Within the realm of destructive natural phenomena, a raging inferno commands both awe and trepidation. This relentless fury of flames possesses an uncanny ability to decimate vast landscapes, leaving behind a trail of devastation and despair. The intricate tapestry of factors that give rise to these conflagrations encompasses a nexus of triggers that often eludes our grasp, demanding a comprehensive understanding to not only mitigate their cataclysmic impacts but prevent their occurrence altogether.
When nature's wrath wreaks havoc, buildings crumble, landscapes transform into charred wastelands, and ecosystems teeter on the brink of collapse. The aftermath of such calamities can scar communities, inflicting long-lasting emotional and economic distress. The profound implications of these events, both on a local and global scale, underscore the pressing need to decipher the intricate web of causes that ignites these fiery tempests.
As the ashes settle and the smoke dissipates, it becomes evident that fire's origins, though variegated and complex, can be traced back to a handful of key catalysts. These multifaceted triggers, like enigmatic puzzle pieces, intertwine to create the perfect tinderbox, combustible and primed for conflagration. Unraveling their intricate interplay is the key to unlocking the secrets that will enable us to tame this elemental force.
Through a circuitous exploration of the diverse factors that coalesce to kindle these infernos, we begin to understand the unyielding grip that fire holds over our environment. From weather patterns and climate change to human activities and ecological imbalances, a multitude of influences dance in a delicate equilibrium, rendering even the most serene landscapes vulnerable to the incendiary whims of fate.
The Devastating Effects of Forest Fires

Forest fires have catastrophic consequences that stretch far beyond the mere combustion of trees and vegetation. These natural disasters inflict widespread damage on ecosystems, wildlife habitats, and human communities, leaving a trail of destruction in their wake.
The environmental impact of forest fires is profound. They contribute to air pollution by releasing massive amounts of smoke and harmful gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change. Additionally, the destruction of forests leads to soil erosion, reducing the earth's ability to absorb and filter water, which can result in increased flooding and landslides.
Moreover, forest fires have dire implications for wildlife. Countless species of animals, birds, and insects lose their homes and food sources in the inferno, leading to imbalances in ecosystems and potential population declines. The destruction of habitats can also disrupt migration patterns, further endangering vulnerable species.
Human communities are not immune to the devastating effects of forest fires. The loss of homes, infrastructure, and livelihoods can have severe economic and social repercussions. Health issues arise from the smoke and ash, affecting not only those directly impacted by the fires but also residents in surrounding areas.
| Effects of Forest Fires | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Environmental Impact | The release of smoke and harmful gases contributes to air pollution and climate change. Soil erosion increases the risk of flooding and landslides. |
| 2. Wildlife Disruption | Loss of habitat affects numerous animal species, disrupts ecosystems, and impacts migration patterns. |
| 3. Human Impacts | Loss of homes, infrastructure, and livelihoods, along with health issues caused by smoke and ash, have severe economic and social repercussions. |
Understanding the devastating effects of forest fires reinforces the importance of prevention measures and effective fire management strategies. By mitigating the risks and supporting ecosystem recovery, we can strive to minimize the long-term impacts of these destructive events.
Unraveling the Intricate Catalysts of Wildfires
In the realm of natural disasters, wildfires epitomize the devastating force of nature, instilling a sense of awe and curiosity to comprehend the intricacies behind their occurrence. These catastrophic events are a result of a complex interplay of factors, necessitating a comprehensive examination of the diverse stimuli that lead to the ignition and rapid spread of these hazardous flames.
1. Environmental Conditions: Fueled by the convergence of various environmental elements, fires may emerge as a consequence of combustible materials, such as dried vegetation or fallen trees, coming into contact with external heat sources, including lightning strikes and volcanic activity. Moreover, the prevalence of dry climates, gusty winds, and prolonged droughts amplifies the susceptibility of an area to wildfires.
2. Human Activities: Although nature sets the stage, human actions often act as a spark, enhancing the likelihood and severity of wildfires. Inadvertent causes, such as poorly extinguished campfires, discarded cigarettes, or intentional arson, contribute significantly to the fire's initiation and progression. Additionally, deforestation practices, negligent handling of flammable materials, and land mismanagement practices further exacerbate the vulnerability of ecosystems to accidental or deliberate fire outbreaks.
3. Climate Change: As our planet experiences unprecedented shifts in climate patterns, the relationship between wildfires and the changing environment demands attention. Rising temperatures, reducing soil moisture, and altering precipitation patterns create a conducive setting for the ignition and rapid spread of fires. The intensification and alteration of wildfire regimes serve as stark reminders of the interconnected nature of climate change and these ravaging infernos.
4. Ecological Implications: Wildfires have far-reaching impacts on ecosystems, influencing flora, fauna, and overall biodiversity. While some species exhibit remarkable adaptations to fire, others suffer severe consequences, leading to population declines or even local extinctions. The intricate web of ecological relationships unravels in the aftermath of a fire, often leading to shifts in species composition and ecosystem dynamics.
5. Preventative Measures: In the pursuit of safeguarding lives, homes, and natural habitats, understanding the complex causes of wildfires is instrumental in implementing effective preventive strategies. These measures include promoting education and awareness campaigns, strengthening fire-resistant infrastructure, implementing controlled burns, and adopting responsible land management practices.
In unraveling the complex causes of wildfires, it becomes evident that a multifaceted approach is essential to mitigate the impacts associated with these destructive phenomena. By comprehending the intricate interplay of factors and implementing preventive measures, humanity can strive toward a future where the fury of wildfires is tamed, and the harmony between nature and human activities is delicately restored.
The Impact of Climate Change on the Escalation of Wildfires
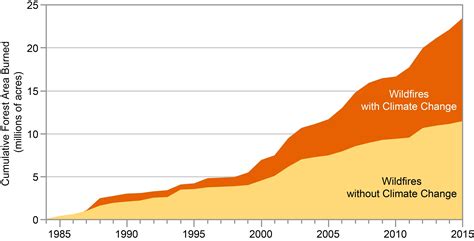
As our planet continues to face the consequences of environmental shifts, the correlation between climate change and the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfire outbreaks has become a topic of great concern. The role of fluctuating weather patterns, rising temperatures, and altered precipitation levels cannot be ignored when investigating the causes and effects of these devastating events.
Understanding the Role of Human Activities in the Ignition Sources and Spread of Fires
In the domain of fire management, it is of utmost importance to acknowledge and comprehend the impact of human activities on the ignition sources and subsequent spread of fires. While natural causes such as lightning strikes contribute to fire incidents, human actions play a significant role in both initiating and facilitating fire outbreaks. By exploring the various ways in which human activities influence the ignition sources and fire spread, we can develop a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics of fire management.
It is evident that certain human practices act as ignition sources for fires. The improper disposal of cigarettes, open flames from activities like campfires or cooking, as well as electrical malfunctions are just a few examples of common ignition sources caused by human actions. Furthermore, industrial activities involving flammable materials and equipment can also unintentionally give rise to fire incidents. Understanding the various ignition sources caused by human activities is essential for implementing preventive measures and promoting responsible behavior.
However, human activities not only contribute to the ignition of fires but also significantly affect their spread. Careless behavior, such as leaving a fire unattended or failing to properly extinguish it, can allow for rapid fire propagation, especially in dry and windy conditions. Additionally, human settlements and infrastructure can create fuel sources that aid in the spread of fires, as buildings, vegetation, and other combustible materials become intertwined with the fire's path. Recognizing the role of human actions in the spread of fires enables us to develop effective strategies for wildfire containment and prevention.
Therefore, by acknowledging the role of human activities in both the ignition sources and the spread of fires, we can work towards minimizing the risk of fire outbreaks. Through education, awareness, and the adoption of responsible practices, we have the power to mitigate the negative impacts of human actions on the occurrence and severity of fires. A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between human activities and fire incidents is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies, ensuring the safety of both human lives and natural ecosystems.
The Devastating Consequences of Wildfires on Biodiversity

Wildfires wreak havoc on the delicate balance of biodiversity, leaving behind a trail of destruction and irreversible consequences. These catastrophic events, characterized by their fierce and uncontrollable nature, have far-reaching impacts on the myriad of plant and animal species that inhabit our planet. The loss of biodiversity, driven by the destructive force of wildfires, poses a grave threat to the intricate web of life that sustains our ecosystems.
The Peril to Human Health and Safety in the Midst of Wildfires
Amidst the raging inferno of a wildfire, the vitality and well-being of human beings face unprecedented threats. When these devastating natural disasters occur, communities are thrust into a state of insecurity and peril, with significant consequences for human health and safety.
Endangered respiratory systems: As wildfires combust, they release a deluge of noxious gases, particulate matter, and toxins into the surrounding air. Inhalation of these hazardous pollutants can lead to severe respiratory issues and exacerbate pre-existing conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The elderly, children, and those with compromised immune systems are especially vulnerable.
Escalating risks of burns and injuries: The ferocity of a wildfire puts lives at risk as it engulfs anything in its path. Not only can individuals suffer from direct burns, but they may also experience injuries from falling debris, collapsing structures, or accidents during evacuation processes. Firefighters, valiantly battling the blaze, face a heightened danger to their safety while striving to protect communities.
Psychological toll and trauma: The psychological impact of wildfires extends far beyond the physical harm caused. Witnessing the destruction of homes, displacement, and the potential loss of loved ones can inflict deep emotional scars on survivors. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and other mental health conditions can develop, requiring long-term support and care for affected individuals and communities.
In order to safeguard human lives amidst the blaze, it becomes imperative to enhance preventive measures, early warning systems, and community preparedness. By understanding and acknowledging the grave consequences wildfires pose to human health and safety, we can strive for effective mitigation strategies to minimize their devastating impacts.
Strategies to Mitigate and Prevent Forest Fires

In this section, we will delve into effective approaches and methods that can be employed to minimize the occurrence and impact of forest fires. By focusing on proactive measures and comprehensive planning, we can actively work towards preserving our valuable ecosystems and protecting lives and property.
1. Fuel Management: One crucial strategy involves the management of fuel loads within the forested areas. This entails the removal of dead trees, clearing of dry leaves and brush, and controlled burns, helping to reduce the amount of flammable material available to wildfires. By implementing regular fuel management practices, we can create defensible spaces between forested areas and human settlements, limiting the potential for fires to spread rapidly.
2. Early Detection and Rapid Response: Developing advanced early detection systems using state-of-the-art technology plays a vital role in preventing the escalation of forest fires. Utilizing satellite imagery, drones, and ground-based surveillance systems, we can promptly identify ignition sources and initiate immediate response actions. By swiftly mobilizing firefighting resources, such as trained personnel and equipment, we can effectively combat and contain wildfires before they spread extensively.
3. Community Education and Awareness: Educating communities living in close proximity to forested areas about fire prevention and safety measures is paramount. Public awareness campaigns and community workshops can impart knowledge on fire prevention strategies, promoting responsible behavior in activities such as campfires and disposal of cigarette butts. By fostering a culture of fire-consciousness, we can encourage individuals to play an active role in keeping the forests safe.
4. Collaboration and Partnerships: Establishing strong collaborations and partnerships among various stakeholders is vital for effective forest fire prevention. This involves coordination between government agencies, firefighting organizations, land managers, and local communities. By working together, sharing resources and expertise, we can develop comprehensive fire management plans, implement preventive measures, and respond swiftly during fire incidents.
5. Climate Change Adaptation: Recognizing and addressing the influence of climate change is crucial to mitigating the risk of forest fires. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered precipitation patterns contribute to the increasing severity and frequency of wildfires. By implementing strategies to adapt to these changes, such as implementing water conservation practices, maintaining healthy forest ecosystems, and promoting sustainable land-use practices, we can enhance the resilience of forests and reduce the vulnerability to catastrophic fires.
By employing a combination of these strategies and continuously adapting our approach based on scientific research and technological advancements, we can make significant progress in mitigating and preventing forest fires. It is imperative that we prioritize the protection and preservation of our forests to ensure a sustainable and resilient future for both nature and humanity.
The Significance of Fire Management Practices
In the field of fire control, there exist a range of strategies and techniques that play an indispensable role in mitigating the adverse effects of fiery incidents. These practices, which contribute to the prevention, control, and suppression of fires, are crucial in safeguarding lives, ecosystems, and valuable resources. By emphasizing proactive measures, systematic planning, and the utilization of advanced technologies, fire management practices aim to mitigate the potential risks associated with fire outbreaks.
Ecosystem Preservation Effective fire management practices ensure the preservation and restoration of diverse ecosystems. By implementing controlled burns and prescribed fire techniques, trained professionals can maintain ecological balance and enhance biodiversity. This approach prevents the dominance of certain species, reduces the risk of destructive wildfires, and promotes the growth of native vegetation. | Protection of Human Life The implementation of sound fire management practices significantly reduces the threat of fires to human communities. It encompasses various aspects such as early detection systems, public education, evacuation planning, and the establishment of fire-resistant infrastructure. These measures enhance community resilience, minimize casualties, and ensure the rapid response of emergency services in the event of a fire emergency. |
Sustainable Resource Management Fire management practices play a vital role in the sustainable management of natural resources. Through the implementation of controlled burns, selective logging, and proper land management techniques, the risk of uncontrolled wildfires that can devastate forests and valuable resources can be mitigated. These practices enable the responsible utilization of forest products, such as timber, while ensuring the long-term health and productivity of ecosystems. | Prevention of Property Damage By employing fire management strategies, the risk of property damage caused by fires can be minimized. These practices include the creation of firebreaks, the development of fire-resistant building codes, and the implementation of effective fire suppression techniques. Through careful planning and the enforcement of preventive measures, the destructive impacts of fire incidents on infrastructure, residential areas, and commercial properties can be significantly reduced. |
In conclusion, the significance of fire management practices lies in their ability to protect ecosystems, preserve human life, ensure sustainable resource management, and prevent property damage. By embracing proactive measures and innovative approaches, society can effectively minimize the dangers posed by fires and work towards a safer and more resilient future.
Community Involvement and Education in Fire Prevention

In the pursuit of safeguarding our surroundings from the devastating effects of destructive incidents that result in the release of intense heat and fierce flames, it is imperative to recognize the importance of active participation and enlightenment within the local population. By fostering a strong sense of community involvement and prioritizing education on preventive measures, we can collectively endeavor to mitigate the occurrence and severity of these destructive occurrences.
Empowering the community: A fundamental pillar in the quest for fire prevention lies in empowering the community to take ownership of their safety. By cultivating a sense of responsibility among residents, fostering a mindset of vigilance and preparedness, and enabling individuals to take action when situations arise, we can significantly reduce the risk and impact of fire incidents.
Education as a catalyst: Education serves as a catalyst for change, arming individuals with the knowledge and understanding necessary to make informed decisions. Through interactive workshops, informative sessions, and engaging campaigns, we can disseminate crucial information on fire prevention techniques, evacuation procedures, and the correct usage of fire safety equipment. Equipping individuals with this knowledge ensures that they possess the tools to protect themselves, their families, and their immediate surroundings.
The role of partnerships: Collaborative efforts between community members, local authorities, and firefighting agencies play a key role in fire prevention. By fostering partnerships and establishing effective communication channels, we can form a united front against fire incidents. Together, we can strategize, develop evacuation plans, conduct drills, and promote a culture of awareness and preparedness within the community.
Instilling a culture of fire safety: Beyond providing education and resources, it is crucial to foster a culture of fire safety within the community. By promoting responsible behavior, emphasizing the significance of early detection and prompt reporting of potential fire hazards, and encouraging the regular maintenance of fire safety equipment, we can ensure the sustained protection of our community.
Through community involvement and prioritizing education, we can create a resilient and proactive society in the face of fire incidents. By embracing the power of collective action and education, we hold the key to a safer future for ourselves and future generations.
FAQ
What are the main causes of fires?
The main causes of fires can vary, but some common causes include electrical malfunctions, cooking accidents, smoking, and arson.
What are the impacts of fires?
The impacts of fires can be devastating. They can destroy homes, buildings, and forests, causing severe property damage and loss of life. Fires also release toxic smoke, contribute to air pollution, and have long-term ecological effects.
How can fires be prevented?
Fires can be prevented by following safety protocols such as regularly checking electrical wiring, using caution when cooking, properly disposing of cigarettes, and being vigilant about fire hazards. Education and awareness campaigns also play a crucial role in fire prevention.
What should I do in case of a fire?
If there is a fire, it is important to stay calm and follow evacuation procedures. Alert others in the vicinity, call emergency services, and exit the building using designated escape routes. Never use elevators during a fire emergency.




