Imagine a captivating spectacle that effortlessly captivates your attention and sparks your imagination. A stunning phenomenon, where tendrils of incandescence intertwine and dance, casting an ethereal glow upon its surroundings. This mesmerizing sight is a kaleidoscope of colors and shapes, a visual symphony that intrigues and enthralls all who witness it.
While it may seem like a surreal painting brought to life, this remarkable display is a very real occurrence in our world. Veils of swirling vapors envelop the air, creating a fascinating interplay of light and shadow. It is a delicately choreographed performance, where every movement tells a story, and each flicker reveals a hidden secret.
Referred to as the "fiery haze," this natural phenomenon has been the subject of curiosity and inquiry for centuries. Its alluring aura has inspired artists, poets, and scientists alike, each attempting to capture its elusive grace and unravel its enigmatic nature. It is a phenomenon that transcends time and space, evoking a sense of wonder and fascination that persists throughout the ages.
Observe closely, and you will witness an intricate tapestry forming before your eyes. Fiery tendrils ascend skyward, reaching out like fleeting fingers, their brilliant hues shifting subtly as they intertwine. The air is imbued with an otherworldly scent, a potent blend of warmth and mystery that adds to the allure of this incredible spectacle.
This captivating display occurs in a multitude of settings, from deep within majestic forests to barren desert landscapes. It enchants both day and night, as the fiery haze adapts to the changing light, casting an ever-evolving spell upon the world. It is a phenomenon that knows no bounds, transcending the boundaries of time, place, and perception.
As we delve deeper into the secrets of this enigmatic beauty, we uncover not only its visual allure but also its profound significance. The fiery haze serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between creation and destruction, of the perpetual cycle of transformation that defines our existence. It is a reminder that beauty can arise even from the most chaotic and destructive forces, reminding us of the resilience and adaptability of the natural world.
The Science Behind Smoke Formation During Fires
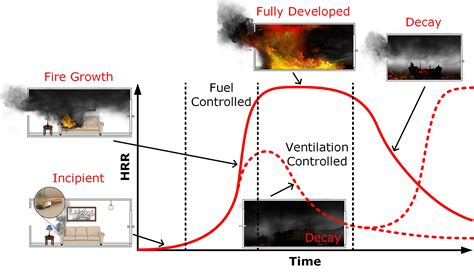
In this section, we will explore the scientific principles responsible for the production of the hazy and intriguing substance that commonly accompanies fires. Understanding the intricate processes involved in the formation of smoke goes beyond mere fascination, as it provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying fire behavior and poses significant implications for safety and pollution control.
Smoke, the captivating byproduct of combustion, arises from the intricate chemical reactions occurring when materials burn in the presence of oxygen. It encompasses a varying combination of solid particles, liquid droplets, and gases, each playing a distinct role in the overall composition and behavior of smoke. The mesmerizing visual effect it creates, with its billowing and swirling patterns, is a result of the complex interplay between these components.
One of the primary contributors to smoke formation is the incomplete combustion of organic matter, which occurs when fuels don't receive ample oxygen to fully burn. This incomplete burning leads to the release of fine particles, known as soot, that give smoke its characteristic dark appearance. Additionally, the presence of liquid droplets, such as tar or oil, adds another dimension to smoke's composition, as they can disperse light and contribute to the overall opacity of the plume.
Another key factor behind smoke formation is the vaporization and subsequent condensation of volatile compounds. As materials are heated during a fire, volatile substances within them transform into gas-phase molecules that mingle with the surrounding air. When this heated gas cools down, it reaches its saturation point, leading to the condensation of these volatile compounds into microscopic liquid droplets or solid particulates, which become integral components of smoke.
The size and composition of the particles present in smoke greatly influence its behavior and potential hazards. Fine particles, less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, are often more abundant in smoke and have a higher propensity to travel over long distances. These particles can also penetrate deep into the respiratory system when inhaled, posing significant health risks. Understanding the science behind smoke formation provides crucial knowledge for the development of effective strategies for fire management, pollution control, and improving the safety of our environments.
The Impact of Smoke on Human Health and the Environment
Smoke, an emitted substance resulting from the combustion of materials, possesses the potential to significantly affect both human health and the environment. This section presents a comprehensive exploration of the consequences brought about by the presence of smoke, deepening our understanding of its ramifications on various aspects.
Wildfires: A Major Source of Haze and Their Devastating Impact

When it comes to natural disasters, few events can rival the destructive force and profound consequences of wildfires. These rampant infernos, characterized by uncontrolled combustion, not only leave behind a trail of devastation but also contribute significantly to the propagation of dense haze that blankets the affected areas.
Ignited by various factors
The origins of wildfires can be diverse and complex, with ignition sources ranging from human activities, such as unattended campfires or discarded cigarettes, to natural causes like lightning strikes. Regardless of their initial spark, once ignited, these fires can spread rapidly across landscapes, fueled by an abundance of dry vegetation and strong winds.
Escalating haze pollution
As the flames devour forests and vegetation, they release an array of particles, gases, and aerosols into the atmosphere. Among these emissions, smoke plays a central role in creating the characteristic haze that engulfs affected areas. The particles suspended in the air can vary in size and composition, including microscopic soot, ash, and other organic compounds.
Environmental repercussions
The devastating effects of wildfires extend far beyond the visible destruction and haze. The dense smoke resulting from these conflagrations poses significant health risks to both humans and wildlife. Short-term exposure to the toxic mixtures can trigger respiratory problems, eye irritation, and exacerbate pre-existing conditions. Additionally, the long-lasting effects of this smoke can contribute to climate change by releasing substantial amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Challenges faced in combatting wildfires
Efforts to control and extinguish wildfires are often met with significant challenges due to their unpredictable nature and the vast areas they can consume. The combination of dry conditions, high temperatures, and strong winds that often accompany wildfires further compounds firefighting efforts. These factors, coupled with the potential for rapid fire spread, make it imperative for efficient coordination and resources to be allocated swiftly and effectively.
Mitigation strategies and future outlook
The mitigation of wildfires and their associated smoke effects require a multifaceted approach that encompasses prevention, early detection, and effective suppression techniques. Integrating technology advancements, such as aerial surveillance and remote sensing systems, can aid in identifying potential fire hotspots and enabling timely response. Additionally, promoting public awareness and implementing strict regulations can contribute to reducing ignition sources and minimizing the devastating impact of future wildfires.
FAQ
What causes a fire to produce smoke?
A fire produces smoke when organic material, such as wood or paper, undergoes incomplete combustion. As the fuel burns, it releases various particles, gases, and vapors that combine to form smoke.
Why is smoke often seen rising from a fire?
Smoke rises from a fire due to the principle of convection. When the fuel burns, hot gases and air molecules become less dense and rise upwards. This upward movement carries the smoke particles along with it, creating the visual effect of smoke rising.
What causes different colors and patterns in smoke?
The colors and patterns in smoke are caused by the presence of certain chemicals or substances in the burning material. For example, the addition of copper compounds can produce a greenish hue, while sodium compounds can create a yellow color. The patterns can be influenced by air currents and turbulence, which disperse and mix the smoke particles in different ways.
Can smoke from a fire be harmful to health?
Yes, smoke from a fire can be harmful to health. It contains a mixture of toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide, as well as fine particles that can irritate the respiratory system and cause breathing difficulties. Prolonged exposure to smoke can lead to serious health issues, especially for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.




