Within the intricacies of women’s health lie a myriad of enigmas, one of which is the mysterious realm of ovarian cysts. These small sacs, nestled within the ovaries, can cause a range of symptoms and complications, making it essential for women to understand and manage them effectively. In this article, we embark on a journey of comprehension and empowerment, shedding light on the intricacies of ovarian cysts and equipping women with the knowledge they need to navigate this delicate aspect of their well-being.
Wrapped in an air of uncertainty, the concept of ovarian cysts often seems shrouded in ambiguity. However, by delving deep into their nature, we can unravel their complexities and grasp their significance within the female reproductive system. Ovarian cysts, endurance artists of the ovary, are fluid-filled sacs that can develop for various reasons, such as hormonal imbalances or abnormal cell growth. Despite their prevalence, the effects of ovarian cysts can vary greatly from woman to woman, presenting a challenge in comprehending and managing this intricate facet of women’s health.
Your voyage into understanding ovarian cysts will be guided by the remarkable stories of women who have braved this uncharted territory. Their shared experiences, emboldened by their enduring strength, form the foundation of this exploration, serving as a source of connection and inspiration. Together, we will embark on a journey that melds scientific understanding with personal narratives, arming readers with both knowledge and empathy as we navigate the thorny path of ovarian cysts.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts

Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries. These sacs can vary in size, from as small as a pea to as large as a grapefruit. They are a common condition that affects many women at some point in their lives.
In this section, we will explore the concept of ovarian cysts, providing a comprehensive understanding of what they are and their potential impact on women's health. We will discuss the different types of ovarian cysts, their causes, symptoms, and potential complications.
Understanding ovarian cysts is essential for women to recognize the signs and symptoms, seek appropriate medical attention, and manage the condition effectively. By gaining a deeper understanding, women can make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
| Topics Covered in this Section: |
|---|
| 1. Introduction to Ovarian Cysts |
| 2. Different Types of Ovarian Cysts |
| 3. Causes and Risk Factors |
| 4. Recognizing Symptoms |
| 5. Potential Complications |
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Recognizing the signs of ovarian cysts is crucial in understanding their impact on women's health. These symptoms vary in intensity and may appear differently from one person to another. It is essential to be aware of these indicators to seek early detection and appropriate medical intervention.
- Abdominal discomfort or pain: Women with ovarian cysts may experience persistent abdominal discomfort or pain, often described as a dull, aching sensation.
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Ovarian cysts can disrupt the normal hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods, including heavy or light bleeding.
- Pelvic pressure: Some women may feel a sense of pressure or fullness in the pelvic area, which is often associated with the presence of ovarian cysts.
- Changes in bladder and bowel habits: Ovarian cysts can exert pressure on neighboring organs, causing frequent urination, difficulty emptying the bladder completely, or changes in bowel movements.
- Unexplained weight gain: The hormonal imbalances caused by ovarian cysts can result in unexplained weight gain or bloating, particularly around the abdominal area.
- Pain during sexual intercourse: In some cases, ovarian cysts can lead to discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse.
- Changes in breast tenderness: Ovarian cysts may cause changes in breast tenderness or sensitivity.
- Risk of fertility issues: Certain types of ovarian cysts can interfere with fertility and increase the risk of complications during pregnancy.
It is important to note that the presence of these symptoms does not automatically indicate the presence of ovarian cysts. Only a medical professional can accurately diagnose and provide the appropriate treatment based on a comprehensive evaluation and diagnostic tests. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are crucial in maintaining women's reproductive health and well-being.
Identifying and Assessing Ovarian Cysts
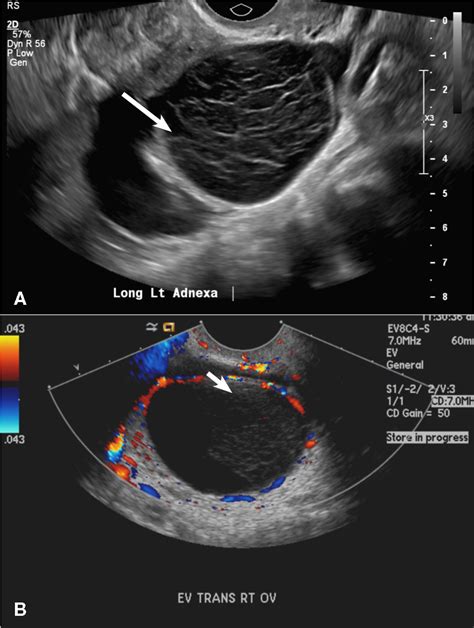
Determining the presence and characteristics of ovarian cysts is a crucial step in diagnosing and evaluating their impact on a woman's health. This section will outline the methods used to identify and assess ovarian cysts effectively, without delving into overly technical terms or medical jargon.
- Medical History: The first step in diagnosing ovarian cysts involves discussing the patient's medical history. A healthcare provider will ask about any past or current symptoms, as well as the duration and intensity of these symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A thorough pelvic examination is often performed to detect signs of ovarian cysts. The healthcare provider will carefully assess the ovaries, uterus, and surrounding areas for any irregularities or tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: Various imaging techniques can offer valuable insights into the presence, size, and characteristics of ovarian cysts. Ultrasound, a commonly used imaging test, uses sound waves to create a visual representation of the ovaries and cysts, aiding in identification and assessment.
- Blood Tests: Hormone levels and tumor markers in the blood can provide further information and help in diagnosing ovarian cysts. These tests may include measuring levels of estrogen, progesterone, and certain proteins that may indicate the presence of a cyst.
- Additional Diagnostic Procedures: In some cases, additional procedures may be required to obtain a more accurate diagnosis. These procedures can include laparoscopy, which uses a thin, lighted tube to examine the ovaries and surrounding structures, or cyst aspiration, which involves draining fluid from the cyst for further analysis.
By combining the information obtained from the patient's medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, blood tests, and potentially additional diagnostic procedures, healthcare providers can effectively diagnose and evaluate ovarian cysts. This comprehensive approach allows for appropriate management and treatment decisions tailored to each individual's unique circumstances and needs.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Exploring the various categories of cysts that can develop on the ovaries provides valuable insight into understanding the diversity of this condition. Knowledge about different types of ovarian cysts is crucial in managing and treating them effectively.
- Follicle Cysts: These cysts form when the follicle, which contains an egg, does not rupture to release the egg during ovulation. Instead, the follicle continues to grow and becomes a cyst.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: These cysts occur after ovulation when the sac that contained the egg does not shrink as it should. Instead, it fills with fluid and creates a cyst.
- Dermoid Cysts: Also known as mature cystic teratomas, dermoid cysts are a type of ovarian tumor that develops from embryonic cells. They can contain various tissues such as hair, teeth, and even bone.
- Endometriomas: These cysts are formed as a result of endometriosis, a condition where the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it. Endometriomas are filled with thick, old blood.
- Cystadenomas: These cysts form from the cells on the surface of the ovary. They can be filled with a watery fluid or a mucous-like substance.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that leads to the growth of numerous small cysts on the ovaries. These cysts can interfere with regular ovulation and cause various symptoms.
Understanding the different types of ovarian cysts is vital for early detection, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment. Each type requires a specific approach, and knowing the characteristics and potential complications associated with different cysts is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts

In this section, we will explore the various approaches available to address and manage the presence of ovarian cysts. These treatment options range from conservative measures to more invasive procedures, and are designed to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent future complications.
1. Watchful Waiting: In certain cases, small ovarian cysts may not require immediate medical intervention. Instead, a healthcare provider may choose to monitor the cysts over time, through regular check-ups and ultrasounds, to ensure that they do not grow or cause any worrisome symptoms. This approach is often recommended when the cysts are small and not causing discomfort.
2. Pain Management: For individuals experiencing pain or discomfort as a result of ovarian cysts, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can offer temporary relief. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medications, especially if there are underlying medical conditions or allergies.
3. Hormonal Birth Control: Another treatment option involves the use of hormonal birth control methods, such as birth control pills or contraceptive patches. These methods work by regulating the menstrual cycle and preventing the development of new ovarian cysts. However, it is important to note that hormonal birth control may not be suitable for everyone and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
4. Surgical Intervention: In cases where ovarian cysts are large, causing severe pain, are suspected of being cancerous, or persist despite other treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. The type of surgery performed depends on various factors, including the size and location of the cysts, as well as the individual's overall health. Surgical options can range from minimally invasive procedures, such as laparoscopy, to more extensive surgeries, such as oophorectomy (removal of the affected ovary).
5. Lifestyle Changes and Alternative Therapies: In addition to medical interventions, certain lifestyle changes and alternative therapies may provide relief and support the management of ovarian cysts. This can include adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and complementary therapies such as acupuncture or herbal remedies. These approaches should always be discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and suitable.
Remember, the choice of treatment option for ovarian cysts will depend on several factors unique to each individual, including the size of the cysts, the severity of symptoms, and overall health. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Managing Ovarian Cysts through Lifestyle Changes
Embracing a healthy lifestyle can play a crucial role in effectively addressing and managing the presence of ovarian cysts. By implementing certain lifestyle changes, individuals can potentially alleviate symptoms, promote hormone balance, reduce the risk of cyst development, and support overall reproductive health.
1. Nourish your body with a balanced diet
Achieving hormonal balance and supporting ovarian health begins with a well-rounded diet. Incorporate a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Moreover, opt for foods that are low in processed sugars and unhealthy fats, as these can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances.
2. Maintain a healthy weight
Obesity and excess weight have been linked to an increased risk of developing ovarian cysts. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through regular physical activity and a balanced diet, individuals can potentially reduce their susceptibility to cyst formation and improve overall reproductive health.
3. Practice stress management techniques
Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and may worsen symptoms associated with ovarian cysts. Implementing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or engaging in enjoyable hobbies and activities can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
4. Engage in regular physical activity
Regular exercise is essential for promoting hormone balance, reducing inflammation, and maintaining a healthy weight. Engage in activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling for at least 30 minutes a day, most days of the week, to support ovarian health and overall wellness.
5. Avoid exposure to toxic substances
Exposure to certain toxins and environmental pollutants can disrupt hormone levels and potentially contribute to the development of ovarian cysts. Minimize exposure to harmful substances by opting for natural and organic personal care products, avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, and maintaining a clean and toxin-free living environment.
6. Prioritize proper sleep hygiene
Adequate sleep is crucial for hormone production and regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night and establish a regular sleep routine to support hormonal balance and overall reproductive health.
By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can strategically manage and support their ovarian health while also potentially reducing the risk of cyst development and alleviating associated symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and management strategies based on individual needs and circumstances.
Potential Complications of Ovarian Cysts
In this segment, we explore the various complications that may arise in relation to cysts located in the ovaries. We delve into the possible risks and adverse effects that can be associated with these fluid-filled sacs, presenting a comprehensive understanding of the potential complications that individuals may encounter.
1. Ruptured cysts: One potential complication of ovarian cysts is their tendency to rupture. This occurs when the cyst's wall breaks, releasing its contents into the surrounding area. A ruptured cyst can cause severe pain, internal bleeding, and infection.
2. Torsion: Another complication arises when an ovarian cyst causes the ovary to twist or shift from its normal position, leading to a condition known as ovarian torsion. This can result in intense pain, restricted blood flow to the ovary, and potential tissue damage.
3. Formation of adhesions: Ovarian cysts can also contribute to the development of adhesions. These abnormal bands of scar tissue can form and attach to surrounding organs, leading to pain, discomfort, and potentially affecting fertility.
4. Infertility: In some cases, ovarian cysts can interfere with reproductive processes, affecting fertility. Cysts may disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries, impeding the release of eggs or altering hormonal balance, making conception more challenging.
5. Cancerous cysts: Though less common, there is a small risk of ovarian cysts being cancerous. This underscores the importance of timely medical evaluation and diagnosis to determine if further intervention is necessary.
6. Complications during pregnancy: For women who become pregnant, certain types of ovarian cysts can lead to complications during gestation. Cysts may increase the risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, or other obstetric complications, requiring careful monitoring and management throughout pregnancy.
7. Impact on hormonal balance: Ovarian cysts have the potential to disrupt the delicate hormonal balance within the body, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, hormonal imbalances, and associated symptoms such as weight gain, acne, and mood swings.
Understanding the potential complications associated with ovarian cysts is crucial in order to recognize symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention promptly. By being informed about these possible adverse outcomes, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and mitigate the risks.
Recognizing the Need for Medical Assistance with Ovarian Cysts
Identifying the appropriate time to seek professional medical guidance for issues related to ovarian cysts is crucial to ensure prompt and appropriate care. Recognizing signs and symptoms that warrant consultation with a healthcare provider empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health.
Understanding the Signs: Awareness of potential indications of significant complications associated with ovarian cysts is vital. These may include persistent pelvic pain or discomfort, sudden and severe pain, unusual menstrual bleeding, changes in menstrual cycle patterns, difficulty with urination or bowel movements, and unexplained weight gain.
Recognizing Risk Factors: Certain factors increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts, and such circumstances may necessitate medical attention. These risk factors include a family history of ovarian cysts or ovarian cancer, hormonal imbalances, endocrine disorders, infertility issues, and previous experiences of ovarian cysts requiring intervention.
Seeking Timely Treatment: If any of the aforementioned signs or risk factors are present, it is advisable to consult a doctor promptly. Medical professionals possess the expertise to evaluate symptoms, conduct appropriate diagnostic tests, and recommend suitable treatment options.
Emphasizing Personal Discomfort: Each individual's experience and tolerance for discomfort differs, so it is essential to trust one's instincts when deciding to seek medical help. If symptoms are causing significant physical discomfort or interfering with daily activities, it is advisable to consult a doctor for personalized guidance.
Empowering Proactive Health Management: Recognizing the importance of timely medical intervention enables individuals to take charge of their health and seek appropriate guidance when necessary. Health professionals can provide accurate diagnoses, offer relevant treatment options, and provide the necessary support to manage ovarian cysts effectively.
FAQ
What are ovarian cysts and how do they develop?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on or inside the ovaries. They develop when the follicles, which normally release eggs, do not rupture to release the egg, causing the follicles to grow and form cysts.
What are the common symptoms of ovarian cysts?
The common symptoms of ovarian cysts include pelvic pain, bloating, irregular menstrual cycles, pain during intercourse, frequent urination, and feeling full quickly while eating.
Can ovarian cysts be cancerous?
While most ovarian cysts are non-cancerous and go away on their own, some cysts can be cancerous. It is important to get regular check-ups and consult with a healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms or have concerns about ovarian cysts.
How are ovarian cysts diagnosed?
Ovarian cysts are often diagnosed through an ultrasound or pelvic examination. Blood tests may also be done to check hormone levels and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for ovarian cysts?
The treatment options for ovarian cysts depend on various factors such as the size, type, and symptoms of the cyst. Small, asymptomatic cysts may not require treatment and can be monitored. However, larger cysts or those causing severe symptoms may require medication, hormonal therapy, or surgical removal.




