Immerse yourself in the ethereal realm of an extraordinary reverie, where nature's enigmatic creatures take center stage. This captivating vision transports us to a world where the boundary between reality and fantasy blur, revealing the silent allure of amphibians. Within this vast kingdom, two distinct figures emerge - one known for its vibrant colors and distinct voice, while the other hides in the shadows, silently observing the world around it.
Delve deeper into this mesmerizing dreamscape and encounter the mystical denizens that captivate both scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Discover the essence of these fascinating beings, not through explicit definitions, but through the allure of their distinct forms and mysterious nature. Watch as they gracefully maneuver through their natural habitats, leaving us spellbound with each subtle movement.
Embrace the strength and resilience that emanates from one of these enchanting inhabitants, marked by a smooth, wet skin that glistens under the moonlight. This creature, known for its melodious croak, possesses a vibrant palette of colors that accentuate its earthly presence. Intriguingly, its vibrant hues serve as signs of royalty and grandeur, silently boasting its place within the intricate tapestry of the natural world.
From Pond Dwellers to Land Explorers: The Evolution of Frogs and Toads
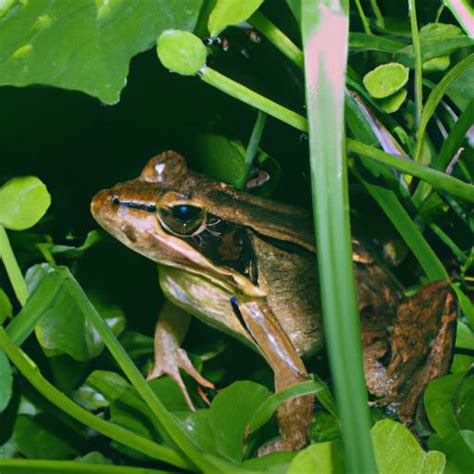

Throughout the ages, nature has witnessed a remarkable transformation in the lives of these amphibious creatures. Embarking on an extraordinary journey from water to land, frogs and toads have undergone a fascinating evolution that has shaped their appearance, behavior, and survival strategies. This article delves into the intriguing story of how these pond dwellers have evolved into skilled explorers of both aquatic realms and terrestrial habitats.
Adapting to Different Environments
As these amphibians transitioned from their aquatic beginnings to seek opportunities on land, they developed unique features and adaptations for survival. Evolving from their common ancestors, frogs and toads have adapted physically to thrive in diverse environments, showcasing distinct characteristics that set them apart. Such evolutionary changes paved the way for their successful colonization of habitats ranging from tropical rainforests to deserts.
The Metamorphosis Process
One of the most captivating aspects of their evolution lies in the transformation they undergo during their lifecycle. The metamorphosis process is a defining characteristic of frogs and toads, encompassing stages from tiny eggs to tadpoles, eventually culminating in the development of fully-formed adult amphibians. This intricate metamorphosis reflects their ability to adapt and survive in different habitats, displaying a remarkable balance between aquatic and terrestrial lifestyles.
Behavioral Adaptations
Beyond physical changes, frogs and toads have also evolved behavioral adaptations to conquer the challenges of land exploration. Their remarkable ability to vocalize through various calls and croaks has played a crucial role in communication, attracting mates, and establishing territories. Additionally, their unique mating behaviors and parenting strategies, such as egg-laying in water or on land, have further contributed to their success as adaptable species.
Diversity and Conservation
As their evolution continued, frogs and toads branched off into numerous species, each with its own unique set of characteristics and ecological niche. From the vibrant colors of poison dart frogs to the camouflaging abilities of certain toad species, this diversity showcases the remarkable adaptability and resilience of these incredible creatures. However, amidst ongoing environmental changes and habitat destruction, the conservation of frogs and toads has become crucial to ensure the preservation of their extraordinary evolutionary history.
In conclusion, the journey of frogs and toads from aquatic dwellers to land explorers is a testament to the wonders of adaptation and evolution. Their physical, behavioral, and ecological transformations highlight their ability to thrive in a wide range of environments. By delving into their story, we gain a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms that shape life on our planet and the importance of conserving these captivating creatures for future generations.
Anatomy Matters: Analyzing the Physical Differences between Frogs and Toads
In this section, we will delve into the significance of anatomy when it comes to differentiating between amphibians commonly known as frogs and toads. By examining their physical characteristics, we can gain a deeper understanding of the distinctions between these fascinating creatures.
Morphological Features:
Frogs and toads possess distinct morphological features that set them apart from each other. These unique characteristics encompass various aspects, such as their body structure, skin texture, and overall appearance. Understanding and analyzing these differences is essential in accurately identifying and classifying these two types of amphibians.
Skin Texture:
One of the primary visual differences between frogs and toads lies in the texture of their skin. Frogs typically have smoother and moister skin, characterized by a slimy or slippery feel. On the other hand, toads have rougher and drier skin, often marked with warts or bumps. This disparity in skin texture serves as a crucial differentiating factor.
Body Structure:
Another fundamental distinction between frogs and toads can be observed in their body structure. Frogs tend to have longer and more streamlined bodies, with longer hind limbs built for leaping. In contrast, toads have shorter and stockier bodies, equipped with stubby hind legs that are more adapted for hopping. These variations in body structure reflect their different locomotion abilities.
Facial Features:
When examining facial features, one can notice noticeable dissimilarities between frogs and toads. Frogs typically possess a more pointed snout and a sleeker face, while toads have a broader and flatter appearance. The size and shape of their eyes can also differ, with frogs often having larger and more prominent eyes compared to toads, which usually have smaller and more recessed eyes.
Addition of Parotid Glands:
One distinguishing characteristic of toads is the presence of parotid glands behind their eyes. These glands secrete toxic substances, also known as bufotoxins, which serve as a defensive mechanism against potential predators. Frogs, on the other hand, generally lack these specialized glands. The presence or absence of these parotid glands plays a significant role in differentiating these two amphibian species.
Vocalizations:
Lastly, an interesting aspect to consider when analyzing the physical differences between frogs and toads is their vocalizations. While both species are known for their ability to produce sounds, the distinct calls they make exhibit differences in pitch, frequency, and pattern. These unique vocalizations allow for further differentiation between frogs and toads, contributing to their intriguing nature.
Disguised in Colors: The Camouflage Techniques of Amphibians

Exploring the world of amphibians unveils an intriguing realm of concealment and deception. These remarkable creatures, commonly known as frogs and toads, possess a remarkable ability to blend seamlessly into their surroundings through the power of coloration. Their clever camouflage techniques not only enable them to hide from potential predators but also allow them to become effective hunters themselves.
One of the primary ways in which frogs and toads achieve their camouflage is through their diverse range of colors. From vibrant greens and browns to muted grays and yellows, these amphibians can seamlessly match the hues of the landscapes they inhabit. By mimicking the colors of surrounding vegetation or blending with the natural textures of rocks or water, frogs and toads effectively disappear from sight, remaining virtually invisible to both predators and prey.
But color alone is not the sole tool in the amphibians' disguise arsenal. Texture plays a crucial role in their camouflage techniques as well. The skin of frogs and toads often possesses a bumpy or warty texture that helps them assimilate with the rough surfaces of their environments. In addition, some species have evolved intricate patterns or markings on their bodies, such as stripes or spots, further enhancing their ability to disappear into the background.
Aside from color and texture, frogs and toads utilize a fascinating mechanism known as disruptive coloration to confuse predators. This technique involves having contrasting or irregular patterns on their body, which break up their outline and make it harder for predators to identify them as prey. By blending both into the environment and disrupting their own body shape, these amphibians successfully evade detection, increasing their chances of survival in the wild.
The camouflage techniques of frogs and toads serve as a testament to the remarkable adaptability and resourcefulness of these creatures. By mastering the art of blending in, they ensure their survival in diverse habitats, whether it be the lush rainforests, arid deserts, or tranquil ponds. Truly, the world of amphibians is a mesmerizing realm of hidden artistry, where nature's paintbrush transforms these creatures into masters of disguise.
To Jump or to Walk: Distinguishing the Locomotion Styles of Anurans
In the fascinating world of anurans, a captivating aspect lies in the distinguishing ways these amphibians move. Observing their locomotion styles provides insights into their unique adaptations and ecological roles. While some anurans are renowned for their remarkable leaping abilities, others prefer a more grounded approach, utilizing walking or hopping techniques. This section aims to explore the contrasting locomotion strategies employed by frogs and toads, revealing the intricacies that lie behind their agile movements.
To begin, let us delve into the mesmerizing world of frogs. Known for their exceptional jumping prowess, frogs utilize a powerful hind limb musculature to propel themselves through the air. Their highly specialized anatomy, including elongated hindlimbs and webbed feet, enables them to generate incredible force and cover substantial distances in a single bound. This unique ability allows frogs to swiftly navigate their surroundings, leaping from lily pads to tree branches with remarkable precision and accuracy.
In contrast, toads exhibit a more terrestrial locomotion style, relying on walking or short hopping movements to navigate their environment. Toads possess shorter hind limbs compared to frogs, which limit their jumping abilities. Instead, they employ a distinctive walking gait, utilizing their strong forelimbs and hindlimbs in a coordinated manner. The toes of toads are adapted for gripping and provide stability as they maneuver across various terrains. This unique locomotion style allows toads to explore diverse habitats, from leaf litter-covered forest floors to grassy meadows.
It is remarkable to witness the contrasting locomotion styles displayed by these anurans. While frogs gracefully soar through the air, propelled by their impressive jumping capabilities, toads conquer the ground with their methodical strides and nimble hops. Understanding the distinguishing characteristics of their locomotion strategies not only aids in identifying these amphibians but also sheds light on their ecological roles within their respective habitats. Whether it is the agile leaps of frogs or the measured steps of toads, each locomotion style showcases their remarkable adaptability and fascinating evolutionary journey.
In the Realm of Melodies: The Unique Serenades of Frogs and Toads

In the enchanting kingdom of chorus dwell amphibian musicians whose captivating melodies reverberate through tranquil nights. This segment uncovers the mesmerizing symphonies created by the denizens of this mystical realm, focusing on the distinguishable calls of these remarkable creatures.
Within this realm, these extraordinary creatures possess an extraordinary talent, using their resonant voices to captivate and communicate with their kin. Reverberating with a sonorous touch, these enchanting calls serve as a means of attracting mates and defending territories, making them an integral part of their intricate ecosystem.
The harmonious repertoire of these melodious creatures reveals a vibrant tapestry of sounds that echo within the enchanting atmosphere. Each species exhibits a distinctive vocalization, each note crowned with a unique quality, often resembling the musical rhythms and tones of a melodic symphony.
The rhythm of these calls varies greatly between different species, with some adopting a pulsating cadence, resembling the beat of a drum, while others emit a silky, undulating tune that mimics the gentle rustle of leaves dancing in the wind. The melodies can range from high-pitched trills reminiscent of a flute's serenade to deep and resonant croaks akin to a bass instrument's soulful reverberation.
Delving into the intricacies of these vocalizations unravels a world of communication and expression, as each call delivers a multitude of messages. From courtship songs that woo potential mates to territorial warnings that defend their domain, these melodious calls signify an incredible display of nature's symphony.
This captivating journey into the auditory realm of the land of chorus unveils the fascinating variations in calls among the frog and toad species. Illuminating both the differences and the harmonies within their serenades, this exploration sheds light on the intricate languages echoing throughout this remarkable kingdom.
Diet Preferences: Exploring the Feeding Habits of Frogs and Toads
When it comes to their dietary habits, both frogs and toads have intriguing and distinct preferences that contribute to their survival in their natural habitats. By delving into the food habits of these amphibians, we can gain a deeper understanding of their ecological roles and adaptations.
1. Diversity in Food Choices
- One captivating aspect of frogs and toads is their diverse range of food choices.
- These amphibians actively seek out various types of prey to meet their nutritional needs.
- Their diet consists of a wide array of invertebrates, such as insects, spiders, worms, and snails.
- Additionally, some species have been known to consume small vertebrates, such as fish or even other amphibians.
2. Foraging Techniques
- To successfully capture their food, frogs and toads employ different foraging techniques.
- Some species utilize their long, sticky tongues to snap up insects with lightning speed.
- Others rely on their excellent vision and agility to pounce and snatch prey from the ground or vegetation.
- Certain frog species are even capable of using their powerful hind legs to leap forward and catch prey mid-air.
3. Seasonal Variation
- Interestingly, the diet preferences of frogs and toads can be influenced by seasonal variations.
- During breeding periods, some species may prioritize consuming larger prey to provide the energy necessary for reproduction.
- In contrast, during less favorable conditions, they may resort to smaller prey or even consume plant matter.
- These adaptability strategies ensure their survival during times of scarcity.
4. Relevance to Ecosystems
- Frogs and toads play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of ecosystems through their feeding habits.
- As predators, they help control populations of insects and other invertebrates, preventing overpopulation and potential damage to vegetation.
- Furthermore, by consuming smaller individuals of their own species, they contribute to regulating their populations.
- Thus, their diet preferences have a significant impact on the overall biodiversity and health of their respective habitats.
By studying the diet preferences and feeding habits of frogs and toads, we can gain insights into their ecological importance and the intricate web of interactions within their ecosystems. Recognizing the significance of their role as bioindicators and understanding their dietary choices ultimately contributes to the conservation and preservation of these fascinating amphibians.
Survival Strategies: How Amphibians Adapt to Their Environment
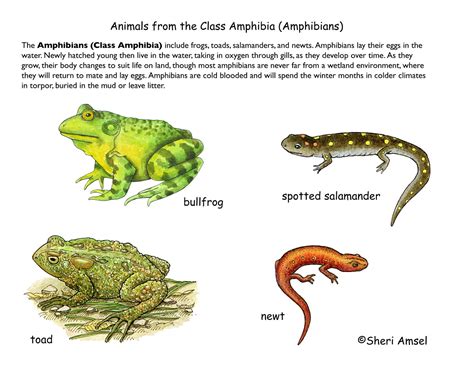
When it comes to surviving in diverse habitats, amphibians rely on a variety of fascinating strategies to adapt to their surroundings. These unique creatures have evolved over time, developing specialized traits and behaviors that allow them to thrive in different ecosystems.
One survival strategy employed by both frogs and toads is their remarkable ability to camouflage themselves. By blending in with their surroundings, these amphibians can effectively hide from predators and increase their chances of survival. Whether it's the frog's vibrant green coloration that helps it blend into the leafy vegetation of the forest floor, or the toad's mottled skin that resembles the rocks and soil it inhabits, camouflage plays a crucial role in enhancing their survival.
In addition to camouflage, frogs and toads have adapted their bodies to suit their respective habitats. For example, some frog species have long limbs that enable them to jump and maneuver effortlessly through grassy areas, while others have muscular bodies and strong legs, allowing them to swim swiftly in aquatic environments. On the other hand, toads have shorter legs and a stout body, which makes them well-suited for hopping and walking on land. These structural adaptations enable them to navigate their surroundings with ease, reducing the risk of predation.
| Frogs | Toads |
|---|---|
| Flexible limbs for jumping and climbing | Shorter legs for hopping and walking |
| Smooth, moist skin for efficient gas exchange and water absorption | Rough, dry skin for water conservation |
| Large eyes and a streamlined body for optimal vision and swimming | Bulging parotoid glands for defense and toxin secretion |
Furthermore, both frogs and toads have developed unique methods of reproduction that aid in their survival. Frogs typically lay their eggs in standing water, such as ponds or marshes, where the tadpoles can develop and eventually metamorphose into adult frogs. Toads, on the other hand, lay their eggs in strings, often wrapping them around aquatic vegetation to provide protection. These diverse reproductive strategies allow them to take advantage of available resources in their specific habitats.
In conclusion, frogs and toads employ a range of survival strategies to adapt to their surroundings. Through camouflage, structural adaptations, and reproductive techniques, these amphibians have successfully carved out niches in various ecosystems. Their ability to adapt showcases the remarkable diversity and resilience of these fascinating creatures.
FAQ
What is the difference between a frog and a toad?
A frog and a toad are both amphibians, but there are several differences between them. Frogs have smooth and moist skin, while toads have dry and bumpy skin. Frogs have longer legs and are better jumpers, while toads have shorter legs and prefer to walk or crawl. Frogs usually live near water bodies, while toads can be found in drier habitats. Lastly, frogs have teeth while toads do not.
How can I differentiate between a frog and a toad by their appearance?
There are a few physical characteristics that can help you differentiate between a frog and a toad. Frogs usually have slim bodies, longer hind legs, and smooth, moist skin. They also have long and slender toes with webbing between them. On the other hand, toads have plump bodies, shorter hind legs, and dry, bumpy skin. Their toes are short and stubby without any webbing. These differences in appearance are helpful in identifying whether you are observing a frog or a toad.
Are all frogs and toads green in color?
No, not all frogs and toads are green in color. While many frogs and toads do exhibit shades of green, they can come in various colors. Some frogs are brown, yellow, red, or even blue. Likewise, toads can be found in colors ranging from brown to gray to olive. The coloration of frogs and toads often serves as camouflage in their natural habitats, helping them blend in with their surroundings.
Can appearance be used to determine the species of a frog or toad?
While appearance can provide some clues, it is not always enough to determine the exact species of a frog or toad. Species identification usually requires a more comprehensive analysis that takes into account not only the physical appearance but also their behavior, habitat, and vocalizations. Moreover, some species of frogs and toads have similar appearances, making it even more challenging to identify them solely based on their looks.
Are there any poisonous frogs or toads with a distinctive appearance?
Yes, there are several species of frogs and toads that are poisonous and have distinct appearances. One example is the poison dart frog, which is known for its bright and vibrant colors, serving as a warning to potential predators. These small frogs showcase combinations of colors like red, blue, green, or yellow, indicating their toxicity. Similarly, some toads, such as the Colorado River toad, have glandular secretions that are highly toxic, and they often have distinctive patterns or markings to deter predators.
What is the difference between a frog and a toad?
A frog and a toad are both amphibians, but they have some differences in appearance. Frogs usually have smooth and moist skin, long legs, and slender bodies. Toads, on the other hand, have dry and bumpy skin, short legs, and stout bodies. Additionally, frogs have a preference for living near water, while toads can be found in a variety of habitats.




