Imagine a scene, a scene that transports you to a world of raw power and hidden potential. Envision a mesmerizing landscape where the earth's treasure lies waiting to be unearthed. In this vision, there is no light, no color, but a deep darkness that hints at the immense energy contained within.
In this twilight realm, a captivating sight unfolds before your eyes. A towering mountain of solid carbon stands proudly, commanding attention with its sheer magnitude. It is a silent testament to the ancient forests that once thrived, transforming under the weight of time into this extraordinary substance we now call anthracite.
As you gaze upon this monumental structure, you cannot help but feel a sense of reverence for its untold power. Each piece, etched with the passage of time, holds within it the capability to ignite flames and fuel the world. It is a potent reminder that even in the darkest of depths, there is light and warmth waiting to be harnessed.
The allure of this ebony monolith is heightened by its mysterious aura. The surface of each fragment reflects an otherworldly sheen, as if the shadows themselves have become tangible. It is a curious dichotomy – a substance born from nature's depths, yet possessing an inexplicable beauty that captivates the soul.
While the individual pieces may appear unremarkable, it is their collective presence that evokes a sense of awe. The chaotic jumble of jagged edges and rough surfaces harmonizes to form a tableau that is both powerful and fragile. It is a reminder that the unity of small elements can create extraordinary strength.
The Strength and Significance of the Carbonic Energy Source
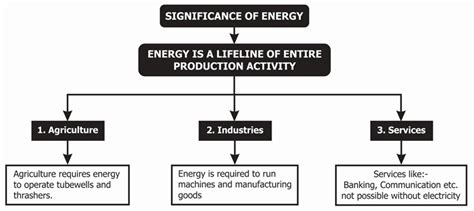
Underneath the surface lies a resource of immense power, hidden deep within the earth's crust. Its influence reaches far and wide, providing an indispensable source of energy that has played a pivotal role in shaping the modern world. This remarkable substance, synonymous with strength and resilience, fuels industries and powers nations, propelling progress and driving economic growth. Its importance cannot be understated, as it continues to be a vital component in meeting the global energy demands of today.
The Fascinating History of Anthracite Mining
Explore the captivating narrative of extracting the highly prized anthracite, as we delve into the historical significance and development of this essential energy resource.
Anthracite mining, a remarkable tale of human ingenuity and industrial advancement, offers a mesmerizing glimpse into the past. Journey back in time to witness the evolution of this invaluable natural resource, its impact on societies, and the arduous labor that shaped civilizations.
Dating back centuries, successive generations have sought and tirelessly toiled to uncover this remarkable fuel source. From its early discovery by ancient civilizations to the modern-day techniques employed, the history of anthracite mining encompasses technological breakthroughs, economic transformation, and environmental implications.
The allure of anthracite mining lies not only in its economic significance but also in its profound influence on cultural and social landscapes. From forging thriving communities in mining towns to fueling industrial revolutions, the extraction of this rich, carbonaceous material has been intrinsically linked to the rise of nations.
Delve deeper into the annals of history as we unravel tales of triumph and tragedy, innovation and exploitation, and the interplay between man and nature. Explore the sociopolitical factors that have shaped the mining industry and the consequences that have paved the way to modern-day sustainability efforts.
Through untold stories and forgotten accounts, discover how anthracite mining has woven itself into the fabric of civilization, forever leaving its mark on the trajectory of human development.
Environmental Impact of Coal Mining and Utilization
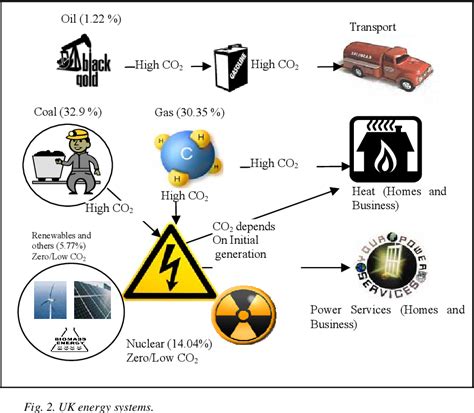
Coal mining and the subsequent utilization of coal have significant impacts on the environment, ecosystem, and human health. This section aims to provide an overview of the environmental consequences associated with coal extraction and usage, emphasizing the importance of sustainable alternatives.
| Environmental Consequences | Synonyms for "Consequences" |
|---|---|
| 1. Air Pollution | Effects on atmospheric quality |
| 2. Water Contamination | Adverse impacts on water quality |
| 3. Soil Degradation | Deterioration of land quality |
| 4. Deforestation | Destruction of forests |
| 5. Climate Change | Alterations in global climate patterns |
| 6. Acid Rain | Corrosive precipitation |
| 7. Ecosystem Disruption | Interference with natural habitats |
| 8. Human Health Risks | Threats to human well-being |
The extraction of coal involves the release of harmful pollutants into the air, negatively affecting atmospheric quality and contributing to climate change. Furthermore, the mining process can contaminate nearby water sources, leading to the deterioration of water quality and posing risks to both aquatic life and human health. The loss of vegetation and the destruction of forests due to mining activities result in habitat disruption and can increase the vulnerability of ecosystems to further degradation.
In addition to the direct environmental consequences, the combustion of coal for energy generation produces greenhouse gas emissions that intensify the greenhouse effect and aggravate climate change. This, in turn, has a range of potential impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions in agricultural systems. Acid rain, a byproduct of coal combustion, can damage infrastructure and further contribute to ecological imbalance.
It is essential to acknowledge these environmental challenges and seek sustainable alternatives to coal as an energy source. The development and adoption of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, offer viable solutions to reduce the environmental impact associated with coal mining and utilization. By prioritizing clean energy sources, we can mitigate the detrimental effects on our planet and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
The Vital Role of Coal in Power Generation
Coal, an abundant and versatile fossil fuel, plays a crucial role in the generation of energy worldwide. With its rich carbon content, coal serves as a reliable source of fuel for power plants, enabling the production of electricity on a massive scale. Moreover, coal exhibits several advantages that make it an attractive option for energy generation.
Firstly, coal offers affordability, as it remains one of the most cost-effective sources of energy. Its widespread availability, combined with efficient mining and extraction techniques, ensures a steady supply of this valuable resource. Furthermore, coal can be easily stored and transported, making it a convenient choice for power generation in various locations.
- Reliability: The consistent and uninterrupted supply of electricity is a critical requirement for modern society. Coal-fired power plants can provide a stable source of energy, as coal reserves are vast and accessible across different regions.
- Energy Efficiency: Coal possesses a high energy density, which means that a relatively small amount of coal can generate a significant amount of energy. This efficiency contributes to reducing overall fuel consumption and lowering the environmental impact.
- Technology Compatibility: The existing infrastructure and technology in power plants are highly compatible with coal combustion. Retrofitting coal-fired power plants with advanced emission control technologies enables the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and improves environmental performance.
- Power Generation Flexibility: Coal combustion can be easily modulated to meet fluctuating demand for electricity. This adaptability ensures stability and reliability in the power grid, supporting the integration of renewable energy sources.
While the environmental impact and CO2 emissions associated with coal combustion are areas of concern, the ongoing advancements in clean coal technologies and the development of carbon capture and storage methods promise a more sustainable future for coal-based power generation.
In conclusion, coal holds a significant position in the energy mix, providing a reliable, affordable, and efficient source of power generation. As the world moves towards a cleaner and greener energy landscape, the responsible and sustainable use of coal remains a critical consideration for meeting the growing global energy demand.
Advancements in the Technological Realm of Mining Fossil Fuel Reserves

In the ever-evolving landscape of extracting natural resources from the Earth's depths, the mining industry has witnessed significant progress propelled by technological breakthroughs. This article aims to explore the paradigm shift in coal mining methods and techniques that have revolutionized the extraction process, amplifying efficiency and safety while reducing environmental impact.
Automated Machinery:
The advent of automated machinery has transformed the coal mining landscape, replacing conventional manual labor with cutting-edge technology. These mechanized systems have led to higher productivity rates and precision in the extraction process. Intelligent machines equipped with sensors and monitoring devices have enabled mining operations to be conducted with enhanced accuracy and minimal human intervention.
For example, the introduction of longwall mining systems has eliminated the need for human operators to physically extract coal seams. Instead, powered supports move along the face, enabling simultaneous cutting and coal extraction, thereby increasing overall efficiency and worker safety.
Remote Sensing and Imaging:
The utilization of remote sensing and imaging technologies has significantly enhanced coal exploration and improved the accuracy of resource estimation. Through aerial surveys, drones equipped with advanced sensors capture high-resolution images of prospective mining sites, facilitating an in-depth analysis of geological formations. This aids in the identification of potential coal reserves and minimizes exploratory disruptions on land.
Furthermore, the integration of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology allows accurate mapping and evaluation of terrain topography, indicating viable access routes and assisting in the development of comprehensive mining plans.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling:
With the rise of big data analytics, the mining industry has embraced sophisticated algorithms and predictive modeling techniques to optimize coal extraction processes. By analyzing vast data sets generated during mining operations, these tools enable proactive maintenance of equipment, facilitating the prevention of machinery failures and reducing downtime.
Moreover, by leveraging machine learning algorithms, mining companies can enhance operational efficiency by predicting potential risks and optimizing coal recovery methods based on historical data patterns. This empowers decision-makers in making informed choices and improving the overall profitability and sustainability of coal mining operations.
In conclusion, the advancements witnessed in the technological realm of coal mining have propelled the industry toward unprecedented levels of efficiency, safety, and environmental responsibility. The integration of automated machinery, remote sensing and imaging technologies, and data analytics has revolutionized the extraction process, ensuring that the vast reserves of this critical fossil fuel are harnessed with utmost precision and sustainability.
The Economical Influence of the Coal Industry
Exploring the vast impact of the coal industry on the economy, this section delves into the significant contribution of this fossil fuel sector in terms of fiscal growth, job creation, energy production, and global trade.
Coal as a Vital Source of Global Energy
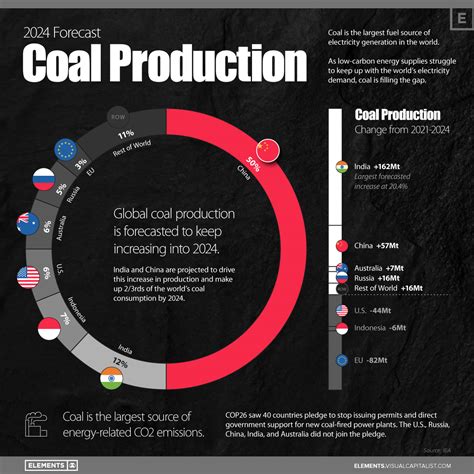
The significance of coal as a cornerstone of energy production around the world cannot be underestimated. This carbon-rich sedimentary rock plays a pivotal role in powering nations, driving economic growth, and meeting the ever-increasing energy demands of a rapidly developing world.
Coal, often referred to as "the black diamond," symbolizes the energy potential derived from ancient organic matter and geological processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years. This highly combustible resource, abundant in various regions, serves as the foundation for generating electricity, supplying heat in diverse industries, and fueling transportation systems.
Coal-fired power plants, a hallmark of modern civilization, dot the landscapes of numerous countries, providing a steady and cost-effective source of electricity. With its remarkable energy density and ease of transport, coal has the capability to generate significant power output while enabling efficient energy distribution.
In addition to its role in electricity generation, coal plays a crucial part in various industrial processes worldwide. The extractive and manufacturing industries rely on coal as a vital feedstock, furnishing raw materials for steel production, cement manufacturing, chemical synthesis, and more. Moreover, coal's versatility extends to being employed as a reducing agent, facilitating mineral extraction, and contributing to the creation of many essential products and materials.
The existence of extensive coal reserves across the globe ensures energy security and independence for numerous nations. Furthermore, coal has historically played a transitional role, enabling the transition from traditional biomass use to more efficient energy sources, thereby advancing societal development and improving living standards. As environmental concerns arise, the effective management of coal resources becomes crucial to minimize the impact of coal mining and combustion on air quality, land degradation, and climate change.
In conclusion, the economic, social, and environmental implications of coal as a global energy resource are manifold. Understanding and harnessing the potential of coal in a sustainable manner while prioritizing responsible mining practices and embracing clean coal technologies are essential steps towards achieving a secure and diverse energy future.
The Future of Coal: Challenges and Opportunities
In this section, we explore the prospects and potential hurdles surrounding the utilization of a valuable and versatile energy resource. The future of coal presents a dynamic landscape of challenges and opportunities that will shape the energy sector and its sustainability.
1. Shifting Energy Demands: As global energy demands continue to evolve, the coal industry must adapt to changing market dynamics. The increasing focus on renewable energy sources and the transition towards cleaner energy alternatives have created a significant shift in the global energy mix.
2. Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of coal mining and combustion has become a topic of immense concern, necessitating stringent regulations and the development of cleaner technologies. Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigate air pollution, and ensure the reclamation of mining sites pose both challenges and opportunities for the coal industry.
3. Technological Innovations: Advancements in clean coal technologies offer a promising path for the future of coal. Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies, along with improved efficiency in coal combustion and the utilization of waste heat, aim to minimize environmental footprints and enhance the sustainability of coal as an energy source.
4. Economic Implications: The economic viability of coal remains a key factor in its future utilization. While the declining cost of renewable energy sources presents a substantial challenge, coal's abundance and affordability in certain regions provide opportunities for continued utilization, especially in developing economies.
- 5. Coal-to-Products: Diversification of coal utilization through the development of high-value products, such as carbon fibers and chemicals, offers a potential avenue for the coal industry. These innovations can add value to coal and reduce its reliance solely on energy production.
- 6. Transition Support: As the energy landscape evolves, support mechanisms and strategies are vital to facilitate the transition away from coal-dependent economies. Investments in education, job retraining, and infrastructure development can create new avenues for economic growth, while ensuring a just and sustainable transition for communities reliant on coal.
While the challenges faced by the coal industry are significant, addressing them presents an opportunity for innovation and collaboration. By navigating the environmental concerns, embracing technological breakthroughs, and reimagining the role of coal in the energy mix, the future of coal can be shaped in a way that balances economic growth, sustainability, and environmental stewardship.
FAQ
What is the article "A Dream of a Pile of Black Coal" about?
The article "A Dream of a Pile of Black Coal" is about a dream that someone had, where they saw a large pile of black coal.
Who had the dream mentioned in the article "A Dream of a Pile of Black Coal"?
The dream mentioned in the article "A Dream of a Pile of Black Coal" was had by an anonymous individual.
What does the pile of black coal symbolize in the dream?
The meaning behind the pile of black coal in the dream is not explicitly mentioned in the article. It could be subject to interpretation and personal analysis.
Are there any specific details mentioned in the article about the dream?
Yes, the article briefly describes the dream as someone seeing a large pile of black coal, but it does not provide further specific details.
Does the article provide any analysis of the dream or its significance?
No, the article does not provide any analysis or interpretation of the dream or its significance. It simply mentions the dream and its imagery.




