Picture a formidable force gracefully cascading down the rugged slopes, leaving a trail of devastation in its wake. This captivating spectacle, commonly known as a landslide, represents a fascinating natural phenomenon demanding our attention and understanding. Delving into the depths of this topic reveals a wealth of knowledge about the earth's restless movements, the delicate balance of ecosystems, and the impact on human lives.
Unleashing a tempest of destruction, a landslide commands our respect for its immense power and capability to reshape the environment. The mesmerizing dance between gravity and geological formations gives birth to these breathtaking events, where cliffs crumble, boulders soar through the air, and the ground opens up like a hungry beast. Despite its awe-inspiring nature, we must not overlook the inherent dangers and consequences associated with this tumultuous display.
A landslide ignites a symphony of chaos - a harmonious union of rocks, soil, and water on a grand scale. Each component plays an indispensable role in this natural opera, with soil acting as the star performer. When rainfall drenches the land, it saturates the soil and disrupts its cohesion, weakening its grip on the slopes. The stage is then set for the main act – the force of gravity – which pulls at the loose, unsteady earth, triggering the cascade of a landslide. While these events may be predictable to some extent, the intricacies of their occurrence remain a mystery that scientists continue to unravel.
Understanding the Nature of Landslides
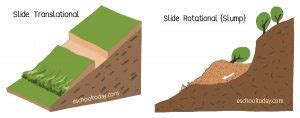
In this section, we will explore the essential elements of landslides to gain a deeper understanding of their nature. By examining their causes, characteristics, and potential impacts, we can better comprehend the complexities of these natural phenomena.
- Causes: Landslides can occur due to a variety of factors, including geological, meteorological, and human-induced causes. Geological causes can involve rock composition, slope angle, and soil properties, while meteorological factors such as heavy rainfall and earthquakes can trigger landslides. Additionally, human activities like deforestation, construction, and mining can weaken slopes and contribute to landslide occurrences.
- Characteristics: Landslides can exhibit diverse characteristics depending on their type and scale. They can range from slow-moving to rapid events, with speeds varying from fractions of a meter per year to several meters per second. Types of landslides include rotational slides, translational slides, debris flows, and rockfalls. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for evaluating the potential risks and implementing appropriate mitigation measures.
- Impacts: Landslides can have severe consequences, affecting both human settlements and the environment. They can lead to property damage, infrastructure disruptions, loss of life, and displacement of communities. The impacts can extend beyond the immediate area of the landslide, causing damage to ecosystems, water resources, and transportation networks. Recognizing the potential impacts is vital for developing strategies to minimize the vulnerability to landslides.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the nature of landslides, we can enhance our ability to identify risk areas, implement preventive measures, and effectively respond to these hazard events. This knowledge is key to mitigating the impacts of landslides and ensuring the safety and resilience of communities living in landslide-prone areas.
The Origins of Landslide Occurrences
Understanding the factors that contribute to the formation of landslides is crucial in comprehending the occurrence of these devastating natural disasters. By exploring the various causes behind landslides, we can gain insight into the mechanisms and triggers that result in the movement of large masses of earth and rock.
One primary factor influencing landslides is the geological composition of an area. Different types of soil and rock exhibit varying degrees of stability, making certain regions more prone to landslides than others. The presence of loose, unconsolidated materials, such as sandy or clayey soils, significantly increases the susceptibility to landslides, especially in hilly or mountainous terrain.
Another vital aspect that contributes to landslides is the geomorphology of an area. The steepness of slopes and the presence of water channels, such as rivers or streams, can significantly impact the stability of land. Excessive rainfall or rapid snowmelt can saturate the soil, reducing its strength and increasing the likelihood of a landslide occurrence.
Human activities also play a significant role in triggering landslides. Activities such as deforestation, mining, excavation, and construction can disturb the natural balance of the land, weakening its stability and making it more susceptible to slope failures. Improper drainage systems and the modification of natural drainage patterns can further exacerbate the risk of landslides.
Furthermore, geological events such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions can have a profound impact on landslide occurrences. The intense ground shaking caused by seismic activity can destabilize slopes, leading to landslides. Similarly, volcanic eruptions can generate pyroclastic flows or release large volumes of water, triggering landslides in the surrounding areas.
By comprehending the multifaceted causes behind landslides, we can better anticipate, mitigate, and respond to these hazardous events. Through proper land management, engineering solutions, and proactive measures, we strive to minimize the devastating consequences of landslides and protect vulnerable communities from the destructive power of nature.
Identifying Areas at High Risk for Landslides

Assessing the vulnerability of regions prone to landslides is crucial for disaster prevention and mitigation efforts. By identifying areas with high potential for landslides, authorities can implement proactive measures to reduce the risks associated with these natural hazards.
One method of determining high-risk locations is through a comprehensive geotechnical assessment. This process involves analyzing various factors such as slope steepness, soil type, and geological features to evaluate the stability of an area. Areas with steep slopes, loose or unstable soils, and a history of previous landslides are more susceptible to future occurrences.
In addition to geotechnical assessments, monitoring techniques can also help identify areas prone to landslides. Continuous monitoring of ground movement, changes in soil moisture levels, and the behavior of cracks or fractures can provide valuable insights into the potential for landslides. These observations allow for early warning systems to be implemented, enabling authorities to evacuate residents and take necessary precautions before a disaster strikes.
| Factors Considered in Identifying High-Risk Areas for Landslides |
|---|
| Slope steepness |
| Soil type |
| Geological features |
| Historical landslide data |
By combining the findings of geotechnical assessments with ongoing monitoring efforts, authorities can create comprehensive landslide risk maps. These maps highlight areas at high risk for landslides, allowing for effective land use planning, infrastructure development, and the implementation of suitable protective measures.
Understanding and identifying high-risk areas is essential for minimizing potential damage and protecting lives in landslide-prone regions. By utilizing scientific techniques and continuously updating risk assessments, communities can better prepare for these natural disasters and ensure the safety and well-being of their residents.
Understanding the Environmental Consequences of Landslides
In the realm of natural disasters, landslides emerge as powerful and impactful events that shape the environment in unforeseen ways. These catastrophic events result in the movement of large volumes of soil and rock down slopes, causing significant disturbances to the natural ecosystems and landscapes they encounter.
Ecological Disruption: The environmental impact of landslides extends beyond the immediate destruction caused by their immense force. As masses of soil and rock shift and settle, entire ecosystems are disrupted and often reshaped. The loss of vegetation and alteration of topography can lead to serious consequences for the stability of animal populations and the delicate balance of an ecosystem's biodiversity.
Soil Erosion: One of the primary consequences of landslides is the accelerated erosion of topsoil. The force exerted by the moving earth strips away the protective layer of soil responsible for supporting plant life and absorbing rainfall. As a result, valuable nutrients are washed away, negatively impacting the fertility of affected areas and hindering agricultural productivity.
Water Contamination: Landslides often disturb natural waterways, leading to the contamination of freshwater sources. The movement of soil and debris introduces sediments and pollutants into rivers, lakes, and groundwater, affecting water quality and potentially compromising the health and survival of aquatic organisms. Furthermore, the alteration of natural drainage patterns can result in increased risks of flooding and further damage to surrounding communities.
Loss of Habitat: The destruction caused by landslides can lead to the loss of critical habitats for various species, exacerbating the ongoing global issue of biodiversity loss. When large sections of land are displaced or buried, the natural habitats and nesting grounds essential for the survival of plants and animals are destroyed. The subsequent fragmentation and isolation of habitats can disrupt migration patterns, create barriers to gene flow, and ultimately endanger species' long-term survival.
Long-term Recovery: While the environmental impacts of landslides are devastating, efforts can be made to initiate long-term recovery and restoration. Measures such as reforestation, erosion control, and land-use planning can mitigate the effects of landslides and promote the restoration of affected ecosystems.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of landslides is far-reaching and multifaceted. Understanding the consequences of these natural disasters is essential for developing strategies to mitigate their effects, protect ecosystems, and support the long-term sustainability of the environment.
The Indicators of an Approaching Landslide

The Warning Signs of an Impending Landslide section aims to shed light on the various indications that hint at the possibility of a landslide occurrence. By recognizing and understanding these signals, individuals can take proactive measures to ensure their safety and minimize potential damage.
- Unusual Soil and Ground Conditions: Changes in soil texture, color, or moisture content, as well as the presence of cracks or sinkholes in the ground, are clear indications of possible landslide activity.
- Sudden Water Presence: The emergence of springs or saturated areas where water was not present before may suggest that excessive water accumulation could trigger a landslide.
- Increased Surface Flow: A significant increase in the flow of water or mud on slopes or hillsides, especially during or after heavy rainfall, can be a warning sign of an impending landslide.
- Failure of Vegetation: Unusual patterns of damage or death among trees and plants, such as tilting trees, exposed roots, or a sudden disappearance of vegetation, may indicate the likelihood of a landslide event.
- Cracking Structures: Structural elements such as walls, foundations, or roads experiencing new cracks or significant shifts can be indicative of ground movement associated with potential landslides.
- Widening and Tilting Structures: Buildings or other structures showing signs of tilting, leaning, or separating from adjacent structures suggest that the ground underneath could be unstable.
- Unusual Sounds and Noises: The occurrence of strange creaking, rumbling, or cracking sounds originating from the ground may be a result of soil movement, indicating an impending landslide.
It is crucial to note that these warning signs should not be considered independently, but rather in combination with each other. Recognizing a combination of these indicators can help assess the potential risk of a landslide and prompt appropriate preventive actions.
Preparing for Landslide Events
In the face of potential natural disasters like landslides, it is crucial to be proactive and well-informed in order to safeguard oneself and the community. This section will focus on the necessary steps and preparations to mitigate the impact of landslide events.
Understanding the Hazards:
Before one can effectively prepare for a landslide event, it is essential to comprehend the characteristics and potential risks associated with such occurrences. By gaining knowledge about the geological and environmental factors that contribute to landslides, individuals can identify vulnerable areas and better assess their level of exposure to these hazards. Familiarity with the warning signs, such as changes in the landscape or ground movement, is equally important in recognizing imminent landslide events.
Evaluating Vulnerability:
Once one understands the hazards, it is crucial to assess the vulnerability of the surroundings. This involves analyzing the terrain, slope stability, and land use patterns in the area. Consultation with experts or local authorities can provide invaluable information on past landslide incidents and the potential for future occurrences. Evaluating the vulnerability allows for the implementation of appropriate measures tailored to the specific risks and conditions of the area.
Developing an Emergency Plan:
Developing a comprehensive emergency plan is essential for preparedness in the event of a landslide. This plan should include evacuation routes, designated meeting points, and communication channels to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals. It is crucial to regularly review and practice the emergency plan with all members of the community to ensure everyone is familiar with the procedures and can act swiftly in the face of an emergency.
Maintaining Awareness:
Continuous monitoring and staying informed about potential landslide threats are vital in staying prepared. This can be achieved through maintaining regular contact with local authorities, subscribing to alert systems, and monitoring weather conditions. By staying vigilant, individuals can be proactive in taking necessary precautions and responding promptly to any warnings or alerts.
Taking Preventive Measures:
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the impact of a landslide event. These measures may include constructing retaining walls, installing drainage systems, and planting vegetation to reinforce slopes and stabilize the soil. Additionally, practicing responsible land management practices, such as minimizing earthwork and avoiding deforestation, can help maintain the stability of the land and minimize the likelihood of landslides.
In conclusion, preparing for landslide events involves understanding the hazards, evaluating vulnerability, developing an emergency plan, maintaining awareness, and implementing preventive measures. By taking proactive steps and being well-prepared, individuals and communities can minimize the risks and potential damages caused by landslide events.
Effective Strategies for Preventing Landslides
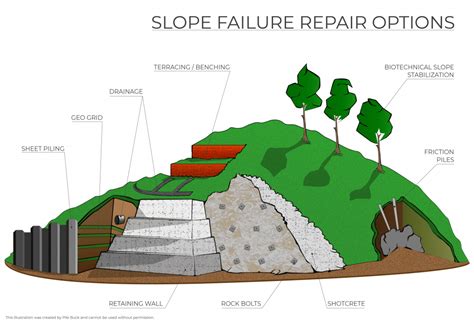
In this section, we will explore various approaches and techniques that can be employed to minimize the occurrence of landslides. These strategies aim to mitigate the risks associated with slope instability and promote safer environments for human habitation and infrastructure development.
One key aspect of landslide prevention is land-use management. Proper planning and zoning can play a crucial role in identifying areas prone to landslides and ensuring that appropriate measures are taken to minimize their impact. By understanding the geological and topographical characteristics of a region, authorities can create regulations and guidelines for construction practices that adhere to safe slope stability principles.
In addition to land-use management, engineering solutions are essential in landslide prevention. Structural interventions, such as the installation of retaining walls, soil stabilization techniques, and drainage systems, can help stabilize slopes and reduce the risk of landslides. These measures often involve the use of geosynthetic materials, geo-textiles, and rock bolts to reinforce the stability of slopes and prevent soil erosion.
Vegetation management also plays a significant role in landslide prevention. Planting and maintaining vegetation on slopes act as a natural barrier against erosion and slope failures. The roots of trees and plants help bind the soil, reducing the likelihood of landslides triggered by heavy rainfall or seismic activity. Additionally, the implementation of green infrastructure practices, such as green roofs and permeable pavements, can assist in controlling stormwater runoff, minimizing erosion, and maintaining the stability of slopes.
Early warning systems are another vital component of landslide prevention. Monitoring technologies, including geotechnical instrumentation and remote sensing, allow for the detection of potential landslide hazards in advance. Effective early warning systems can provide timely alerts, enabling evacuation measures and risk mitigation strategies to be implemented promptly, thereby saving lives and minimizing property damage.
Education and awareness are crucial elements in the fight against landslides. Public knowledge about the causes, signs, and potential impacts of landslides can empower individuals to take appropriate precautions and report any potential risks to the authorities. By fostering a culture of preparedness and resilience, communities can actively participate in landslide prevention efforts and contribute to the overall safety and well-being of their surroundings.
Response and Recovery in the Aftermath of a Landslide
When a landslide strikes, a community must come together to respond and recover from the devastating effects. In the aftermath of such a natural disaster, it is crucial to have a well-coordinated and efficient response plan in place to ensure the safety of affected individuals and to begin the recovery process.
- Immediate Response: The immediate response to a landslide involves assessing the extent of the damage and ensuring the safety of the affected population. Emergency services, such as rescue teams and medical personnel, play a vital role in providing immediate assistance and support. Evacuation of affected areas and establishing temporary shelters for displaced individuals are essential during this phase.
- Damage Assessment: Once the initial response is underway, it is crucial to conduct a thorough assessment of the damage caused by the landslide. This includes evaluating the stability of remaining structures, determining the extent of infrastructure damage, and identifying potential hazards in the affected areas. This information is vital for planning and prioritizing recovery efforts.
- Recovery Planning: In the aftermath of a landslide, recovery planning plays a crucial role in rebuilding and restoring affected communities. This involves developing comprehensive recovery strategies, coordinating resources, and engaging stakeholders to ensure a coordinated and efficient recovery process. The goal is to facilitate the return of normalcy and resilience to the affected areas.
- Infrastructure Rehabilitation: One of the key aspects of post-landslide recovery is rehabilitating damaged infrastructure. This includes repairing or reconstructing roads, bridges, utilities, and other critical structures that have been affected. Reconstruction efforts must prioritize safety and resilience to prevent future disasters.
- Psychosocial Support: In the aftermath of a landslide, individuals and communities may experience trauma and emotional distress. Providing psychosocial support is essential to help affected individuals cope with the aftermath of the disaster. This can involve counseling services, support groups, and community engagement initiatives to promote healing and resilience.
- Long-term Resilience: Building long-term resilience is a key component of recovery in the aftermath of a landslide. This involves incorporating disaster risk reduction measures into urban planning, implementing early warning systems, and promoting sustainable land management practices. By enhancing resilience, communities can better prepare for future landslides and reduce their vulnerability to similar disasters.
In conclusion, effective response and recovery efforts are crucial in the aftermath of a landslide. By coordinating emergency response, conducting damage assessments, planning for recovery, rehabilitating infrastructure, providing psychosocial support, and promoting long-term resilience, impacted communities can begin the process of rebuilding and healing after such a devastating event.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring and Predicting Landslides

Technology plays a crucial role in the monitoring and prediction of landslides, providing valuable insights into their occurrence, behavior, and potential consequences. By harnessing state-of-the-art tools and techniques, scientists and experts are able to enhance our understanding of this natural hazard and develop strategies to mitigate its impact on human lives and infrastructure.
One of the key technologies used in landslide monitoring is remote sensing, which involves the collection of data from a distance. Satellites, aerial imagery, and ground-based sensors provide detailed information about the environment, including topography, vegetation, and geological composition. This data is then analyzed to identify areas prone to landslides and monitor any changes in slope movements over time.
In addition to remote sensing, geotechnical instruments and monitoring systems are essential for detecting and measuring critical factors that contribute to landslides. These instruments, such as inclinometers, piezometers, and strain gauges, are installed in landslide-prone areas to measure ground movement, pore water pressure, and deformation. By continuously monitoring these parameters, experts can assess the stability of slopes and issue early warnings when necessary.
Advancements in computer modeling and simulations have also revolutionized landslide monitoring and prediction. Through the use of sophisticated algorithms and mathematical models, scientists are able to simulate various landslide scenarios and evaluate their potential impact on nearby infrastructure and communities. These models consider multiple variables, including soil properties, rainfall intensity, and geological features, to generate accurate predictions and assess the likelihood of landslide occurrence.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as satellite imagery, ground-based instruments, and computer modeling, enables real-time monitoring of landslides and the development of early warning systems. By combining data from various sources and analyzing it in a comprehensive manner, experts can make informed decisions and implement measures to prevent or minimize the devastating effects of landslides.
| Key Technologies in Landslide Monitoring |
|---|
| Remote sensing: Satellites, aerial imagery, and ground-based sensors |
| Geotechnical instruments: Inclinometers, piezometers, strain gauges |
| Computer modeling and simulations |
Promoting Awareness and Education on Landslide Preparedness
In this section, we will explore the importance of spreading knowledge and understanding about landslide preparedness. By increasing awareness and educating the public on this subject, we can empower individuals and communities to take proactive measures and reduce the impact of landslides.
1. Understanding Landslides: First and foremost, it is crucial to provide a clear and comprehensive explanation of what landslides are and how they occur. This involves describing the different types of landslides, such as debris flows, rock slides, and slope failures, and explaining the contributing factors such as heavy rainfall, earthquakes, or human activities. By enhancing understanding, individuals can recognize the warning signs and potential risks associated with landslides.
2. Recognizing Vulnerable Areas: Identifying and mapping areas at high risk of landslides is another essential aspect of promoting preparedness. By utilizing geological survey data and specialized tools, it becomes possible to pinpoint locations prone to landslides. This information can then be used to raise awareness among residents, local authorities, and emergency responders, enabling them to take appropriate precautions and respond effectively if a landslide occurs.
3. Developing Early Warning Systems: Establishing efficient early warning systems is crucial in reducing the loss of life and property caused by landslides. By investing in advanced technologies such as remote sensing, ground-based sensors, and meteorological monitoring, it becomes possible to detect the early signs of ground instability and rainfall-triggered landslides. Timely notifications and alerts can then be disseminated through various communication channels, ensuring that residents and authorities have enough time to evacuate or implement precautionary measures.
4. Community Engagement and Training: Encouraging community involvement and participation is key to fostering a culture of preparedness and resilience. By organizing educational campaigns, workshops, and training sessions, individuals can learn about the importance of early preparedness and the implementation of protective measures. Engaging with schools, community centers, and local organizations can help create a network of informed citizens who actively contribute to reducing landslide vulnerabilities.
5. Developing Guidelines and Resources: Providing easy-to-understand guidelines and resources is essential in empowering individuals and communities to take action. These materials can include step-by-step instructions on how to prepare an emergency kit, develop a family emergency plan, and secure properties against potential landslides. Accessible resources, such as brochures, videos, and online platforms, can further enhance the dissemination of valuable information and ensure its wide accessibility.
By focusing on promoting awareness and education on landslide preparedness, we can equip individuals and communities with the necessary knowledge and tools to mitigate risks and increase resilience in the face of a landslide event. Remember, preparedness begins with understanding, and together, we can make a significant difference in reducing the impact of landslides.
FAQ
What is the article "A Dream of a Landslide: What You Need to Know" about?
The article "A Dream of a Landslide: What You Need to Know" provides information and insights about landslides, including their causes, effects, and preventive measures.
How common are landslides?
Landslides are relatively common natural disasters, occurring in many parts of the world. However, their frequency and severity may vary depending on geographical factors such as terrain, climate, and human activities.
What are the main causes of landslides?
Landslides can be triggered by various factors, including heavy rainfall, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, slope instability, human activities (such as deforestation and construction), and changes in groundwater levels. Sometimes, a combination of these factors can lead to a landslide.
What are the potential effects of a landslide?
A landslide can have devastating effects, both on the environment and human life. It can cause property damage, disrupt transportation and communication systems, lead to loss of lives, and result in the displacement of communities. Additionally, landslides can create dammed lakes, block rivers, and contribute to the loss of fertile soil.
What can be done to prevent landslides?
Preventive measures for landslides include slope stabilization techniques, proper land use planning, reforestation efforts, the construction of retaining walls and drainage systems, and early warning systems. It is also crucial to raise awareness and educate communities about the risks and safety measures related to landslides.
What is the article "A Dream of a Landslide: What You Need to Know" about?
The article is about providing information and raising awareness about landslides, their causes, and the precautions that individuals need to take to prepare for and respond to such natural disasters.
How common are landslides?
Landslides are quite common around the world. They occur in all geographic regions and can happen at any time of the year. However, the frequency and severity of landslides may vary depending on factors such as geological conditions and weather patterns.




