Imagine a world where the marvels of nature continue to astound us with their ingenuity and resilience. In the animal kingdom, the ability to adapt and survive in the face of daunting challenges is truly awe-inspiring. One group of creatures, in particular, has fascinated scientists and nature enthusiasts alike: reptiles.
Reptiles, with their ancient lineage and remarkable adaptations, have long captivated our imagination. From their robust armor-like scales to their unique physiological mechanisms, these cold-blooded creatures have continuously surprised us with their extraordinary abilities. However, one astonishing trait that often goes unnoticed is their incredible aptitude for navigating aquatic environments while in a state of slumber.
While most animals would succumb to the dangers of drowning in water during sleep, reptiles, with their unparalleled design, seem to effortlessly defy this peril. Whether they are classified as lizards, snakes, or turtles, these fascinating creatures have developed an intricate system that allows them to remain buoyant and safely asleep, despite the presence of surrounding water.
Within the realm of reptiles, this unique phenomenon has sparked curiosity and a quest for understanding. How do these creatures manage to avoid the affliction of drowning while in a state of vulnerability? What mechanisms do they possess that enable them to peacefully coexist with the element that is often seen as a threat to other organisms? Join us as we delve into the captivating world of reptiles and unravel the secrets behind their astonishing ability to navigate water during slumber.
The Remarkable Respiratory System of Lizards
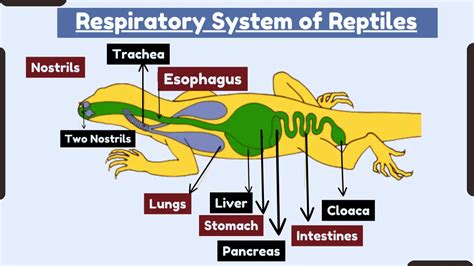
Within the fascinating world of reptiles, lizards possess a truly remarkable respiratory system that has evolved to suit their unique needs. This system allows them to efficiently exchange gases, ensuring their survival in diverse environments.
One key aspect of this evolved respiratory system is the adaptation of their lungs, which enables lizards to breathe in a variety of situations. Unlike humans and many other animals, lizards can regulate their breathing patterns and control the volume of air they inhale and exhale. This ability allows them to conserve water in arid habitats and adjust their metabolism accordingly.
Another adaptation is the presence of specialized organs known as cloacal bursae, which aid in gas exchange. These bursae contribute to the efficient absorption of oxygen, allowing lizards to thrive in environments with limited oxygen availability. The bursae also play a role in the elimination of carbon dioxide, helping maintain the delicate balance of gases within their bodies.
In addition to these adaptations, lizards utilize a unique form of respiration called "cutaneous respiration." This process involves the absorption of gases through their skin, particularly in aquatic species. Through cutaneous respiration, lizards are able to extract oxygen from water, ensuring their survival even when submerged.
Furthermore, lizards have an increased lung capacity compared to other reptiles, allowing for enhanced oxygen uptake during physical activities. This is particularly advantageous for arboreal species that require quick bursts of energy for climbing and leaping.
To summarize, the respiratory system of lizards is a marvel of evolution, allowing them to thrive in a wide range of habitats. From their adaptable lungs to the specialized cloacal bursae and the unique cutaneous respiration, lizards exemplify the incredible ability of animals to adapt and survive in their environments.
The Remarkable Adaptations for Oxygen Conservation
Within the realm of the astonishing capabilities displayed by certain species of lizards, a particular focus lies on their unparalleled adaptations for effective oxygen conservation. These remarkable physiological and behavioral traits equip them with the ability to optimize oxygen usage and ensure their survival in various environments.
Oxygen-carrying mechanisms
One of the key adaptations observed in these lizards involves their unique physiological mechanisms for carrying oxygen. Through intricate adaptations in their blood vessels and respiratory systems, these creatures are able to efficiently extract and transport oxygen, ensuring its availability even in challenging conditions or low-oxygen environments.
Respiratory adjustments
In addition to their specialized oxygen-carrying mechanisms, these lizards demonstrate exceptional respiratory adaptations. They possess the ability to regulate their breathing rates and depths, exhibiting remarkable control over their oxygen intake. This flexibility allows them to conserve oxygen during periods of rest or in oxygen-deprived environments, ensuring their sustained survival.
Metabolic adaptations
The unique metabolic adaptations seen in these lizards further contribute to their astonishing ability to conserve oxygen. Along with their optimized oxygen-carrying systems and respiratory adjustment capabilities, these creatures have evolved specific metabolic pathways that enhance their overall energy efficiency. This advantageous trait not only enables them to sustain prolonged periods without oxygen but also facilitates their survival in varied habitats.
Behavioral strategies
Complementing their physiological adaptations, these lizards have also developed intricate behavioral strategies to conserve oxygen. They exhibit behaviors such as basking in the sun to absorb heat, thus raising their metabolic rate and optimizing oxygen utilization. Additionally, they employ efficient movement patterns and utilize preferred microhabitats that facilitate enhanced oxygen availability, all contributing to their exceptional survival abilities.
Evolutionary significance
The unique adaptations displayed by these lizards for oxygen conservation hold significant evolutionary importance. These remarkable traits have not only facilitated their survival in diverse environments but have also contributed to their ecological success. Through their astonishing ability to maintain oxygen homeostasis, these lizards have carved a niche for themselves, demonstrating the intricate interplay between physiological adaptations and evolutionary fitness.
How Lizards Regulate Their Breathing Patterns During Sleep

In this section, we will explore the fascinating mechanisms behind the control of respiratory rhythm in lizards while they are in a state of slumber. During sleep, lizards exhibit remarkable adaptations to ensure effective oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion without the typical conscious effort seen in their wakeful states.
One fundamental aspect of understanding how lizards regulate their breathing during sleep involves examining their respiratory centers' function. These centers, responsible for coordinating breathing patterns, exhibit distinct behaviors during different stages of sleep, allowing lizards to adapt their respiration according to their physiological needs. This intrinsic ability serves to optimize oxygenation and maintain the metabolic equilibrium essential for their survival.
Control of Breathing During Different Sleep Phases
During the initial stages of sleep, known as non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, lizards exhibit shallow and regular breathing. The respiratory rate slows down, ensuring a steady exchange of gases while conserving energy. As lizards transition to the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep phase, their breathing patterns vary significantly. Intermittent deep breaths interspersed with irregular pauses characterize this stage. This unique respiratory pattern might be linked to the fascinating phenomenon of dreaming in lizards.
The Intriguing Role of Brain Activity
Research suggests that the brain's activity during REM sleep plays a vital role in regulating the irregular breathing patterns exhibited by lizards. While the exact mechanism is yet to be fully understood, it is believed that neural impulses originating from specialized regions in the lizard's brain, such as the brainstem, influence the respiratory centers, resulting in the distinctive breathing patterns observed during this sleep phase.
Adaptations for Efficient Gas Exchange
Another intriguing aspect encompassing lizards' breathing during sleep relates to their ability to maintain efficient gas exchange despite the intermittent breathing patterns. Special adaptations in their respiratory organs and lung structure contribute to this remarkable feat. For instance, their lungs possess a high surface area to volume ratio, allowing for optimized gas exchange even during shallow breaths. Furthermore, the presence of specialized air sacs aids in the smooth flow of oxygen-rich air to various regions of their lungs, ensuring efficient respiration.
Understanding the intricate mechanisms underlying lizards' control of breathing during sleep sheds light on the astonishing adaptations these reptiles have developed to thrive in various habitats and environmental conditions.
The Fascinating Implications for Future Research
Exploring the remarkable abilities exhibited by lizards in water and the potential impact on scientific knowledge presents an exciting avenue for future research. This incredible phenomenon offers intriguing possibilities for understanding the intricate workings of the dream state in non-human species and its potential applications in various fields.
Unraveling the underlying mechanisms behind lizards' capacity to stay afloat and navigate through water despite their dream-induced physiological inactivity can shed light on a host of scientific inquiries. This discovery ignites the curiosity of researchers in the fields of neurobiology, physiology, and evolutionary biology, encouraging them to delve deeper into the complexities of the lizard brain and its remarkable adaptability.
One significant aspect that future research could focus on is the identification of the specific neural pathways and brain regions responsible for enabling lizards to remain buoyant and react to external stimuli even while immersed in water. Exploring these neural circuits can provide invaluable insights into the evolution of sleep and dreaming, potentially leading to a greater understanding of the purpose and function of these states across different species.
The implications of this fascinating ability extend beyond the realm of basic science. Understanding how lizards maintain their equilibrium and actively resist drowning in water during dreaming offers potential applications in enhancing human water safety systems and designing innovative aquatic technologies. By extrapolating the biological mechanisms employed by these reptiles, researchers could develop novel ideas for life-saving devices and improve human performance and safety in water-related activities.
Furthermore, future investigations could also explore the potential implications of this phenomenon in the field of biomimicry. The ability of lizards to remain unharmed and exhibit autonomous behavior in water while dreaming opens up avenues for replicating their adaptive strategies in the development of advanced underwater robots and vehicles. By mimicking the physiological and behavioral characteristics observed in lizards, researchers may create more efficient and resilient technologies for underwater exploration and environmental monitoring.
In conclusion, the astonishing capacity of lizards to survive and navigate in water while dreaming opens up a wealth of possibilities for future research. The interdisciplinary nature of this subject invites collaborations between various scientific disciplines, potentially leading to groundbreaking discoveries in the study of sleep, neurobiology, and technological advancements, with broad applications in both human and environmental contexts.
FAQ
How do lizards manage to not drown in water while they are dreaming?
According to the study mentioned in the article, lizards have a fascinating ability to close their nostrils tightly while sleeping, preventing water from entering their respiratory system. This allows them to stay safe and avoid drowning even when surrounded by water.
Are there any other animals that have a similar ability to lizards?
While the article mainly focuses on lizards, it states that some other reptiles, such as turtles and crocodiles, also possess the ability to close their nostrils tightly. This ensures that they can survive in water without inhaling it into their respiratory system.
What is the significance of the findings from this study?
The findings from this study provide a better understanding of the remarkable adaptations that lizards have developed to survive in various environments. By learning more about their ability to prevent drowning while sleeping, scientists can gain insights into respiratory adaptations in other animals as well.




