In the realm of software, the diverse range of licensing options available for Microsoft operating systems is a topic of great significance and interest for tech enthusiasts and everyday users alike. These licenses serve as the gateway to accessing the world of Windows, allowing individuals to unleash the full potential of their devices. With an array of licensing options offered by Microsoft, it's crucial to understand the differences that exist within this vast landscape.
When it comes to utilizing Microsoft operating systems, it's important to grasp the intricacies of the licensing models that cater to various user needs. The unique combinations of permissions and rights associated with each licensing option make them suitable for different types of individuals, businesses, and organizations. These licenses ensure not only compliance with legal requirements but also provide access to an array of features and functionalities that enhance the user experience.
One of the primary licensing options available is the perpetual license. This type of license grants users the freedom to use specific versions of the operating system indefinitely, offering a sense of permanence and stability. Perpetual licenses are often preferred by individuals or businesses who are content with sticking to a particular version of the operating system, without seeking frequent updates or upgrades. It provides the reassurance of longstanding familiarity and the convenience of unrestricted usage.
Understanding Windows Licenses: The Basics

In this section, we will delve into the fundamental concepts that underpin the various licenses associated with the popular operating system from Microsoft. By gaining a clear understanding of the essentials, you can make informed decisions when selecting a license that best suits your needs.
One of the key aspects to comprehend is the diversity among the licenses Microsoft offers to its users. These licenses serve as legal agreements that grant individuals or organizations the right to use and access the software. It is crucial to distinguish between the different types of licenses available, as they have varying terms, usage restrictions, and entitlements.
To aid in understanding, we will explore the core components that characterize the licensing landscape. This includes examining the scope of usage rights, the duration of license validity, and the level of support and updates provided. Additionally, we will address the implications of license transfers and restrictions, and the potential for upgrades or downgrades.
| Key Points Covered in this Section |
|---|
| 1. Types of licenses and their distinctions |
| 2. Usage rights and limitations |
| 3. Validity periods and renewal options |
| 4. Support and updates availability |
| 5. License transfers and restrictions |
| 6. Options for upgrades and downgrades |
By grasping the basics of Windows licenses, you will be empowered to navigate the licensing landscape effectively and make informed decisions that align with your requirements and budget. Let's dive into the details of each aspect in the following sections.
The Significance of Licensing for Windows Users
When it comes to employing the full range of functions and features that an operating system can offer, having a valid license plays a pivotal role. Acknowledging the value of licensing for the Windows operating system is essential for consumers who seek to maximize their computing experience and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
Enhanced Accessibility and Functionality
By obtaining a legitimate license, users gain access to a myriad of tools and utilities that are designed to enhance their overall computing experience. Licenses provide the necessary permissions to unlock advanced features, performance improvements, and compatibility with a wide range of software applications. This enables users to fully utilize and customize their Windows operating system to meet their specific needs.
Security and Protection
Valid Windows licenses are crucial in safeguarding users from potential security risks and vulnerabilities. Regular updates, security patches, and antivirus software are some of the crucial components that can be obtained through licensing. These measures ensure that users have a reliable and secure operating system that can counteract emerging threats and maintain the privacy of their data.
Compliance and Legal Obligations
Being in possession of a valid Windows license ensures compliance with the legal requirements set by the software manufacturer. It establishes the legality of using the operating system and helps users avoid the consequences of copyright infringement. Furthermore, having a valid license ensures that users are entitled to technical support, warranty coverage, and other benefits provided by the manufacturer.
Peace of Mind
When consumers have a legitimate license, they can enjoy peace of mind knowing that they have acquired a genuine product. This reduces the risk of compatibility issues, system malfunctions, and the installation of unauthorized or counterfeit software. Additionally, it eliminates the concerns associated with potential legal actions or penalties that may arise from unauthorized usage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, obtaining a valid license for the Windows operating system is paramount for consumers who aim to fully harness its potential. Licensing not only grants access to a plethora of features and functionalities but also ensures compliance, security, and peace of mind for users. Hence, it is imperative to recognize the significance of licensing in order to optimize the Windows operating system experience.
A Detailed Overview of Different Windows Licensing Options
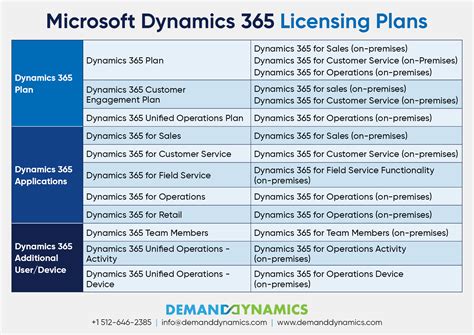
In the diverse landscape of Windows licensing, there exists a multitude of options that cater to various user requirements and preferences. This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the different licenses offered by Microsoft, each offering unique features and capabilities.
One notable licensing option is the Perpetual License, which grants users the right to use a specific version of Windows indefinitely. This type of license is typically associated with a one-time purchase and offers the benefit of receiving updates and support for a predefined period of time.
Another popular choice is the Subscription License, which provides users with continuous access to the latest Windows version for a fixed duration. This type of license is commonly used by individuals or businesses that prefer the flexibility of paying for the software on a periodic basis.
For those seeking a comprehensive package of Microsoft products, the Volume Licensing option is an ideal choice. Typically designed for businesses or educational institutions, volume licensing provides cost-effective and centralized management of Windows installations on multiple devices.
In addition, Microsoft offers specialized licensing options tailored for specific use cases and industries. These include Embedded Licenses, which are designed for devices in fields such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation that require customized and embedded Windows solutions.
Furthermore, Microsoft offers licensing options for virtual environments like Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Remote Desktop Services (RDS). These licenses enable users to access Windows from virtual machines or remote environments, delivering increased flexibility and scalability.
It is worth mentioning that the availability and features of these licenses may vary depending on the specific version of Windows and the region in which they are offered. Thus, it is advisable to thoroughly research and understand the licensing options available to make an informed decision based on individual needs and requirements.
Understanding the various Windows licensing options empowers users to choose the most suitable license that aligns with their usage scenarios, budget, and long-term goals. Each license type brings its own set of advantages and considerations, ensuring that there is a licensing option available to cater to the diverse needs of individuals and organizations alike.
Retail Licenses: The Popular Choice for Individual Users
When it comes to acquiring software for personal use, individual users have a variety of options to choose from. One of the most popular choices among consumers is retail licenses. These licenses offer a flexible and convenient way for individuals to obtain and use different software products without being tied to specific hardware or purchasing agreements.
Flexibility and Convenience
Retail licenses provide users with the freedom to install and use software on any compatible device of their choice. This means that individuals can easily switch between devices or upgrade their hardware without any limitations imposed by the license. Moreover, retail licenses allow users to reinstall and activate the software on a different device, making it a practical choice for technologically dynamic individuals.
Diverse Product Range
With retail licenses, users are not limited to a single software product. They have access to a wide range of applications and operating systems, enabling them to meet their specific needs and preferences. Whether it's for productivity, creativity, or entertainment purposes, retail licenses offer a plethora of options to cater to individual users' interests and requirements.
Upgrades and Support
Individual users who opt for retail licenses also get the advantage of receiving updates and support directly from the software vendor. This ensures that they can always stay up to date with the latest features and security patches, providing them with a more seamless and protected experience. Additionally, users can rely on the vendor's support channels for any technical assistance or troubleshooting they may require.
Conclusion
For individual users seeking flexibility, a diverse product range, and ongoing support, retail licenses are the go-to choice. These licenses empower users to make the most of their software on their terms, allowing them to stay at the forefront of technology and enjoy a personalized computing experience.
Exploring the Advantages of Retail Microsoft licenses
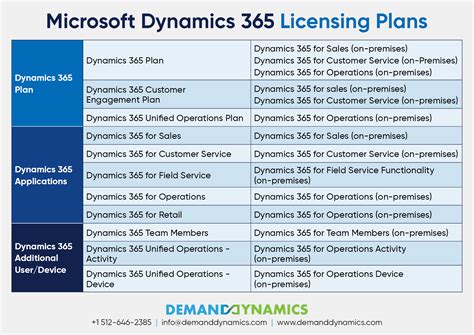
When it comes to acquiring a genuine operating system for your computer, retail Microsoft licenses offer numerous benefits that are worth considering. These licenses provide users with access to a range of features and functionalities, granting them the ability to personalize their computing experience and maximize their productivity.
One of the key advantages of retail Microsoft licenses is the flexibility they provide. Whether you are a home user, a small business owner, or a professional in a specific industry, retail licenses offer different editions tailored to meet your specific needs and requirements. This means that you can choose the version that offers the right balance of features and functionalities to support your work or leisure activities.
Another notable advantage is the ability to receive software updates and security enhancements directly from Microsoft. With a valid retail license, you can enjoy the peace of mind knowing that you are using a genuine and up-to-date version of the operating system. This ensures that you have access to the latest patches, bug fixes, and improvements, helping to enhance the overall performance and stability of your computer.
In addition, retail licenses offer the flexibility to install the operating system on multiple devices. This is particularly beneficial for those users with multiple computers or those who regularly upgrade their hardware. With a retail license, you can easily transfer the operating system to a new device without the need to purchase a new license, saving both time and money.
Furthermore, retail Microsoft licenses typically come with a higher level of technical support. Whether it's through online forums, knowledge bases, or direct assistance from Microsoft's technical experts, users with retail licenses can tap into a wealth of resources to help troubleshoot any issues they may encounter.
| Advantages of Retail Microsoft licenses: |
|---|
| Flexibility to choose the right edition for your needs |
| Access to software updates and security enhancements |
| Ability to install the operating system on multiple devices |
| Higher level of technical support |
Understanding the Limitations of Retail Licenses for Windows
When it comes to acquiring the rights to use a particular operating system, it is crucial to understand the restrictions that come with different types of licenses. In the case of Microsoft's popular operating system, various retail licenses are available for purchase, each with its own set of limitations and conditions.
1. Activation Limitations: Retail licenses for Windows often come with restrictions on the number of devices the license can be activated on. This means that if you purchase a retail license for Windows, you may only be able to activate it on a specified number of machines. It is important to consider this limitation if you plan on using the operating system on multiple devices.
2. Transferability: Another important aspect to be aware of when it comes to retail Windows licenses is their transferability. While some licenses may allow you to transfer the license to a different computer, others may prohibit such transfers. This restriction could impact your ability to upgrade or replace your hardware without needing to purchase a new license.
3. Upgrade Options: Retail licenses for Windows also have limitations when it comes to upgrading to newer versions or editions of the operating system. Depending on the specific license, you may only be entitled to upgrades within a certain timeframe or to specific editions. This limitation should be considered if you anticipate the need to upgrade your operating system in the future.
4. Support and Updates: Retail licenses may also have restrictions when it comes to accessing support and software updates. While some licenses may provide ongoing support and updates for a specified period, others may only grant access to these services for a limited time. It is essential to be aware of these limitations as they can impact the functionality and security of your operating system.
Having a clear understanding of the limitations imposed by retail licenses for Windows is crucial when making a decision about which license is best suited to your needs. Consider these restrictions alongside your usage requirements and future plans to ensure that you make an informed choice when purchasing a Windows license.
OEM Licenses: The Preferred Option for Manufacturers

When it comes to procuring licenses for operating systems, manufacturers have a distinct preference for OEM licenses. These licenses, which cater specifically to original equipment manufacturers, offer a range of advantages that make them the preferred choice in the industry.
One key advantage of OEM licenses is their ability to provide manufacturers with significant cost savings. Compared to retail licenses, OEM licenses are often available at a lower price point, enabling manufacturers to reduce their overall production costs. This cost-effectiveness makes OEM licenses an attractive option for manufacturers looking to optimize their budget without compromising on the quality and functionality of the operating system.
In addition to cost savings, OEM licenses also offer manufacturers the flexibility to customize the operating system according to their specific hardware requirements. This customization option allows manufacturers to tailor the user experience to their devices and differentiate themselves from competitors in the market. By having the ability to modify and fine-tune the operating system, manufacturers can deliver a seamless and integrated user experience, enhancing the overall value proposition of their products.
Moreover, OEM licenses come with specialized technical support from the operating system provider. This dedicated support ensures that manufacturers receive prompt assistance and guidance in case of any issues or challenges. The availability of technical support helps manufacturers streamline their production processes, minimize downtime, and deliver high-quality products to the market more efficiently.
- Cost-effective option for manufacturers
- Customization to meet specific hardware requirements
- Dedicated technical support from the operating system provider
In conclusion, OEM licenses stand out as the preferred option for manufacturers due to their cost-effectiveness, customization capabilities, and comprehensive technical support. These licenses empower manufacturers to create and deliver superior products that align with their hardware specifications, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
The Pros and Cons of OEM Windows Licenses
When considering the options available for obtaining an operating system for personal use, one may come across the possibility of acquiring an OEM Windows license. These licenses, while distinct from those offered to general consumers, have their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
1. Cost-effectiveness: OEM licenses are typically offered at a lower price compared to their retail counterparts, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious individuals.
2. Bundled hardware: OEM licenses are often bundled with new computers or computer components, eliminating the need for separate software purchases and simplifying the setup process.
3. Warranty coverage: Since OEM licenses are tied to specific hardware, they are typically covered under the manufacturer's warranty, providing an added layer of protection and support.
Disadvantages:
1. Lack of transferability: Unlike retail licenses, OEM licenses are generally not transferable to another computer. If you upgrade or replace your hardware, you may need to purchase a new license.
2. Limited support: OEM licenses usually have more limited support options compared to retail licenses. While basic troubleshooting assistance may be available, dedicated customer support may be lacking.
3. Software limitations: OEM licenses may come with certain restrictions or limitations, such as the inability to upgrade to a higher edition of the operating system or the exclusion of certain features. It is important to review the specifics of the license to ensure it meets your requirements.
It is important to carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of OEM Windows licenses before making a decision. While they may offer cost savings and convenience, they may also come with limitations that could impact your future needs or flexibility.
Understanding the Distinctions Between OEM and Retail Windows Licensing

When it comes to acquiring a legal copy of the operating system, consumers are presented with various options that abide by licensing agreements tailored for different purchasing contexts. Two common types of licenses available for acquiring Windows are OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) licenses and retail licenses. While these licenses serve the same purpose of granting legal access to Windows, it is essential to understand the key differences between them to make an informed decision.
OEM licenses, as the name suggests, are designed for original equipment manufacturers who pre-install Windows on their devices before distributing them to end-users. These licenses are typically tied to the hardware on which they are installed and cannot be transferred to another device. They often come at a lower cost compared to retail licenses, making them an attractive option for manufacturers and system builders. Additionally, OEM licenses do not come with technical support directly from Microsoft, as the responsibility lies with the manufacturer or system builder.
On the other hand, retail licenses are intended for individual consumers and can be purchased separately from hardware. Retail licenses allow users to install and activate Windows on a device of their choice, providing more flexibility in terms of hardware upgrades or replacements. Unlike OEM licenses, retail licenses are transferable to another device as long as they are used on only one device at a time. Additionally, retail licenses typically include technical support from Microsoft during the validity period.
While both OEM and retail licenses grant legal access to Windows, it is crucial to consider your specific requirements and usage scenario before making a decision. OEM licenses are suitable for those purchasing new devices from manufacturers or building their own systems, whereas retail licenses are suitable for individual consumers who require more flexibility in terms of hardware and support options.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What are the different types of Windows licenses available for consumers?
There are several types of Windows licenses available for consumers. The most common ones include Windows OEM License, Windows Retail License, and Windows Volume License.
What is a Windows OEM License?
A Windows OEM License is a license that is specifically designed for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) who sell pre-installed Windows operating systems on their devices. This license is tied to the hardware it was originally installed on and cannot be transferred to another device.
What is a Windows Retail License?
A Windows Retail License is a license that is purchased by individual consumers from retail stores or Microsoft's official website. This license can be installed on a device of the user's choice and can also be transferred to another device as long as it is deactivated on the previous one.
What is a Windows Volume License?
A Windows Volume License is a license that is primarily intended for businesses and organizations. It allows them to install Windows operating systems on multiple devices using a single license key. Volume licenses are typically purchased in bulk and offer additional benefits such as centralized license management.
What is the difference between a Windows OEM License and a Windows Retail License?
The main difference between a Windows OEM License and a Windows Retail License is the way they are sold and the terms of usage. An OEM License is pre-installed on a device by the manufacturer, while a Retail License is purchased separately by individual consumers. Additionally, an OEM License is tied to the original hardware and cannot be transferred, whereas a Retail License can be transferred to another device.
What are the different types of Windows licenses available for consumers?
There are primarily three types of Windows licenses available for consumers: the full packaged product (FPP), original equipment manufacturer (OEM), and volume licensing.




