization can also be used to create a dual boot system. Virtualization allows users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical machine. By setting up a virtual machine, users can install Linux and Windows as separate operating systems within a virtual environment, effectively achieving dual boot functionality without requiring separate partitions on the hard drive.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Partitioning | Create separate disk partitions for Linux and Windows |
| Boot Loaders | Configure a boot loader to choose between operating systems |
| Virtualization | Run Linux and Windows concurrently within a virtual environment |
When deciding on the method for dual booting, it is important to consider factors such as system requirements, user preferences, and technical expertise. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, and selecting the most suitable approach will depend on individual needs and circumstances.
FAQ
Can Linux and Windows be installed on the same computer?
Yes, it is possible to have both Linux and Windows installed on the same computer. This is known as dual-booting, where you can choose which operating system to boot into every time you start your computer.
What are the advantages of dual-booting Linux and Windows?
Dual-booting allows you to have access to both Linux and Windows, which lets you take advantage of the strengths and applications of both operating systems. For example, Linux is often preferred by developers for its flexibility and customization options, while Windows is commonly used for gaming and compatibility with certain software.
Is it complicated to set up a dual-boot system?
The complexity of setting up a dual-boot system depends on your level of technical knowledge and the specific hardware configuration of your computer. However, there are user-friendly tools and step-by-step guides available that can make the process relatively simple for most users. It is always recommended to backup your data before attempting any dual-boot installation.




