Imagine a peaceful night's sleep, where dream-filled adventures take you to magical places, and you wake up feeling refreshed and ready to conquer the day. Unfortunately, for many parents, this ideal scenario is shattered by the unsettling sound of their child grinding their teeth during sleep. This phenomenon, also known as bruxism, affects a significant number of children worldwide and can lead to various dental issues if left untreated.
Bruxism can be a perplexing issue to address, as its underlying causes are not always clear-cut. However, through research and expert insights, we can gain a better understanding of the potential triggers behind this unpleasant habit. While the exact etiology may differ between individuals, a myriad of factors have been identified as possible contributors to childhood bruxism.
One possible cause is stress or anxiety experienced by children, which may manifest during nighttime as teeth grinding. The pressure to excel academically, perform well in extracurricular activities, or navigate social interactions can create significant emotional strain, leading to bruxism as an outlet for this tension. Moreover, disturbances in the sleep cycle, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, can also contribute to teeth grinding, as the body tries to compensate for inadequate rest. In addition, anatomical factors, such as an abnormal bite or misaligned teeth, can play a role in the development of bruxism.
Understanding Bruxism in Children

Examination of the phenomenon of teeth grinding in children can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes, contributing factors, and potential remedies for this condition. By delving into the intricacies of bruxism in young individuals, it is possible to gain a deeper understanding of the various aspects surrounding this oral health concern without explicitly discussing its causes, solutions, or the specific age group affected.
Exploring the Origins
When children experience involuntary grinding, clenching, or gnashing of their teeth during sleep, the occurrence is commonly referred to as bruxism. This puzzling phenomenon is characterized by the repetitive and unintentional action of moving the mandible, which can result in a range of consequences affecting the dentition, muscles, and overall well-being of the child. In order to comprehend the true nature of bruxism in children, it is important to delve into the potential factors that contribute to this condition.
Unraveling Possible Influences
While the exact etiology of bruxism in children remains elusive, numerous factors have been postulated as potential contributors to this perplexing behavior. Among these influential elements, both psychological and physiological aspects may play a significant role. Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, or an imbalance in emotional well-being, have been suggested to trigger or exacerbate bruxism. Furthermore, physiological factors, such as abnormal tooth alignment, jaw misalignment, or an imbalance in the bite forces, may also contribute to the occurrence of bruxism in children.
Recognizing Potential Implications
Despite the notably benign nature of bruxism in most cases, it is important to acknowledge the potential implications associated with this condition. The effects of teeth grinding during sleep may extend beyond oral health concerns and can manifest in various ways. From tooth sensitivity and enamel wear to facial muscle pain and headaches, bruxism can elicit a range of discomforts, warranting attention and effective management.
Examining Management Approaches
The multifaceted nature of bruxism necessitates a comprehensive approach to its management in children. While a definitive cure for this condition may not yet be established, there are numerous strategies that can be employed to minimize its impact. These approaches can include behavioral interventions, stress reduction techniques, orthodontic measures, and the use of protective devices, all aimed at alleviating symptoms, promoting relaxation, and safeguarding dental structures. By employing a combination of these strategies, it is possible to improve the well-being of children affected by bruxism and mitigate its adverse effects.
In conclusion, gaining a comprehensive understanding of bruxism in children encompasses exploring its origins, unraveling potential influences, recognizing implications, and examining effective management approaches. By delving into these aspects surrounding the phenomenon, valuable insights can be obtained, contributing to the development of strategies aimed at mitigating the adverse effects of bruxism in children.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Bruxism in Children
While there are multiple factors that contribute to the grinding of teeth in children during sleep, it is important to acknowledge the role of psychological influences. Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and emotional disturbances can significantly impact a child's oral habits and contribute to the development of bruxism.
- Emotional Disturbances: Emotional disturbances, such as anger, frustration, or sadness, can manifest during sleep as teeth grinding. These emotions may be triggered by various factors, including family discord, academic pressure, or social difficulties.
- Anxiety and Stress: Children may experience stress or anxiety due to various reasons, such as school-related stress, interpersonal conflicts, or performance pressure. These psychological factors can lead to increased muscle tension, including the jaw muscles, resulting in teeth grinding during sleep.
- Sleep Disorders: Certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, can cause discomfort and disrupt a child's sleep quality. The resulting fragmented sleep can contribute to teeth grinding as the body seeks relief from the discomfort.
- Traumatic Experiences: Children who have experienced trauma, such as witnessing violence or going through a significant life change, may exhibit bruxism as a response to their emotional distress. Teeth grinding serves as a coping mechanism or an outlet for their pent-up emotions.
- Mental Health Conditions: Children diagnosed with mental health conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or depression may be more prone to teeth grinding. Psychological symptoms associated with these conditions can intensify bruxism during sleep.
It is essential for parents and caregivers to be aware of these psychological factors and their potential impact on a child's teeth grinding habits. Identifying and addressing these underlying psychological issues can be an important step in managing and treating bruxism in children.
Physical Factors Influencing Bruxism in Children
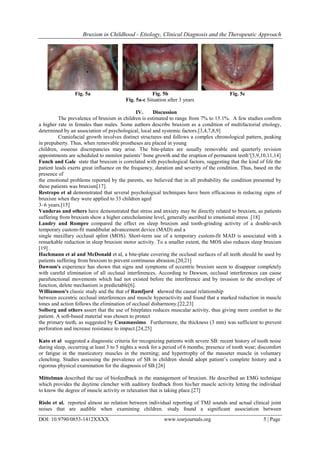
Bruxism in children, the rhythmic grinding of teeth during sleep, is a common concern among parents and healthcare providers. While various causes contribute to this condition, it is essential to explore the physical factors that influence bruxism in children. Understanding these factors can lead to effective preventive measures and treatments.
Anatomical factors: The structure and alignment of a child's jaw and teeth can play a significant role in the occurrence of bruxism. Dental misalignments, such as malocclusion, may cause uneven contact between the upper and lower teeth, leading to grinding behavior during sleep. Additionally, certain oral habits, such as thumb sucking or tongue thrusting, can exert abnormal pressure on teeth, contributing to bruxism.
Muscle tension and coordination: The development and coordination of jaw muscles in children can affect bruxism tendencies. Increased muscle tension or imbalances between the muscles that control chewing and jaw movement may result in grinding. Additionally, factors like stress, anxiety, or hyperactivity can contribute to heightened muscle activity and exacerbate bruxism episodes during sleep.
Neurological factors: The functioning of the central nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating sleep patterns, including involuntary movements like teeth grinding. Neurological conditions such as developmental disorders or conditions affecting the basal ganglia can increase the likelihood of bruxism in children. Furthermore, medications that influence neurological activity may cause or worsen bruxism as a side effect.
Airway obstruction and breathing difficulties: In some cases, physical factors related to the airway and breathing can contribute to bruxism. Children who experience obstructed breathing, either due to enlarged tonsils or respiratory conditions like sleep apnea, may grind their teeth as a subconscious attempt to open the airway during sleep. Correcting such underlying issues can often alleviate bruxism symptoms.
Dietary factors: Certain dietary factors may contribute to the physical aspects of bruxism in children. Consuming foods or drinks that contain stimulants, such as caffeine or sugary beverages, can increase muscle activity and potentially trigger teeth grinding during sleep. Maintaining a healthy diet and limiting intake of these substances can help reduce the prevalence of bruxism.
In conclusion, understanding the physical factors influencing bruxism in children is essential for effectively addressing this condition. By taking into account anatomical considerations, muscle tension and coordination, neurological influences, airway obstruction, and dietary factors, healthcare professionals and parents can develop comprehensive strategies to mitigate bruxism and promote oral health in children.
The Genetic Factors Behind Childhood Bruxism
When it comes to the frequent grinding and clenching of teeth during sleep in children, there exists a complex interplay of genetic factors that contribute to this common dental condition, commonly known as bruxism. This section aims to shed light on the role of genetics in the manifestation and development of childhood teeth grinding, offering insights into familial patterns and inherited predispositions.
Although the causes and solutions for child teeth grinding are multifaceted, genetics plays a significant role in determining an individual's susceptibility to bruxism. Research suggests that children with a family history of bruxism are more likely to experience this condition themselves. This genetic predisposition indicates that certain genes may be responsible for influencing the development of the nervous system and the regulation of muscle activity during sleep.
Studies have shown that variations in specific genes, such as those involved in neurotransmitter regulation and muscle function, can contribute to the occurrence of bruxism in children. Genetic factors can affect the communication between brain cells, leading to an imbalance in neurotransmitters that control muscle movements. This imbalance can result in involuntary nighttime grinding and clenching of the jaws.
Additionally, genetic factors may influence the development of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and tooth structure, making some children more prone to bruxism. Differences in the alignment of the teeth, jaw size, and muscle strength can affect how the upper and lower teeth fit together, potentially increasing the likelihood of teeth grinding during sleep.
Understanding the role of genetics in child teeth grinding not only provides valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of bruxism but also highlights the importance of identifying familial patterns and genetic markers for early detection and effective management. Further research into the specific genes and their interactions may ultimately lead to targeted interventions and preventive measures to alleviate the impact of childhood bruxism on oral health and well-being.
The Impact of Inadequate Sleep Patterns on Bruxism in Children
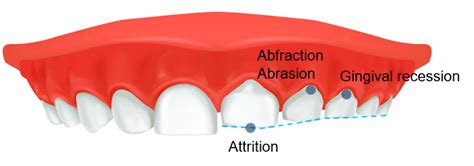
Insufficient or improper sleep routines can have a significant influence on the occurrence and severity of bruxism in young individuals. Bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding, is a condition where an individual involuntarily grinds or clenches their teeth, often during sleep. This article explores the correlation between poor sleep habits and bruxism in children, shedding light on the detrimental effects of inadequate sleep patterns on their overall oral health.
1. Disrupted sleep cycles: In children with erratic sleep schedules or inconsistent bedtime routines, the natural sleep-wake rhythm can be disrupted. This can lead to fragmented and insufficient sleep, provoking increased episodes of bruxism during the night. Poor sleep quality may serve as a contributing factor to the development and persistence of teeth grinding.
2. Psychological factors: The negative impact of poor sleep habits extends beyond physical fatigue. Children who do not get adequate rest may experience increased levels of stress, anxiety, or irritability. These psychological factors can contribute to the manifestation of bruxism, causing them to grind their teeth unconsciously during periods of disturbed sleep.
3. Sleep respiratory disorders: Certain sleep-related breathing disorders, such as sleep apnea, can significantly impact a child's quality of sleep. The presence of such disorders can heighten the likelihood of bruxism episodes during sleep. The efforts made by the body to maintain proper airflow during sleep apnea episodes can lead to teeth grinding as a response mechanism.
4. Association with daytime tiredness: Inadequate sleep can result in daytime tiredness and fatigue in children. The exhaustion experienced during the day due to insufficient sleep can increase the occurrence of bruxism. The connection between insufficient rest and teeth grinding highlights the need for establishing healthy sleep habits to alleviate the symptoms of bruxism.
5. Importance of addressing sleep issues: Recognizing the impact of poor sleep patterns on bruxism is crucial in devising holistic approaches to manage and prevent the condition in children. Encouraging regular sleep schedules, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and implementing relaxation techniques before bedtime are necessary steps to improve the quality of sleep and reduce the occurrence of bruxism.
By understanding how poor sleep habits can directly influence bruxism in children, parents and caregivers can take proactive steps to address sleep-related issues and promote overall oral health and well-being.
Managing Stress to Prevent Bruxism in Children
Excessive stress can negatively impact children's oral health, leading to the occurrence of bruxism during sleep. Taking proactive measures to manage and reduce stress in children can help mitigate the risk of teeth grinding. By addressing stress-related factors, parents and caregivers can create a supportive environment that promotes relaxation and better sleep quality for children, ultimately preventing the development of bruxism.
| Stress Management Strategies |
1. Open Communication: Encouraging children to express their feelings and concerns candidly provides them with an outlet to alleviate stress. Actively listening and offering reassurance can help children cope with emotional pressures more effectively. |
2. Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and ensuring sufficient sleep can significantly reduce stress levels in children. These lifestyle habits promote overall well-being and contribute to a calmer and more relaxed state of mind. |
3. Relaxation Techniques: Teaching children relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, visualization, and muscle relaxation methods can equip them with valuable tools to manage stress. These techniques can be practiced before bedtime to promote relaxation and enhance sleep quality. |
4. Establishing Routines: Implementing consistent daily routines, including designated quiet time and regular bedtime, can instill a sense of security and stability in children. Such routines help reduce anxiety and stress levels, creating a conducive environment for better sleep. |
5. Creating a Calm Sleep Environment: Designing a serene and comfortable bedroom environment can aid in stress reduction for children. Eliminating distractions, using soft lighting, and incorporating soothing elements like music or white noise can promote relaxation and contribute to a peaceful sleep experience. |
By implementing these stress management strategies, parents and caregivers can better support children in handling stressors, ultimately preventing bruxism and promoting overall oral health. Encouraging a positive and relaxed mindset can contribute to healthier sleep patterns for children, ensuring their long-term oral well-being. |
Link Between Oral Health Conditions and Bruxism in Children
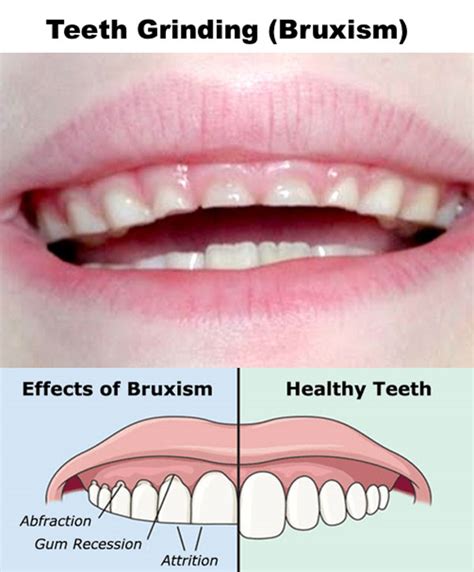
Bruxism, a condition characterized by excessive teeth grinding and clenching, can be influenced by various oral health conditions present in children. This section explores the connection between these conditions and the occurrence of bruxism.
- Malocclusion: The misalignment of teeth and jaws can lead to an imbalance in the bite, causing strain on the teeth and jaw muscles. Children with malocclusion may be more prone to developing bruxism as their teeth try to find a more comfortable position during sleep.
- Dental Decay: Cavities and tooth decay can result in tooth sensitivity and discomfort, triggering bruxism as a subconscious response to relieve the pain. Identifying and treating dental decay early on is crucial to prevent the development of bruxism.
- Tension and Stress: Psychological factors, such as anxiety, tension, and stress, can manifest in children as bruxism. These emotional factors can also contribute to the development of oral health conditions like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, further exacerbating the grinding habit during sleep.
- Respiratory Issues: Certain respiratory conditions, such as allergies or sleep apnea, can affect the quality of sleep in children. Frequent disruptions in sleep patterns can lead to bruxism as the body responds to the discomfort and inadequate oxygen intake by grinding the teeth.
- Mouth Breathing: Chronic mouth breathing can alter the natural posture of the tongue and cause the tongue to rest on the roof of the mouth instead of the palate. This can create imbalances in the oral muscles and contribute to bruxism in children.
Understanding the relationship between oral health conditions and bruxism in children is vital for effective prevention and treatment. It is essential to address these underlying oral health issues to alleviate the symptoms of bruxism and promote optimal oral well-being in children.
The Significance of Early Intervention in Addressing Childhood Nocturnal Bruxism
Ensuring timely intervention when it comes to nocturnal bruxism in children is pivotal for preventing potential dental and overall health complications. By promptly identifying and addressing the underlying factors contributing to this common sleep-related condition, parents and healthcare providers can effectively safeguard the well-being and dental health of youngsters.
A proactive approach in dealing with paediatric bruxism aids in minimizing potential long-term consequences while promoting optimal oral health. Early recognition and management of this condition not only alleviate discomfort and potential pain but also reduce the risk of irreversible damage to the teeth, jaw, and surrounding structures.
Awareness regarding the significance of early intervention in mitigating child teeth grinding is crucial for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals alike. Through education and proactive measures, such as regular dental examinations, it becomes possible to identify potential causes, implement suitable preventive strategies, and offer appropriate treatment options tailored to each child's unique needs.
| Key Points |
|---|
| 1. Early intervention is essential in managing and preventing complications related to child teeth grinding. |
| 2. Timely identification of underlying factors contributing to bruxism allows for targeted interventions. |
| 3. Addressing nocturnal bruxism in children aids in reducing discomfort and potential pain. |
| 4. Proactive measures, such as regular dental check-ups, play a crucial role in early detection and appropriate management. |
| 5. Educating parents, teachers, and healthcare providers about the importance of early intervention is paramount for successful outcomes. |
By recognizing the importance of early intervention in tackling child teeth grinding, society can ensure the best possible oral health outcomes for children. Through collaborative efforts and a well-informed approach, the detrimental effects of nocturnal bruxism can be minimized, promoting a lifetime of healthy smiles and overall well-being.
Effective Strategies for Treating Bruxism in Children

Bruxism, a common oral health condition in children, can lead to a range of dental problems if not addressed in a timely manner. This section discusses effective strategies that can be employed for the treatment of bruxism in children, focusing on preventative measures and therapeutic interventions that promote healthier oral habits.
- Dental Examination: A comprehensive dental examination plays a vital role in identifying potential causes of bruxism in children. By assessing the alignment of teeth, jaw structure, and overall oral health, dentists can determine specific factors contributing to bruxism and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
- Mouthguards: Custom-fitted mouthguards or dental splints are often recommended as a preventive measure to protect teeth and reduce the impact of bruxism during sleep. By providing a cushioning effect, these devices aid in minimizing tooth enamel wear and alleviate excessive jaw muscle tension.
- Stress Management: Recognizing that stress and anxiety are often underlying causes of bruxism in children is crucial. Encouraging open communication, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, and engaging in calming activities can help alleviate the psychological triggers of bruxism.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent bedtime routine and promoting good sleep hygiene can contribute to reducing bruxism episodes in children. Creating a relaxing atmosphere, limiting electronic device usage before bed, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment are essential components of maintaining optimal oral health during sleep.
- Behavioral Modification: Implementing behavior modification strategies can aid in eliminating bruxism habits in children. This may involve positive reinforcement techniques, such as rewards for not grinding teeth during sleep, as well as providing alternative outlets for releasing tension, like stress-relief toys or activities.
- Orthodontic Intervention: In some cases, orthodontic treatment may be necessary to correct misaligned teeth or improve jaw positioning, which can contribute to bruxism. Consultation with an orthodontist can help determine if orthodontic intervention is required to address the underlying causes of bruxism in children.
By implementing a combination of these effective strategies, parents and caregivers can significantly reduce the impact of bruxism on a child's oral health. It is essential to consult with dental professionals for personalized guidance and to ensure the most appropriate treatment plan is tailored to address the unique needs of each child.
FAQ
What are the causes of child teeth grinding during sleep?
The causes of child teeth grinding during sleep can vary. It could be due to stress or anxiety, misaligned teeth or jaws, allergies, or even as a result of sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.
Is teeth grinding during sleep harmful to a child?
Teeth grinding during sleep, also known as bruxism, can be harmful to a child's oral health. It can lead to tooth damage, jaw pain, headaches, and even earaches. It is important to address this issue timely to prevent any long-term consequences.
How can I determine if my child is grinding their teeth during sleep?
There are several signs that can indicate teeth grinding during sleep in a child. These include worn down or flattened teeth, sensitivity or pain in the teeth, complaints of jaw pain or headaches upon waking up, and in some cases, a grinding noise that can be heard during sleep.
What are some solutions to help prevent child teeth grinding during sleep?
There are a few solutions that can help prevent or reduce child teeth grinding during sleep. These include managing stress or anxiety levels through relaxation techniques or counseling, ensuring a calm and comfortable sleep environment, using a dental nightguard, and addressing any underlying dental or medical issues that may be contributing to the grinding.
When should I seek professional help for my child's teeth grinding during sleep?
If your child's teeth grinding is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as facial pain or difficulty chewing, it is advisable to seek professional help. A dentist or pediatrician can evaluate the situation and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.
What are the causes of child teeth grinding during sleep?
Child teeth grinding during sleep, also known as sleep bruxism, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes include stress or anxiety, misaligned teeth or jaw, response to pain from teething or an earache, hyperactivity or ADHD, and certain medications or medical conditions.
How can I know if my child is grinding their teeth during sleep?
There are several signs that may indicate your child is grinding their teeth during sleep. These include a grinding or clenching sound during sleep, complaints of a sore jaw or face upon waking up, worn down teeth, increased tooth sensitivity, headaches, and difficulty sleeping. If you suspect your child is grinding their teeth, it is best to consult with their dentist or pediatrician for a proper diagnosis.




