Embarking on a voyage in the realm of containerization, enthusiasts often encounter a myriad of choices that can be both exhilarating and overwhelming. In the pursuit of finding the perfect synergy between an operating system and Docker, individuals find themselves on a quest to decipher the most fitting solution. This endeavor is characterized by the exploration of Linux distributions that can seamlessly integrate with Docker, paving the way for resource-efficient and secure container deployment.
As the technologically rich landscape of Linux distributions unravels before us, the daunting task of selecting the most compatible and efficient option comes to the forefront. Seeking a partner that harmonizes with Docker's underlying infrastructure grants developers the capability to leverage the full potential of containerization. From a sea of options, one must navigate through the intricately woven web of choices, delving into the diverse features and performance aspects that the Linux distributions have to offer.
Within this intricate tapestry of possibilities, an ideal match can be found. An alliance between Docker and the most appropriate Linux distribution sets the stage for optimal productivity, enhancing accessibility, performance, and security. Empowered by this synergy, developers are poised to deliver cutting-edge solutions, unencumbered by compatibility constraints and armed with the tools necessary to realize their visions.
Choosing the Suitable Linux Distro for Docker Containers

When it comes to determining the ideal Linux distribution for running Docker containers, the selection process can be a crucial factor in achieving optimal performance and efficiency. Making the right choice entails considering various factors like compatibility, stability, security, support, and customization options. This section aims to delve into the process of selecting the most appropriate Linux distribution for effectively deploying and managing Docker containers, taking into account the unique requirements and objectives of individual users.
Exploring the Advantages of Linux Distributions Tailored for Docker
In this section, we delve into the myriad benefits that Linux distributions offer when it comes to seamlessly integrating with Docker containerization technology. From enhanced performance and reliability to simplified deployment and management, there are numerous advantages to be discovered.
Efficient Resource Utilization: Linux distributions optimized for Docker provide efficient resource utilization, enabling containers to run smoothly within isolated environments. These distributions offer lightweight components and streamlined architectures that maximize system resources, resulting in improved performance and overall productivity.
Robust Security Measures: Linux distributions commonly incorporate robust security measures designed to protect containerized applications and data. With built-in isolation mechanisms, secure software repositories, and timely security updates, these distributions ensure that Docker containers remain protected from potential threats, providing peace of mind for developers and operations teams.
Seamless Integration: Linux distributions tailored for Docker seamlessly integrate with containerization technology, enabling easy deployment and management of containers. These distributions often come bundled with Docker tools and utilities, simplifying the installation process and reducing compatibility issues, making it easier for developers and system administrators to adopt and utilize Docker effectively.
Ecosystem Support: Docker-friendly Linux distributions benefit from extensive community and ecosystem support. This means that users can access a vast range of documentation, tutorials, forums, and community-driven resources, facilitating the learning process and troubleshooting efforts. Additionally, these distributions often have repositories with pre-configured Docker images, allowing users to quickly find and utilize popular containerized applications and services.
Flexibility and Customization: Linux offers a high degree of flexibility and customization, providing users with the ability to tailor their Docker environment to suit their specific requirements. Whether it's choosing from a wide variety of Linux distributions, optimizing kernel parameters, or fine-tuning networking configurations, the flexibility of Linux allows developers and operations teams to create a Docker environment that perfectly aligns with their needs.
In the following sections, we will explore some notable Linux distributions that excel in supporting Docker containerization and highlight their distinctive features and strengths.
Selecting a Linux Distribution that Meets Docker's Requirements
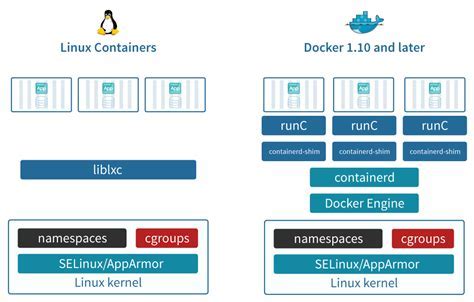
In the world of containerization, choosing the right Linux distribution is crucial to ensure seamless integration with Docker. When it comes to selecting a Linux distribution that supports Docker's requirements, there are several key factors to consider.
First and foremost, compatibility is of utmost importance. The chosen distribution should offer comprehensive support for Docker's features and functionalities, allowing for efficient management and deployment of containers. Additionally, it is essential to consider the distribution's level of stability and reliability, as Docker heavily relies on the underlying operating system for optimal performance.
Another factor to take into account is the availability of the latest Docker updates and security patches. Regular updates are necessary to ensure compatibility with Docker's evolving ecosystem and to address any vulnerabilities that may arise. A Linux distribution with a reputable track record of timely updates will help maintain a secure and up-to-date Docker environment.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the level of community support and active development surrounding the chosen distribution. A vibrant and engaged community can provide valuable resources, documentation, and troubleshooting assistance, which can significantly aid in the smooth implementation and management of Docker containers.
Last but not least, performance should be a key consideration when selecting a Linux distribution for Docker. Efficient resource utilization, minimal overhead, and optimized networking capabilities all contribute to a superior Docker experience. A distribution that excels in these areas will ensure optimal container performance without unnecessary bottlenecks or limitations.
In conclusion, selecting a Linux distribution that meets Docker's requirements requires careful consideration of compatibility, stability, update availability, community support, and performance. By evaluating these factors, one can find a Linux distribution that seamlessly integrates with Docker, providing a reliable, secure, and efficient containerization experience.
Comparing the Leading Linux Distributions for Efficient Docker Deployment
In this section, we will delve into an in-depth analysis of the top-notch Linux distributions that excel in facilitating seamless Docker deployment. By closely examining these distros, we aim to offer valuable insights into their unique strengths and features, enabling you to make an informed decision when choosing the ideal Linux distribution for efficient Docker utilization.
| Linux Distribution | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu | Ubuntu offers a user-friendly interface and extensive community support. It is well-suited for developers and beginners due to its simplicity and vast software availability. | However, some users might find the large number of pre-installed applications overwhelming and unnecessary for Docker-focused deployments. |
| Debian | Debian provides stability, security, and a wide range of software packages. Its devotion to free and open-source software makes it an ideal choice for privacy-oriented individuals and organizations. | Nonetheless, Debian's release cycles can be lengthy, which could result in outdated packages for Docker deployments. |
| CentOS | As a highly stable and enterprise-focused Linux distribution, CentOS is trusted by many businesses. It offers long-term support, security updates, and a vast software repository. | However, the conservative approach to software updates might cause delays in receiving the latest Docker features. |
| Fedora | Fedora emphasizes cutting-edge technologies and software advancements. It provides frequent releases with up-to-date packages, making it an attractive choice for those seeking the latest Docker capabilities. | The rapid release cycle might result in potential stability issues and a higher learning curve for inexperienced Docker users. |
Each Linux distribution comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages when it comes to Docker deployment. Considering factors like community support, software availability, stability, and update frequency will guide your decision towards selecting the most fitting Linux distribution to maximize your Docker utilization and streamline your development workflow.
How to quickly deploy a Linux distribution with GUI applications via a container
How to quickly deploy a Linux distribution with GUI applications via a container by How To Make Tech Work from TechRepublic 2,253 views 2 years ago 3 minutes, 30 seconds
The Linux Tier List
The Linux Tier List by Chris Titus Tech 843,672 views 9 months ago 27 minutes
FAQ
What is Docker and why is it important for Linux distributions?
Docker is a popular open-source containerization platform that allows developers to package their applications and their dependencies into containers. It is important for Linux distributions because it provides a consistent and isolated environment for running applications, making it easier to deploy, manage, and scale applications across different systems.
How do I choose the best Linux distribution for running Docker?
Choosing the best Linux distribution for Docker depends on various factors such as your requirements, level of experience, and preference. Popular choices include Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, and Debian. It is recommended to consider factors like community support, ease of use, security, and compatibility with Docker when making your decision.
I'm new to Docker. Which Linux distribution would be the best choice for beginners?
If you are new to Docker, Ubuntu would be a great choice as it is one of the most widely used and beginner-friendly Linux distributions. It has a large community and extensive documentation, making it easier for beginners to find support and resources while learning Docker.
Which Linux distribution is best for running Docker in a production environment?
For running Docker in a production environment, CentOS is often recommended. It is known for its stability, long-term support, and strong security features. Many organizations prefer CentOS for running Docker in production due to its reliability and enterprise-grade support.
Can I use Docker on a lightweight Linux distribution?
Yes, you can use Docker on lightweight Linux distributions like Alpine Linux. Alpine Linux is designed to be small, secure, and resource-efficient, making it an ideal choice for running Docker in environments with limited resources or in situations where a smaller footprint is desired.
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that enables developers to automate the deployment and running of applications in containers. It allows applications to be packaged with all the required dependencies and run consistently on any environment.
Why is choosing the right Linux distribution important for Docker?
Choosing the right Linux distribution for Docker is important because Docker heavily relies on the underlying operating system's kernel features. Different distributions may have different default configurations, kernel versions, package managers, and support for Docker itself. It is crucial to use a compatible and well-supported distribution to ensure optimal performance, stability, and security of Docker containers.




