In the vast realm of entomology, the sighting of a noteworthy insect is often akin to stumbling upon a hidden treasure trove. A recent discovery has sparked excitement within the scientific community, as an astounding observation of a particularly substantial flying insect has been reported. This astounding find has the potential to shed light on various ecological aspects and leave an indelible mark on our understanding of these bloodsucking creatures.
With its distinct buzzing resonance and devious nature, this remarkable mosquito exhibits a grandeur that surpasses any regular specimen. Its sheer size engenders awe and wonder, inspiring notions of both fright and fascination. Every aspect of this arthropod seems to defy conventional expectations, leaving researchers and enthusiasts eagerly delving into its potential implications.
While the vast majority of mosquitoes that we encounter are synonymous with annoyance and discomfort, this extraordinary individual harbors the potential for groundbreaking discoveries. Through careful observation and meticulous analysis, scientific minds aim to decipher the hidden messages embedded within its colossal wingspan and venomous proboscis. The implications of this momentous sighting are vast, stretching beyond the mere act of its observation.
The presence of such a remarkable mosquito raises intriguing questions about its ecological role and its potential impact on public health. Could this oversized insect be an outlier or part of a newly emerging species? Is this sighting indicative of a larger-scale phenomenon? The answers to these pressing inquiries remain shrouded in mystery, compelling experts from various fields to convene in pursuit of knowledge and understanding.
The potential implications for public health

One aspect of the recent observation of a sizeable presence of a certain type of insect species holds significant implications for the health and well-being of the general population. The emergence of an ample number of these specific insects could potentially lead to several adverse consequences and impact the overall public health.
Spread of diseases: One of the most critical concerns arising from the notable abundance of these insects is the potential for the transmission of various diseases. As the population of these insects grows, so does the risk of diseases they carry. This increased transmission of diseases poses a considerable threat to the overall public health. |
Ecological disruption: The substantial presence of these specific insects may also have a profound impact on the local ecological balance. These insects may disrupt the natural ecosystem by preying on other beneficial organisms or competing for limited resources. Such disruptions can lead to cascading effects on the environment, potentially affecting public health indirectly. |
Allergic reactions and discomfort: Large numbers of these insects can cause allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. Bites from these insects can result in skin irritations, itching, and discomfort, leading to reduced quality of life and potential health complications. Addressing this issue is crucial to safeguarding the public from unnecessary health risks. |
Increased economic burden: The presence of a sizable population of these insects may also burden the healthcare system and place an additional strain on public resources. Managing the potential increase in disease cases, addressing allergies, and implementing adequate pest control measures requires significant financial investment. Thus, the potential implications for public health extend beyond the immediate health risks. |
Therefore, it is imperative to carefully assess and respond to the large-scale sighting of these insects to mitigate the potential adverse consequences for public health. Effective strategies need to be developed to monitor their populations, educate individuals on prevention measures, implement targeted interventions, and raise public awareness regarding the associated health risks.
Examining the environmental factors contributing to the presence of these insects
In this section, we will delve into the various environmental factors that play a role in the abundance and prevalence of these insects. By understanding these factors, we can gain valuable insights into the reasons behind their increased presence and potentially develop effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
- 1. Climate:
- 2. Habitat:
- 3. Vegetation:
- 4. Urbanization:
- 5. Water Management:
The climate of a particular region can greatly influence the presence of mosquitoes. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation levels can create ideal breeding grounds for these insects. Rising temperatures and increased humidity provide suitable conditions for mosquito larvae to thrive, contributing to their population growth.
The natural habitats of mosquitoes can vary significantly, and understanding their preferences is essential in determining their presence. Mosquitoes typically inhabit areas with stagnant water, such as ponds, marshes, and puddles. When these habitats are in close proximity to human settlements, the likelihood of mosquito sightings and bites increases.
The presence of certain types of vegetation can act as attractants or repellents for mosquitoes. Vegetation that retains moisture, such as dense shrubs or plant overgrowth, can create favorable environments for mosquitoes to breed and rest. Conversely, certain plants and herbs, such as citronella, lavender, and eucalyptus, possess natural repellent properties, potentially reducing mosquito activity in their vicinity.
The process of urbanization can significantly impact mosquito populations. Urban areas with an abundance of artificial containers, such as discarded tires, buckets, and gutters, provide ample breeding sites for these insects. Additionally, increasing human population densities create more opportunities for mosquitoes to find hosts for blood meals, leading to a higher prevalence of these insects.
The management and control of water resources play a crucial role in mosquito control. Proper water drainage systems and regular cleaning of stagnant water sources can reduce breeding opportunities for mosquitoes. Additionally, the implementation of larvicide treatment programs in bodies of water, such as lakes and ponds, can help control their populations.
By examining these key environmental factors, we can gain a better understanding of why large mosquito sightings occur and develop strategies to minimize their presence. The interplay between climate, habitat, vegetation, urbanization, and water management is complex, but by addressing each factor, we can make significant progress in reducing the impact of these insects on human populations.
Understanding the Reproduction Patterns of Mosquitoes
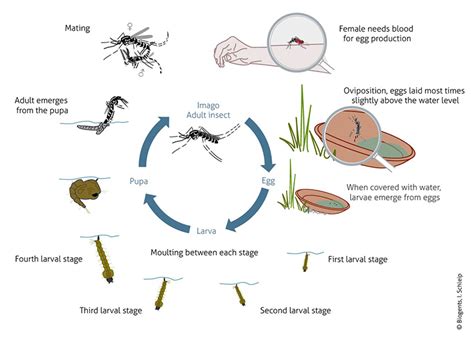
One of the key areas in comprehending the behavior and impact of mosquitoes rests in unraveling their breeding habits. By gaining a deeper understanding of how mosquitoes reproduce, scientists and researchers can devise effective strategies to mitigate the spread of mosquito-borne diseases and prevent population explosions.
The reproduction process of mosquitoes is a complex and intricate mechanism that plays a vital role in their survival and proliferation. It involves several distinct stages, including mating, egg development, and hatching. Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities for intervention.
Mosquitoes rely on stagnant water sources to lay their eggs, with different species exhibiting preferences for specific breeding sites. Clogged gutters, ponds, puddles, and even discarded containers filled with rainwater can serve as breeding grounds for these pesky insects. Understanding the types of habitats mosquitos prefer can aid in identifying and eliminating potential breeding sites.
Upon mating, female mosquitoes seek out suitable oviposition sites to lay their eggs. These sites are carefully selected to provide optimal conditions for the survival and development of the offspring. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and nutrients contained in the breeding site play a crucial role in determining the success of the eggs and subsequent larvae.
By studying and comprehending the intricacies of mosquito breeding, scientists can develop targeted interventions to disrupt the reproductive process and limit mosquito population growth. Strategies such as larvicide treatments, source reduction efforts, and the promotion of natural predators can effectively control and reduce mosquito populations in specific areas.
Understanding the breeding habits of mosquitoes not only provides valuable insights into their life cycle but also helps in devising efficient and sustainable methods of mosquito control. By disrupting their reproduction patterns, we can protect ourselves from the health risks associated with these disease-carrying insects, ultimately creating safer and healthier environments for humans and animals alike.
The Impact of Climate Change on Mosquito Population Growth
As the Earth’s climate continues to undergo significant changes, scientists and researchers are increasingly studying the various effects that these changes have on the environment and ecosystems. One area of particular interest is the impact of climate change on mosquito populations.
Mosquitoes, commonly known as disease vectors, have long been a cause for concern due to their ability to carry and transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and West Nile virus. Understanding the relationship between climate change and mosquito population growth is crucial in mitigating the potential risks posed by these disease-carrying insects.
Climate change can influence mosquito populations in several ways. Rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns can directly affect their breeding habits and survival rates. Warmer temperatures can accelerate mosquito development, increasing their reproductive capacity and shortening their life cycle. Changes in rainfall patterns can create favorable conditions for mosquito breeding, as stagnant water bodies are essential for their reproductive cycle.
Furthermore, climate change can also indirectly impact mosquito populations by altering the distribution and habitat suitability of their preferred hosts and food sources. Changes in vegetation patterns and land-use practices can modify the availability of suitable feeding grounds, influencing the survival and reproductive success of mosquitoes.
The complex relationship between climate change and mosquito population growth necessitates continuous monitoring and research. These studies can inform the development of effective strategies for mosquito control and disease prevention, highlighting the importance of proactive measures to mitigate the potential threats associated with the rise in mosquito populations.
| Climate Change Factors | Impact on Mosquito Populations |
|---|---|
| Rising temperatures | Accelerated mosquito development, increased reproductive capacity, and shortened life cycle. |
| Changes in precipitation patterns | Creation of favorable breeding conditions due to the availability of stagnant water bodies. |
| Altered distribution and habitat suitability of hosts and food sources | Influences on survival and reproductive success of mosquitoes. |
Considering the Impact on Local Ecosystems
Exploring the consequences of an abundant appearance of a particular kind of insect can shed light on its potential influence on the surrounding environment. Examining the effects on the local ecosystems can provide valuable insights into the intricate relationships between various organisms and their habitats.
In assessing the impact on local ecosystems, it is essential to consider the potential ramifications on flora, fauna, and overall biodiversity. A surge in the population of any species can trigger a cascade of effects, resulting in noticeable changes in the delicate balance of nature.
- 1. Ecological Disruption: The proliferation of a plethora of mosquitos may disrupt the existing ecological dynamics by altering the availability and distribution of resources. This disruption can have widespread implications for other organisms within the ecosystem.
- 2. Threat to Native Species: Mosquitos may serve as vectors for various diseases that pose a threat to native wildlife. These diseases can spread rapidly, leading to decreased populations of vulnerable species and potential shifts in species composition.
- 3. Impact on Aquatic Systems: Mosquito larvae primarily inhabit stagnant bodies of water. A sudden influx of these larvae can result in altered aquatic ecosystems and reduced water quality. This change can negatively impact aquatic flora and fauna, including fish populations, by restricting oxygen availability.
- 4. Disrupted Pollination: In some cases, mosquitos can disturb the pollination process by interfering with the activities of essential pollinators, such as bees and butterflies. This interference can have adverse effects on plants that rely on specific insects for pollination.
- 5. Predation Patterns: A surge in mosquito populations can impact the feeding behaviors of predators that rely on them, leading to a potential shift in predation patterns that may trickle down the food chain and affect the overall structure of the ecosystem.
Considering the potential consequences of a considerable mosquito sighting on local ecosystems is crucial for understanding the broader implications of their presence. By comprehending these impacts, appropriate measures can be taken to mitigate any adverse effects and maintain the ecological integrity of the surrounding environment.
Exploring the potential for transmission of diseases
Within the broader context of analyzing the implications of a substantial mosquito presence, it is crucial to delve into the potential for disease transmission they might carry. By understanding the magnitude of this possibility, we can gain insight into the potential risks to public health and, consequently, develop effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
Examining the disease vector capabilities of mosquitoes
One of the key aspects to consider when evaluating the potential for disease transmission is to examine the vector capabilities of the mosquitos in question. Mosquitoes possess a remarkable ability to serve as carriers or vectors for various diseases, including but not limited to malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and West Nile virus. Understanding the mechanisms by which these diseases are transmitted is essential in assessing the degree of threat posed by the observed mosquitoes.
Evaluating the prevalence of disease-causing pathogens
Another significant factor in exploring the potential for disease transmission is to assess the prevalence of disease-causing pathogens within the mosquito population. This entails investigating the presence and abundance of specific pathogens, such as parasites or viruses, within the mosquito population. Analyzing the prevalence provides valuable insights into the likelihood of disease transmission, as well as the potential impact on local communities.
Assessing the vulnerability of the exposed population
Furthermore, understanding the vulnerability of the population exposed to the large mosquito sighting is essential. Factors such as host susceptibility, access to healthcare, and environmental conditions all play a role in determining the potential impact of mosquito-borne diseases on public health. Examining these aspects enables a more accurate assessment of the potential consequences and facilitates the development of targeted preventive measures.
In conclusion, exploring the potential for disease transmission in the context of a significant mosquito sighting provides critical insights into the associated risks and enables the formulation of appropriate response strategies. By delving into the disease vector capabilities, prevalence of pathogens, and vulnerability of the exposed population, we can effectively assess the potential for disease transmission and take proactive measures to safeguard public health.
Strategies for Mosquito Control and Prevention
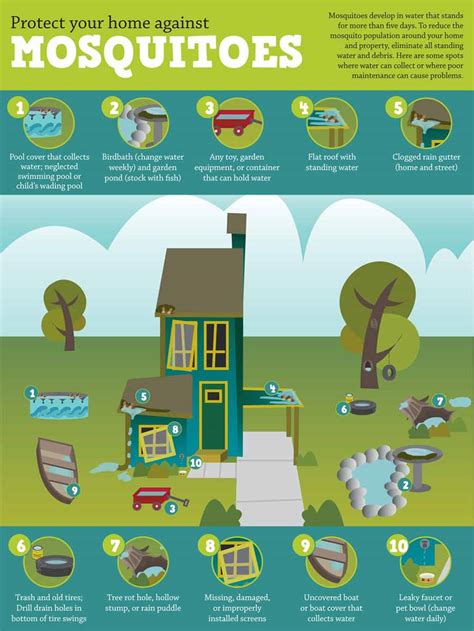
In this section, we will explore effective measures to control and prevent the proliferation of these disease-carrying insects. By implementing these strategies, individuals and communities can significantly reduce the impact of mosquitoes' presence on human health and well-being.
- Eliminate standing water sources: Mosquitoes require stagnant water to lay their eggs and breed. To minimize their breeding grounds, it is crucial to regularly empty, cover, or treat any containers that can collect water, such as buckets, flower pots, and bird baths.
- Maintain proper sanitation: Keeping the surrounding areas clean and well-maintained is vital for mosquito control. Regularly mowing lawns, trimming vegetation, and disposing of any discarded objects that can hold water will deprive mosquitoes of suitable breeding and resting grounds.
- Use mosquito nets and screens: Sleeping under mosquito nets and keeping windows and doors screened can create a physical barrier between mosquitoes and humans, reducing the risk of bites and potential disease transmission.
- Apply insect repellents: Use of mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or other approved ingredients can provide effective personal protection against mosquito bites. Remember to follow the instructions on the product for safe and proper application.
- Encourage biological control: Introducing mosquito predators and natural enemies in the environment, such as fish that feed on mosquito larvae or dragonflies that prey on adult mosquitoes, can help control their populations naturally.
- Implement community-wide measures: Mosquito control efforts are most effective when conducted collectively. Communities can organize campaigns to educate residents, coordinate neighborhood clean-ups, and implement regular mosquito surveillance and control programs.
- Consider mosquito-repellent plants: Certain plants, such as citronella, lavender, and basil, have natural repellent properties that can help deter mosquitoes. Planting these around homes, gardens, and outdoor gathering areas can provide an additional layer of protection.
By applying these strategies, individuals, communities, and governments can work together to minimize the risk of mosquito-borne diseases and create safer and more comfortable living environments for all. Remember, mosquito control and prevention should be an ongoing effort to ensure long-term success.
FAQ
What does it mean if I see a large number of mosquitoes in my area?
If you spot a large number of mosquitoes in your area, it generally indicates an increase in mosquito population. This could be due to various factors such as stagnant water sources, favorable weather conditions, or a decrease in mosquito control measures. It is advisable to take necessary precautions to protect yourself from mosquito-borne diseases in such situations.
Is the presence of many mosquitoes a cause for concern?
The presence of many mosquitoes should raise some concerns. Mosquitoes are known carriers of diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. A large number of mosquitoes can potentially increase the risk of transmission of these diseases. It is important to stay vigilant and take necessary preventive measures against mosquito bites to avoid any health complications.
How can I interpret the significance of a large mosquito sighting?
A large mosquito sighting can be significant in several ways. Firstly, it could indicate a higher risk of mosquito-borne diseases, as the abundance of mosquitoes increases the chances of disease transmission. Additionally, it may indicate potential breeding sites nearby, such as stagnant water or other favorable breeding conditions. It is crucial to report such sightings to local authorities for proper mosquito control measures to be undertaken.
What should I do if I notice a sudden increase in mosquito activity?
If you notice a sudden increase in mosquito activity, it is advisable to take immediate action. Start by eliminating any stagnant water sources around your property, as they serve as breeding grounds for mosquitoes. It is also recommended to use mosquito repellents, wear protective clothing, and avoid outdoor activities during peak mosquito activity times, typically dawn and dusk. If the problem persists or escalates, contact local authorities or pest control services for further assistance.




